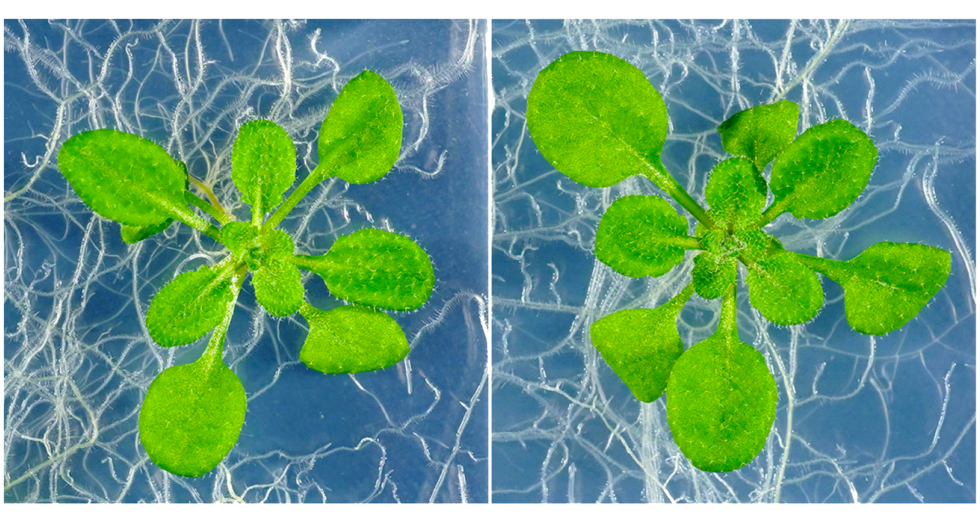
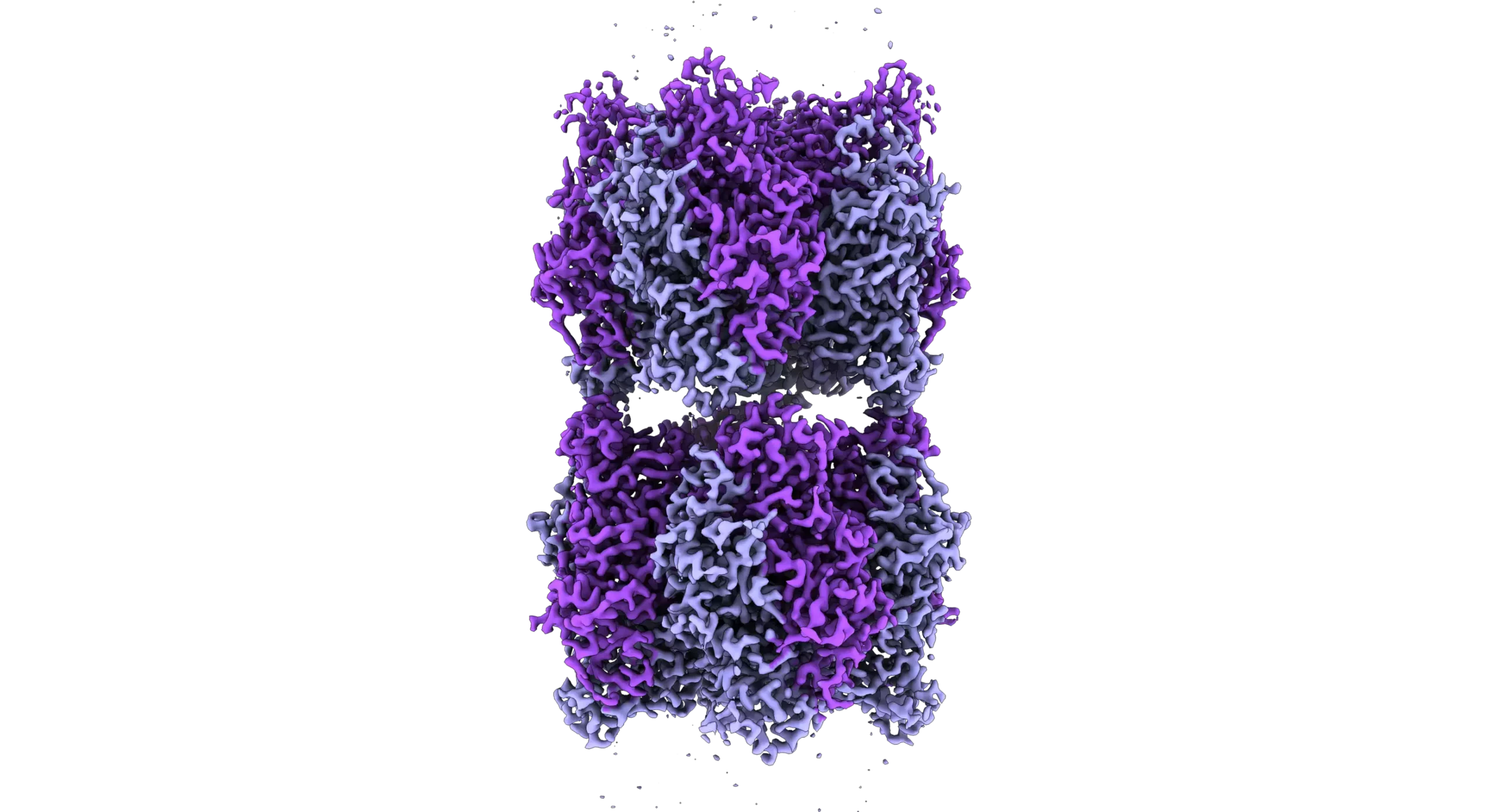
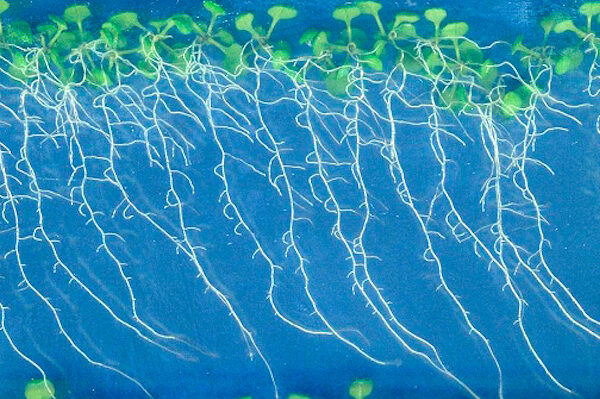
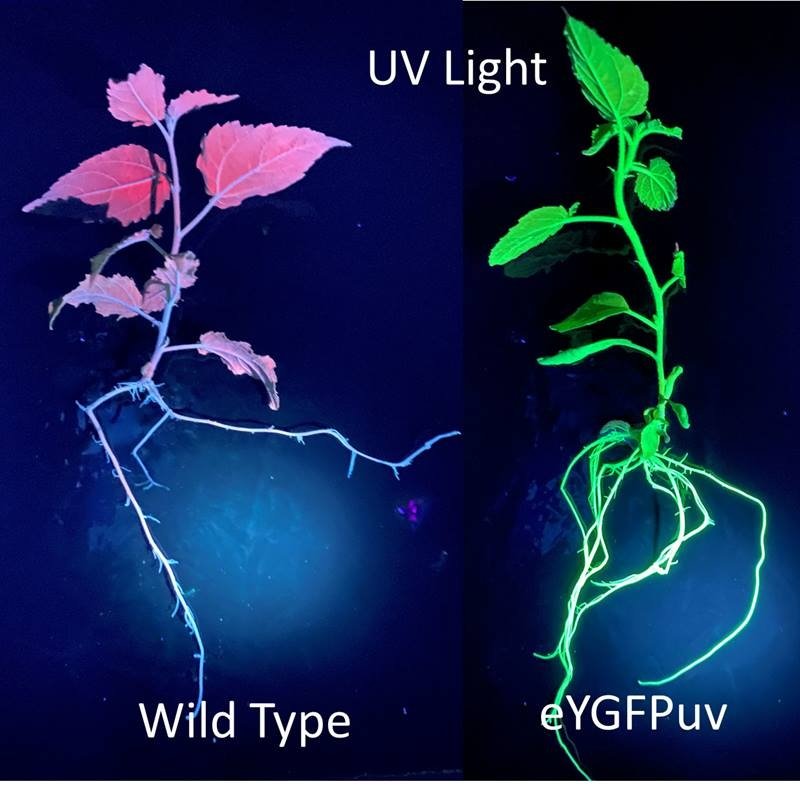
Crops often face harsh growing environments. Instead of using energy for growth, factors such as disease, extreme temperatures, and salty soils force plants to use it to respond to the resulting stress. This is known as the “growth-stress response trade-off".…
Read More