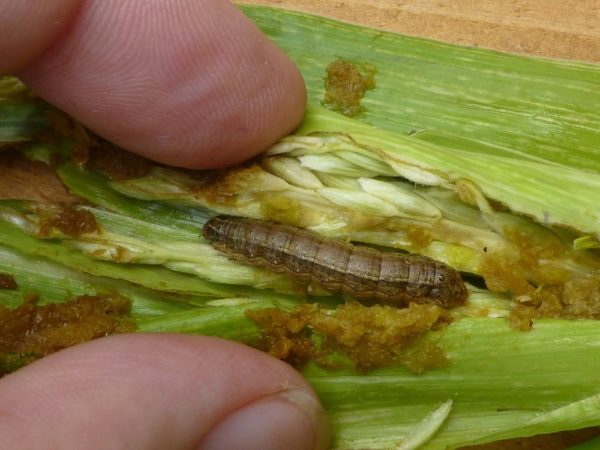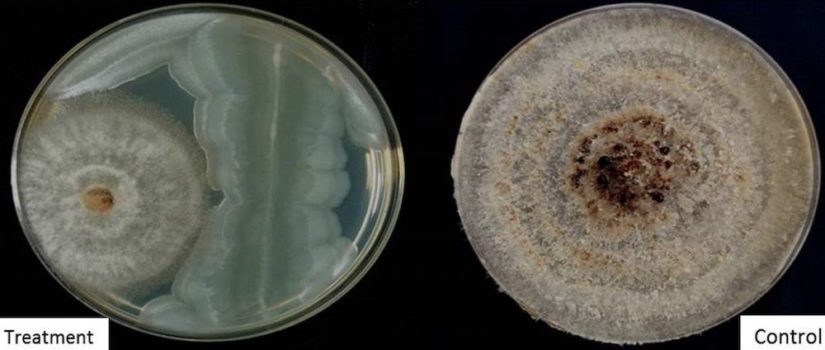
The effective management of plant diseases is of fundamental importance for forestry, food, and other plant-derived product productions, as well as for the sustainability of natural environments. Changing global climate patterns and the trade of planting materials across the borders…
Read More