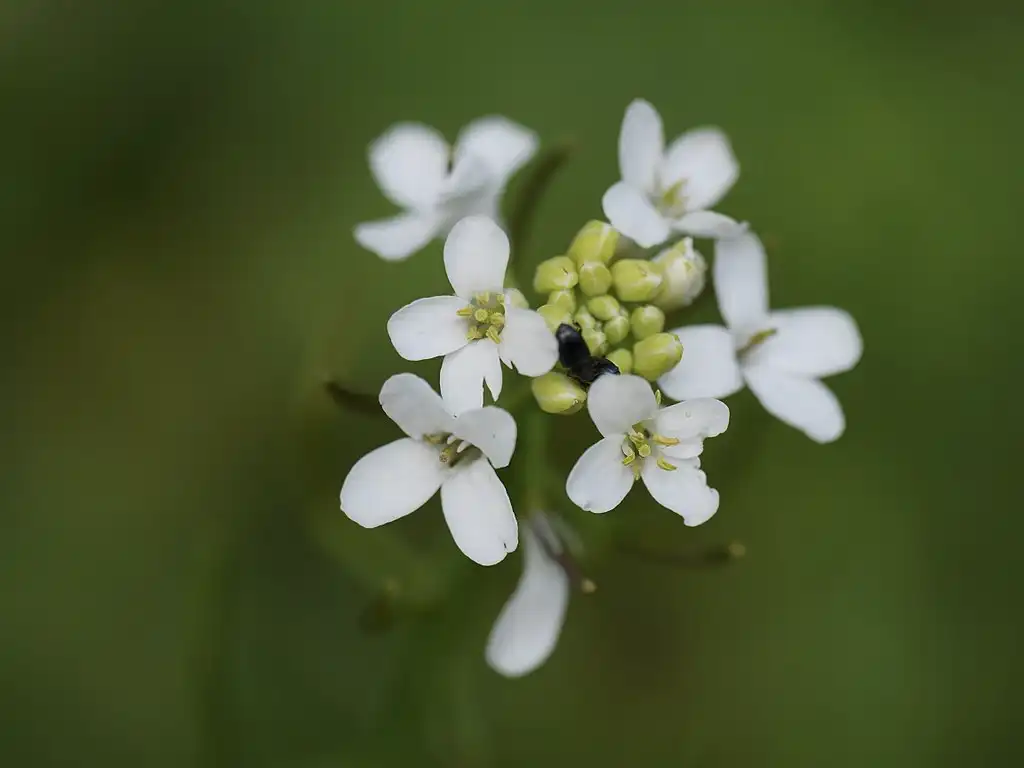
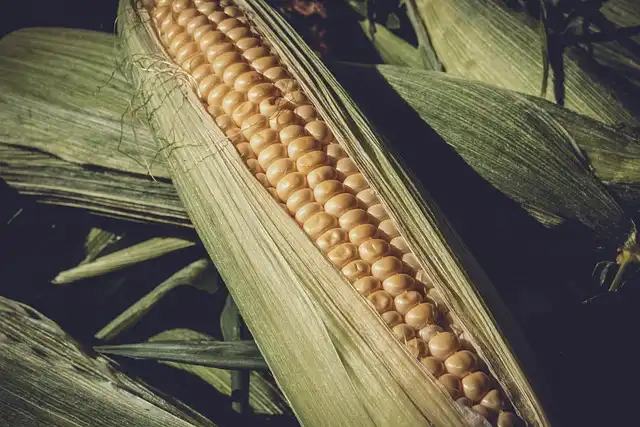
An international team of researchers led by biologists has examined how seed formation is coordinated with fruit growth. In their report, they explain the genetic control mechanisms underlying the process. If you open up a pea pod, you will find that all of the peas inside are the same size and the same distance apart. The same is true of princess beans, runner beans and soybeans as well as various other peas and beans, and it also applies to non-pulses. This is surprising because both the seed size and number and the pod size differ substantially from one variety to the next.