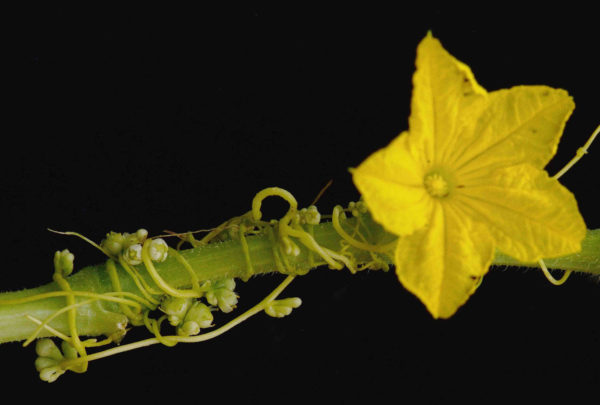
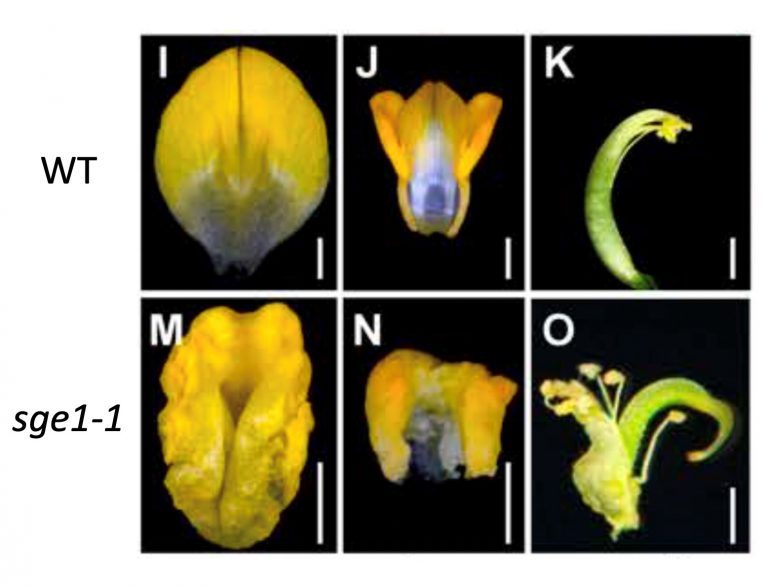
About 4,000-5,000 parasitic plant species exist. Among these, dodders (Cuscuta, Convolvulaceae) are distributed worldwide. Compared with normal autotrophic plants, they have a unique morphology – they are rootless and leafless and carry out no or very little photosynthesis.
Read More