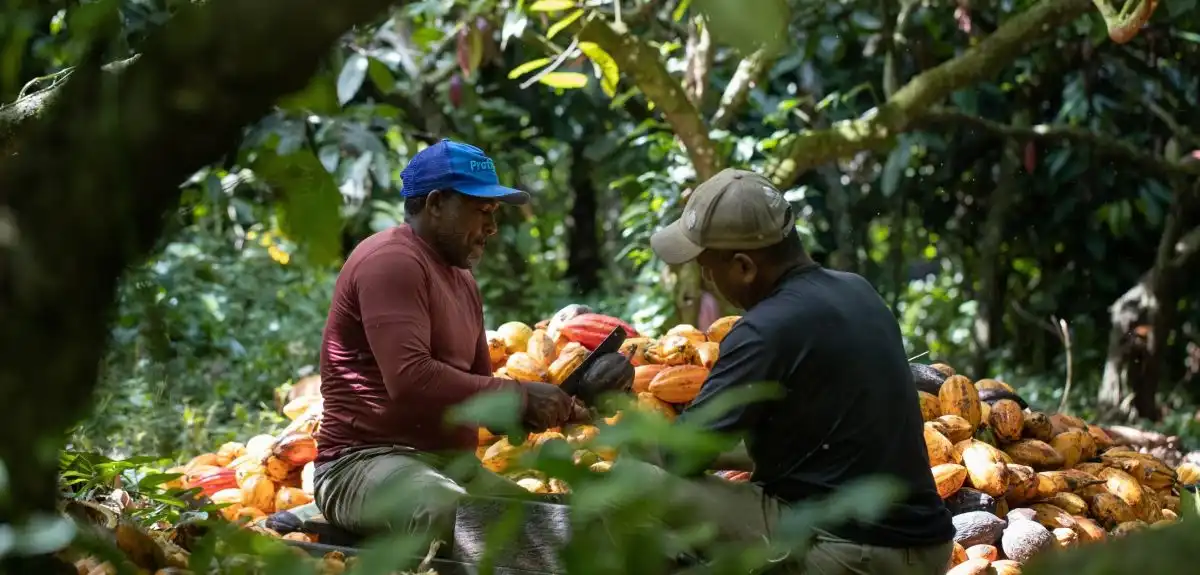
A study reveals that sustainable agricultural practices can future-proof cocoa production. By enhancing pollination and mitigating climate risks, cocoa yields can increase without expanding plantations, supporting millions of farmers and the USD 100 billion chocolate industry while safeguarding biodiversity.
Read More