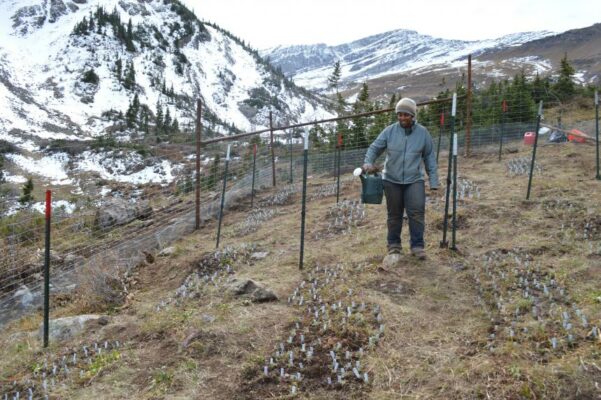








Some native plants do not appear to be adapting to warming conditions.
Native Australian alpine plants may not be able to adapt or migrate quickly enough to survive rapid changes in climate change, a UNSW study has found.
The study of 21 plants from Kosciuszko National Park, published in Ecology and Evolution, found that 20 were not responding to warming conditions.
Only one species – the Star Plantain (Plantago muelleri) – showed that it was adapting to warmer conditions by displaying an increase in plant size.
The second plant that showed evidence of a change in plant traits was the Cascade Everlasting (Ozothamnus secundiflorus), but it decreased in leaf thickness over a 125-year time period.
“We predicted leaves would become more thicker, as this would be advantageous if plants were facing longer growing seasons and increasing temperatures,” lead author Meena Sritharan said.



“Our findings suggest that native alpine plants may not be adapting to the substantial local climate change occurring in Australian alpine regions.
“Australian native alpine plants face a bleak future in the face of rapid climate change.”
Ms Sritharan is a PhD research scholar at ANU who participated in the study as an honours student in the Evolution & Ecology Research Centre at UNSW Science’s School of Biological, Earth and Environmental Sciences.
The point of the study was to gauge whether alpine plants in the southern hemisphere had changed in morphology, or their physical form, over time in response to recent climate warming.
Ms Sritharan said the 21 alpine plants exist in one of the ecosystems known to be least resistant to the effects of climate change.
“Alpine environments are facing higher-than-average increases in temperature in the last century,” Ms Sritharan said.
“But rapid changes in the environment can promote rapid changes in species.”
“Consequently, we expected that a rapid increase in temperature would result in a change in the plant traits we measured, such as size and leaf shape. These changes in plant traits would suggest that alpine plants may be changing in response to a changing climate.”
Previous studies have also shown that both native and invasive plants are capable of rapid changes in their morphology.
The researchers used herbarium (preserved) plant specimens collected between 1890 and 2016, and modern specimens collected in February, 2017.
Examples of the alpine plants they studied included Cushion Caraway (Oreomyrrhis pulvinifica), Alpine Rice flower (Pimelea alpine), Carpet Heath (Pentrachondra pumila) and Snow Aciphyll (Aciphylla glacialis).
The researchers measured five different plant traits: plant size, leaf shape, leaf area, leaf width and specific leaf area (the ratio of the leaf area to leaf dry mass).
Ms Sritharan said the study findings are surprising as the results were contrary to what they expected and what species in the northern hemisphere are facing.
She said plants in the northern hemisphere are changing substantially and adapting to changed environmental conditions brought by climate change.
“For instance, some British plant species (such as White Nettle (Lamium album) and Kenilworth ivy (Cymbalaria muralis) are flowering earlier than expected in the past decade compared to the previous four decades,” Ms Sritharan said.
“The plant height of species growing in tundra ecosystems (treeless regions in cold climates) have also increased with warming over the past three decades.”
Scientists also forecast that plant species will migrate to higher elevations to escape the effects of climate warming.
But Ms Sritharan said she was surprised to find that a shrub – Cascade Everlasting (Ozothamnus secundiflorus) – had moved downslope over time rather than to a higher elevation.
“This indicates that we should look into if, and where, other native Australian alpine species may be migrating to, in the face of climate change,” she said.
Ms Sritharan’s supervisor, the director of UNSW’s Evolution & Ecology Research Centre, Professor Angela Moles, is currently investigating whether Australian alpine plants are shifting their distributions uphill.
“This summer we will be doing heatwave experiments to measure how Australian alpine plants respond to an increased duration of heatwaves, which is what climate researchers forecast for the future,” Prof. Moles said.
Read the paper: Ecology and Evolution
Article source: University of New South Wales
Author: Diane Nazaroff
Image credit: allylester / Pixabay

Climate change induced yield reductions can be compensated by cultivar adaptation and global production can even be increased.
Global agriculture both is one of the major drivers of climate change and strongly affected by it. Rising temperatures are among the main reasons for yield reductions. Therefore, the agricultural sector is faced with the major challenge of adapting to climate change in order to ensure food security in the future. According to a new study carried out by international researchers, the use of locally adapted cultivars can significantly contribute to achieve this goal. The study was led by LMU geographer Dr. Florian Zabel.
For four different climate scenarios, he and his colleagues simulated the impacts of climate change on the global production of maize, rice, soy and wheat and investigated how locally adapted cultivars would affect crop yields. Thereby, the scenarios represent different socio-economic pathways that result in temperature increases ranging between 1.4 and 3.9°C in global average.
Our results show that, at least under moderate warming, we could even increase global yields by almost 20% until the end of the century.
Florian Zabel
“Our results show that, at least under moderate warming, we could generally adapt well to climate change and even increase global yields by almost 20% until the end of the century. Thereby, the increase of atmospheric CO2 partly attributes to the yield increase for some crops, due to positive effects on the efficiency of photosynthesis.” says Zabel.
Strong warming threatens adaptation
If global warming can be restricted to below 1.5°C, as specified in the Paris Agreements, the simulations suggest that 85% of the global cropland area can be optimally cultivated with already available cultivars.
The stronger the warming, the more new cultivars will be needed and the higher the risk that a required locally adapted cultivars that can cope with the changed local conditions will not be available.
In the worst-case scenario, almost 40% of global cropland could require new cultivars.
Florian Zabel
“In the worst-case scenario, almost 40% of global cropland could require new cultivars, of which some would need to have traits that currently do not exist,” says Zabel. Thereby, a critical point is that this even affects globally important production regions, such as North America’s Corn Belt, the world’s most important region for maize production.
“In addition, there are some regions where cultivar adaptation will not be possible, for instance due to a change in future precipitation and possible droughts,” says Zabel. The simulations consider local and regional effects of climate change, and therefore allow identifying regions where locally adapted cultivars could be particularly beneficial for yields. These include large areas of Europe, China and Russia. However, in other parts of the world – including Turkey, Northeastern Brazil, Texas, Kenya and parts of India – adapted cultivars are predicted to have little or no effect on yields, due to a reduction of available water for crops.
Innovative and more efficient breeding methods offer a possible solution. “Conventional breeding approaches often take years,” Zabel points out. “New methods such as CRISPR-Cas could help to develop required cultivars that are specifically adapted to local conditions more quickly and in a more targeted way,” Zabel adds.
The study appears in the journal Global Change Biology. In addition to the authors based at LMU, researchers at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, the Technical University of Munich (TUM), the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, at Columbia University in the City of New York (USA), the University of Chicago (USA), the Université de Liège (Belgium), the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (Austria), China Agricultural University in Beijing, the University of Birmingham (UK) and Lund University (Sweden).
Read the paper: Global Change Biology
Article source: Ludwig- Maximilians-Universität München
Image credit: Ludwig- Maximilians-Universität München
