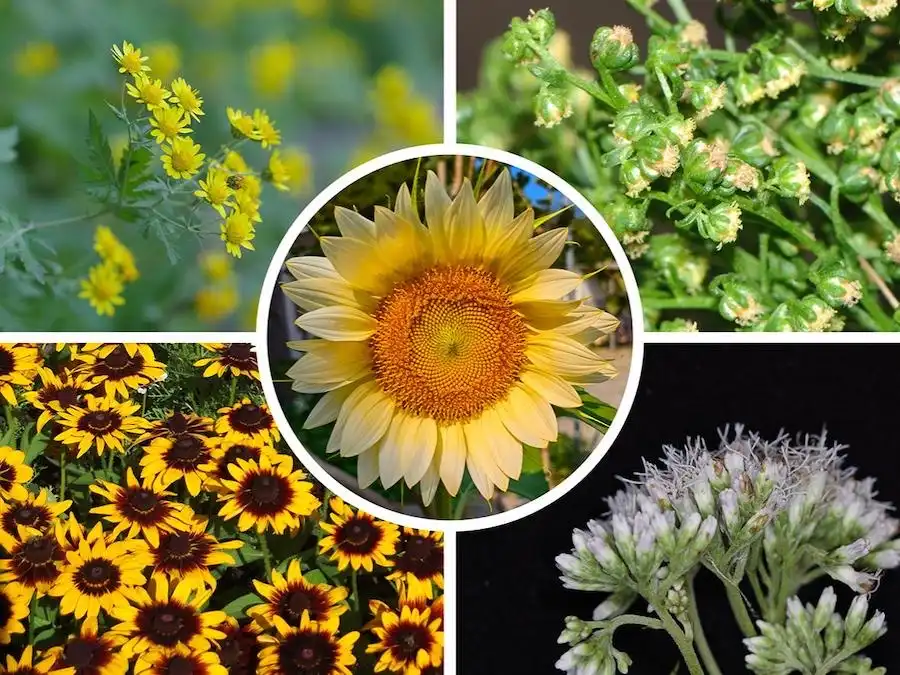
The sunflower family's intricate evolutionary history, unveiled through genetic analysis, showcases the fascinating phenomenon of convergent evolution. Flower symmetry, a key trait, has independently evolved multiple times within this diverse plant group. Insights gleaned may aid in breeding plants with…
Read More