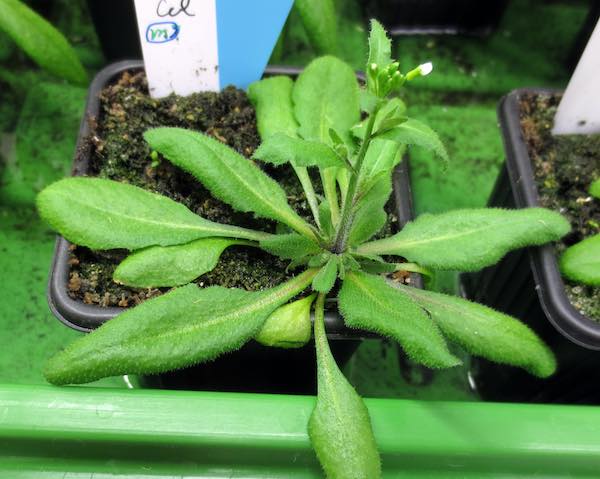
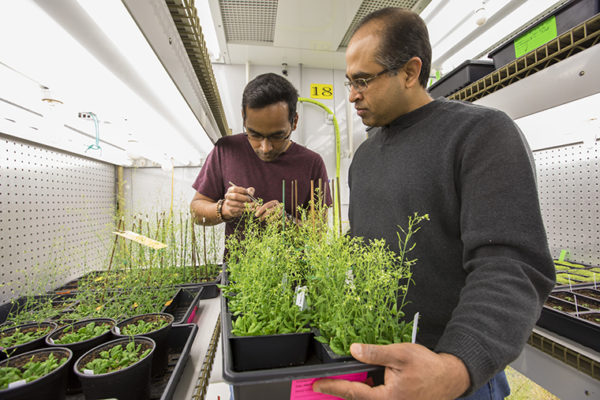
Producing fewer sperm cells can be advantageous in self-fertilizing plants. An international study has identified a gene in the model plant Arabidopsis that reduces the number of pollen. In addition to supporting the evolutionary theory, these findings could help to…
Read More