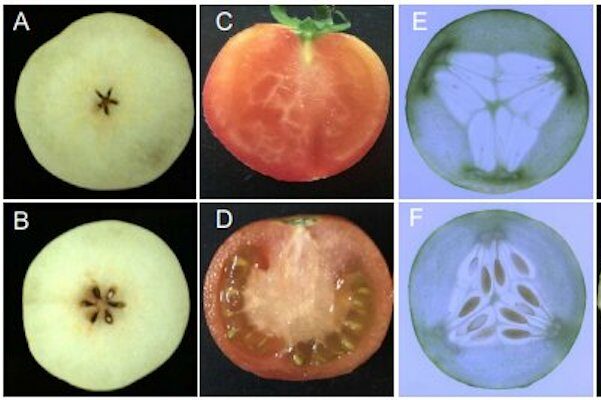
Plant hormones are well known for their important roles in plant development, including fruit development, and many researchers have devoted significant effort towards understanding the relationship between plant hormones and parthenogenesis. What are the latest research advances in hormones and…
Read More











