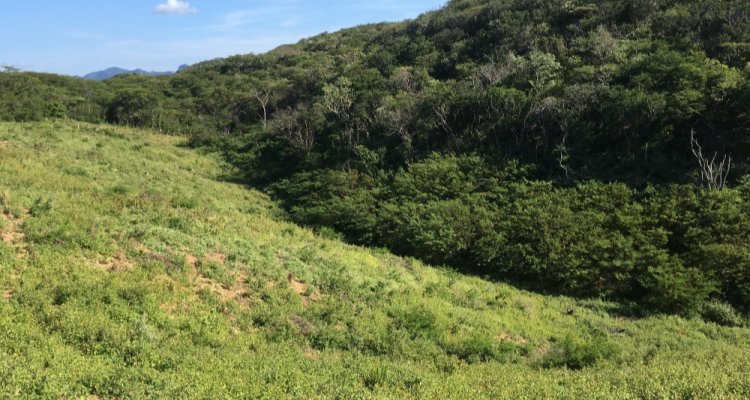
Tropical forests are disappearing at an alarming rate through deforestation, but they also have the potential to regrow naturally on abandoned lands. This has been shown by an international study led by scientists from Wageningen University. How a forest recovers,…
Read More