


The scientists’ research indicates that the storage root was an already-existing trait that predisposed the plant for cultivation and not solely the result of human domestication, as previously thought. This discovery, published in Nature Plants, is part of a comprehensive monographic study of the morning glories, the biggest study of this group of plants to date, which also contributes important insights to the taxonomy and evolution of this megadiverse group of plants.
The researchers also discovered that sweet potato is not the only species of morning glory that produces storage roots. In fact at least 62 other species in the group also produce these underground organs, some of them as big as those of the sweet potato and many also edible.
Dr Pablo Muñoz, from Oxford‘s Department of Plant Sciences, whose PhD thesis formed a significant part of the paper, said: ‘Most other studies trying to understand the evolution of the sweet potato assumed that its storage root is a product of domestication by humans whereas this study demonstrates that storage roots evolved many times independently in different species including sweet potato before humans.’
The plant genus Ipomoea, commonly known as morning glories, is one of the largest groups of flowering plants in the world. It includes over 800 species, including many ornamental plants and one of the most important crops for human consumption: the sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas). However, despite their importance and widespread distribution, most species of morning glories are very poorly known and have never been studied across their entire geographical range, hindering the understanding of this important group of plants.
Researchers at the University of Oxford’s Department of Plant Sciences have led the first comprehensive monographic study of the morning glories at a global scale. It is a long-term collaboration with colleagues at the International Potato Center, in Peru, Oregon State and Duke Universities in the US and the Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh. Their results include the description of 63 new species (almost 10% of the species known in the whole genus) and the identification of a large number of synonyms — entities described in different places under different names that are, in reality, the same species.
Their methods could offer a solution to the massive backlog in documenting and describing the bulk of the world’s plant species.
The scientists demonstrate how a monographic taxonomic study, carried out at a global scale, can make massive contributions to our understanding of the diversity existing in poorly known groups of organisms. By working out the evolution of the morning glories, they were also able to investigate several questions pertaining to the origin and evolution of the sweet potato.
The research uses herbarium specimens — dried plants preserved in botanical gardens, museums and other institutions — for both morphological comparative studies and molecular analyses. Herbarium specimens constitute an unparalleled resource with which to address the study of inadequately known groups of plants and is the only feasible way to study megadiverse tropical groups across their entire distribution.
Lead author, Professor Robert Scotland, said: ‘We hope this study acts as a catalyst in demonstrating the scale of progress that can be achieved. Taxonomy has often been perceived as a merely descriptive science, a continuation of the work carried out by 18th and 19th century naturalists and no longer necessary.
‘However, we believe that an accurate, up-to-date taxonomy is necessary to tackle the biodiversity crisis. A large percentage of tropical plant species are so poorly known that, in practice, they are invisible to conservation studies. Taxonomy is the science that underpins biology and provides our basic knowledge of what species there are and where they live. Our study demonstrates the potential of taxonomy, through the integration of morphological studies and molecular analyses, to contribute to understanding much of the plant diversity existing on Earth.’
Professor Robert Scotland said
Read the paper: Nature Plants
Article source: University of Oxford
Image credit: Chang Min SHIN / Pixabay


Atmospheric nitrogen is not directly usable by most living things. In nature, specialized microbes in soils and bodies of water convert nitrogen into ammonia — a crucial form of nitrogen that life can easily access — through a process called nitrogen fixation. In agriculture, soybeans and other legumes that facilitate nitrogen fixation can be planted to restore soil fertility.
An additional obstacle in the process of making nitrogen available to the plants and ecosystems that rely on it is that microbial nitrogen “fixers” incorporate a complex protein called nitrogenase that contains a metal-rich core. Existing research has focused on nitrogenases containing a specific metal, molybdenum.
The extremely small amount of molybdenum found in soil, however, has raised concerns about the natural limits of nitrogen fixation on land. Scientists have wondered what restrictions the scarcity of molybdenum places on nature’s capacity to restore ecosystem fertility in the wake of human-made disturbances, or as people increasingly search for arable land to feed a growing population.
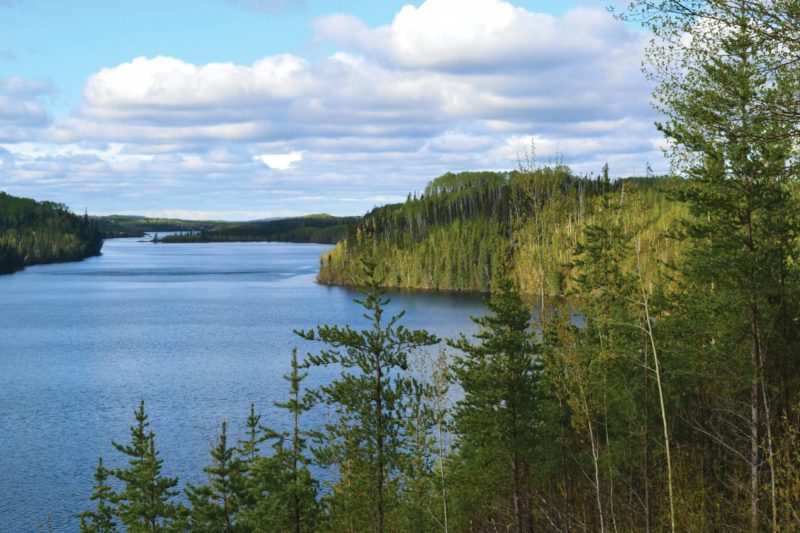
Princeton University researchers have found evidence that nitrogen fixation can be facilitated by metals that are more abundant in soil, which suggests that nitrogen fixation may be more resilient to molybdenum scarcity than previously thought, according to a study published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Science. Working in a 372 mile (600 kilometer) stretch of boreal forest in Canada, the researchers found that nitrogen fixation at an ecosystem scale can also be catalyzed by the metal vanadium, particularly in northern regions with limited natural nitrogen inputs.
“This work prompts a major revision of our understanding of how micronutrients control ecosystem nitrogen status and fertility,” said senior author Xinning Zhang, assistant professor of geosciences and the Princeton Environmental Institute.
“We need to know more about how nitrogen fixation manifests in terms of nutrient budgets, cycling and biodiversity,” she said. “One consequence of this finding is that current estimates of the amount of nitrogen input into boreal forests through fixation may be significantly underestimated. This is a major issue for our understanding of nutrient requirements for forest ecosystems, which currently function as an important sink for anthropogenic carbon.”
First author Romain Darnajoux, a postdoctoral research associate in Zhang’s research group, explained that the findings validate a long-held hypothesis in the scientific community that different metal variants of nitrogenase exist so that organisms can cope with changes in metal availability. The researchers found that vanadium-based nitrogen fixation was only substantive when environmental molybdenum levels were low.
“It would seem that nature evolved backup methods to sustain ecosystem fertility when the environment is variable,” Darnajoux said. “Every nitrogen-cycle step involves an enzyme that requires particular trace metals to work. Molybdenum and iron are typically the focus of scientific study because they’re considered to be essential in the nitrogen-fixing enzyme nitrogenase. However, a vanadium-based nitrogenase also exists, but nitrogen input by this enzyme has been unfortunately largely ignored.”
Darnajoux and Zhang worked with Nicolas Magain and François Lutzoni at Duke University and Marie Renaudin and Jean-Philippe Bellenger at the University of Sherbrooke in Québec.
The researchers’ results suggest that the current estimates of nitrogen input into boreal forests through fixation are woefully low, which would underestimate the nitrogen demand for robust plant growth, Darnajoux said. Boreal forests help mitigate climate change by acting as a sink for anthropogenic carbon. Though these northern forests do not see as many human visitors as even the most lightly populated metropolis, human activities can still have major impacts on forest fertility through the atmospheric transport of air pollution loaded with nitrogen and metals such as molybdenum and vanadium.
“Human activities that substantially change air quality can have a far-reaching influence on how even remote ecosystems function,” Zhang said. “The findings highlight the importance of air pollution in altering micronutrient and macronutrient dynamics. Because air is a global commons, the connection between metals and nitrogen cycling and air pollution has some interesting policy and management dimensions.”
The researchers’ findings could help in the development of more accurate climate models, which do not explicitly contain information on molybdenum or vanadium in simulations of the global flow of nitrogen through the land, ocean and atmosphere.
The importance of vanadium-driven nitrogen fixation extends to other high-latitude regions, and most likely to temperate and tropical systems, Darnajoux and Zhang said. The threshold for the amount of molybdenum an ecosystem needs to activate or deactivate vanadium nitrogen fixation that they found in their study was remarkably similar to the molybdenum requirements of nitrogen fixation found for samples spanning diverse biomes.
The researchers will continue the search for vanadium-based nitrogen fixation in the northern latitudes. They’ve also turned their eyes toward areas closer to home, initiating studies of micro- and macronutrient dynamics in temperate forests in New Jersey, and they plan to expand their work to tropical systems.
Read the paper: Proceedings of the National Academy of Science
Article source: Princeton University
Author: Joseph Albanese
Image credit: Marie Renaudin, University of Sherbrooke


Genomic information from plants can be used to enhance agricultural production and improve food security in a sustainable manner. Through better understanding of the relationship between a plant’s genetic information and the resulting behaviour, improved crops with better traits (resistance to diseases, tolerance to drought, etc.) can be developed. This can be achieved through cross pollinating plants with selected traits to produce a hybrid with the desired characteristics.
A research team led by Prof Eunyoung CHAE from the Department of Biological Sciences, NUS has discovered that in selective plant breeding, the genes responsible for providing defence responses against powdery mildew (RPW8) in the Arabidopsis thaliana plant, when duplicated as multiple copies in the genome, can misregulate immune receptors to trigger autoimmunity in hybrid plants. This can cause the premature gradual death of the foliage in these hybrids, known as hybrid necrosis.
The researchers applied a technique known as the genome-wide association mapping study (GWAS) to the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana in this research. GWAS is an important tool to identify genetic variation in plants which are associated with a particular trait. It allows the researchers to identify Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) which mark the causal natural variation in the genome responsible for growth-immunity trade-off. These SNPs are like postal codes showing the genetic information that are associated with autoimmune symptoms in plants. The SNPs were found to be located adjacent to a multi-gene cluster which is known to confer resistance to powdery mildew (a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants). The team found that having multiple copies of this set of genetic codes (RPW8) in Arabidopsis thaliana is detrimental as it triggers its autoimmunity mechanism even in the absence of pathogens.
Prof Chae said, “The plant Arabidopsis thaliana used in our study belongs to the Brassicaceae family, and the family members include vegetables such as broccoli, kale, cabbage, mustard and bok choy. Our team is currently assessing the variability of the plant immune system, particularly on the powdery mildew resistance gene clusters in this family, and if the variability is associated with heightened resistance and/or trade-off between immunity and growth.”
Read the paper: PLOS GENETICS
Article source: National University of Singapore
Image credit: PLOS GENETICS

