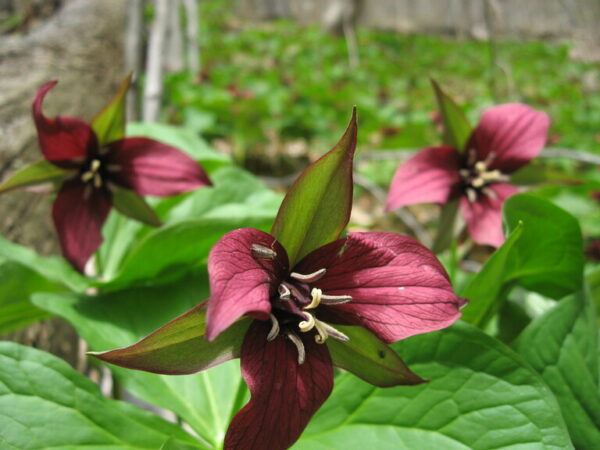
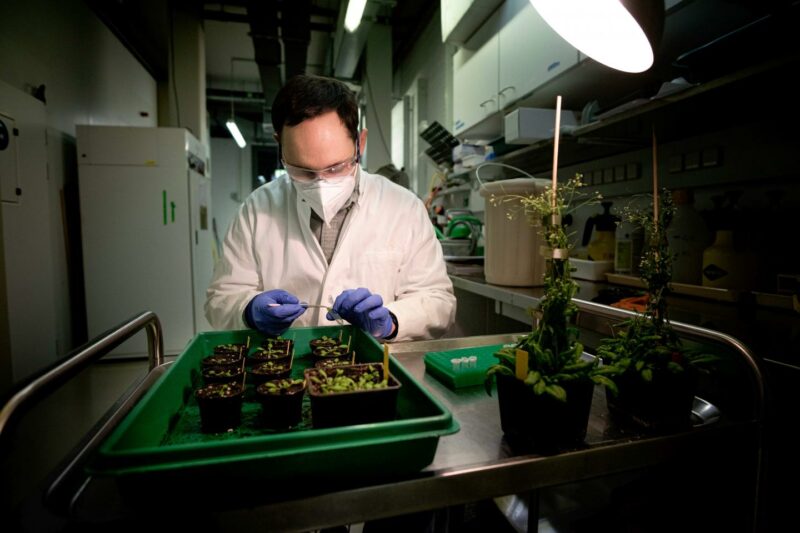
Invasive shrubs in Northeastern forests that sprout leaves earlier in the spring and keep them longer in the fall not only absorb more sunlight than native shrubs, but their foliage lowers air temperatures on the forest floor, likely giving them…
Read More