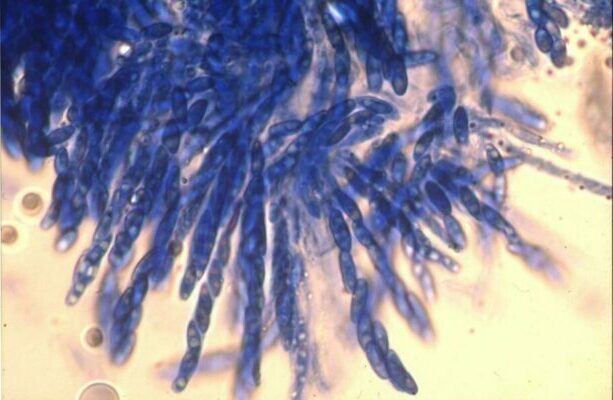
Researchers have re-animated specimens of a fungus that causes coffee wilt to discover how the disease evolved and how its spread can be prevented.

Researchers have re-animated specimens of a fungus that causes coffee wilt to discover how the disease evolved and how its spread can be prevented.

Plant diseases don’t stop at national borders and miles of oceans don’t prevent their spread, either. That’s why plant disease surveillance, improved detection systems, and global predictive disease modeling are necessary to mitigate future disease outbreaks and protect the global food supply, according to a team of researchers.

Due to their complexity and microscopic scale, plant-microbe interactions can be quite elusive. Each researcher focuses on a piece of the interaction, and it is hard to find all the pieces let alone assemble them into a comprehensive map to find the hidden treasures within the plant microbiome. This is the purpose of review, to take all the pieces from all the different sources and put them together into something comprehensive that can guide researchers to hidden clues and new associations that unlock the secrets of a system.

The detrimental impact of pesticides on non-target organisms is one of the most urgent concerns in current agriculture. Double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) represent the most species-specific class of pesticides to date, potentially allowing control of a target pest without effecting other species.

Living beings need elements to develop properly. The study of ionomics measures and analyses the element accumulations in living organisms to determine which mineral nutrients are required and not required for growth.

A recent work describes a new rapid ‘leaf-disk assay’ that uses chlorophyll fluorescence emissions to determine whether a weed is resistant to various systemic and contact herbicides.

A new study shows invasive plants are adapting to new habitats and new climates at an increasing pace – and especially so in tropical environments.

Commentary on Gobert et al. The authors prove the feasibility of an idea through this proof-of-concept work. As they point out, plant antiviral treatments are usually virus-specific, unfortunately for the moment a ‘broad-spectrum’ plant antiviral does not exist.

An international research studied the molecular mechanisms of the plant immune system. They were able to show a connection between a relatively unknown gene and resistance to pathogens.

A new study indicates that agricultural activity confuses the mechanisms that regulate the occurrence of plant diseases in nature. A wider variety of virus species was found in meadows close to agricultural fields compared to those located in natural surroundings, with the richness of plant species having no effect on the number of virus species. However, maintaining biodiversity is worthwhile, as plant richness did reduce the number of viral infections in the meadows.