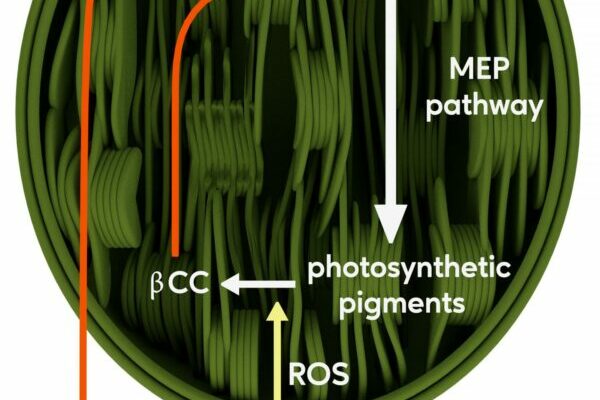
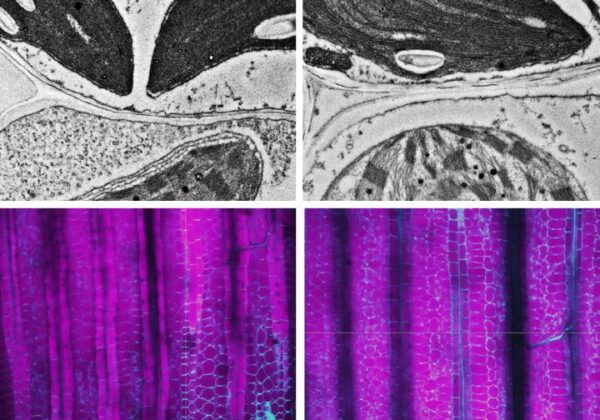
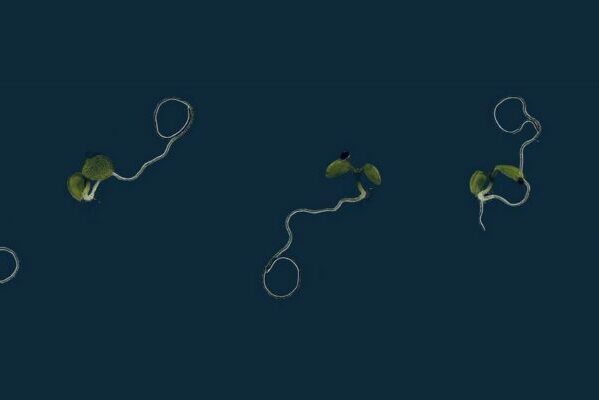
Small to moderate amounts of caffeine can lift your moods and drop the stress levels. Caffeine (trimethylxanthine) is nothing, but a modified form of a related molecule called xanthine, which can also be converted into other smaller molecules that help…
Read More