Reposted with kind permission from the MSU-DOE Plant Research Laboratory. Original article.
By: Igor Houwat, Atsuko Kanazawa, David Kramer

The need for speed: increasing plant yield is one way to increase food and fuel resources. But asking plants to simply do more of the usual is a strategy that can backfire. Photo by Romain Peli on Unsplash
When engineers want to speed something up, they look for the “pinch points”, the slowest steps in a system, and make them faster.
Say, you want more water to flow through your plumbing. You’d find the narrowest pipe and replace it with a bigger one.
Many labs are attempting this method with photosynthesis, the process that plants and algae use to capture solar energy.
All of our food and most of our fuels have come from photosynthesis. As our population increases, we need more food and fuel, requiring that we improve the efficiency of photosynthesis.
But, Dr. Atsuko Kanazawa and the Kramer Lab are finding that, for biological systems, the “pinch point” method can potentially do more harm than good, because the pinch points are there for a reason! So, how can this be done?
ATP synthase: an amazing biological nanomachine
Atsuko and her colleagues at the MSU-DOE Plant Research Laboratory (PRL) have been working on this problem for over 15 years. They have focused on a tiny machine in the chloroplast called the ATP synthase, a complex of proteins essential to storing solar energy in “high energy molecules” that power life on Earth.
That same ATP molecule and a very similar ATP synthase are both used by animals, including humans, to grow, maintain health, and move.
In plants, the ATP synthase happens to be one of the slowest process in photosynthesis, often limiting the amount of energy plants can store.
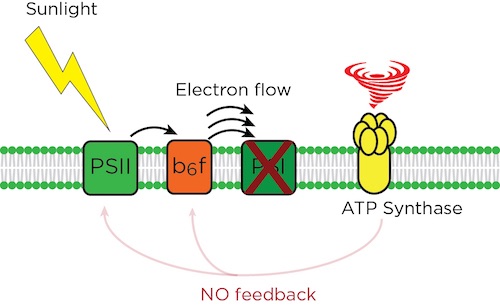
Photosynthetic systems trap sunlight energy that starts the reaction to move electrons forward in an assembly-line fashion to make useful energy compounds. The ATP synthase is one of the “pinch points” that slows the flow as needed, so plants stay healthy. In cfq, the absence of feedback leads to an electron pile up at PSI, and a crashed system. By MSU-DOE Plant Research Laboratory, except tornado graphic/CC0 Creative Commons
Kicking up the gears of plant production
Atsuko thought, if the ATP synthase is such an important pinch point, what happens if it were faster? Would it be better at photosynthesis and give us faster growing plants?
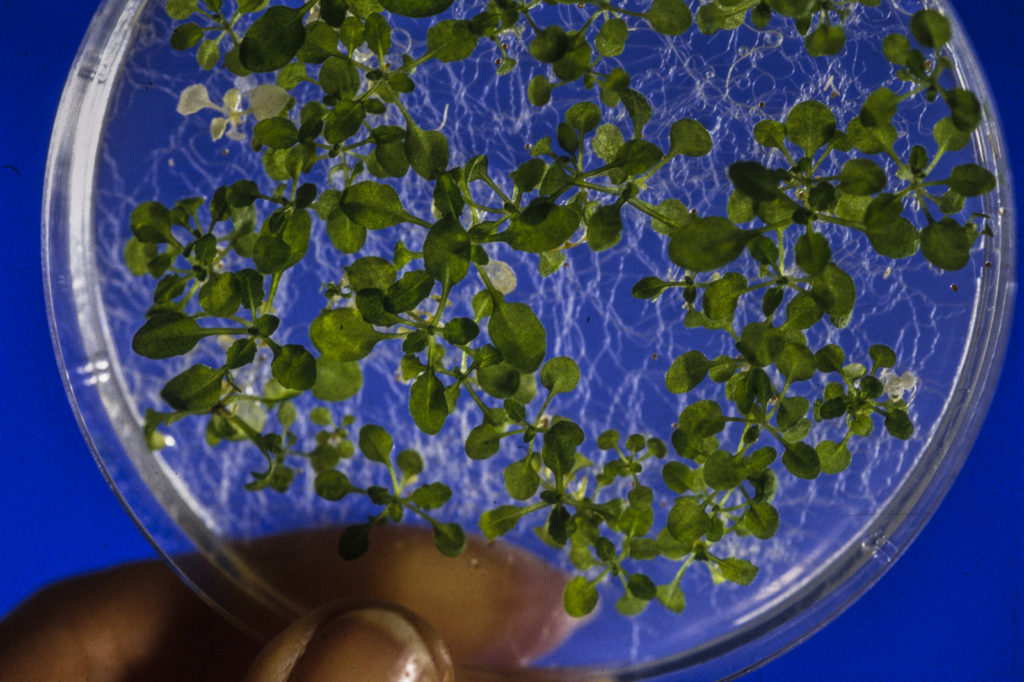
Years ago, she got her hands on a mutant plant, called cfq, from a colleague. “It had an ATP synthase that worked non-stop, without slowing down, which was a curious example to investigate. In fact, under controlled laboratory conditions – very mild and steady light, temperature, and water conditions – this mutant plant grew bigger than its wild cousin.”
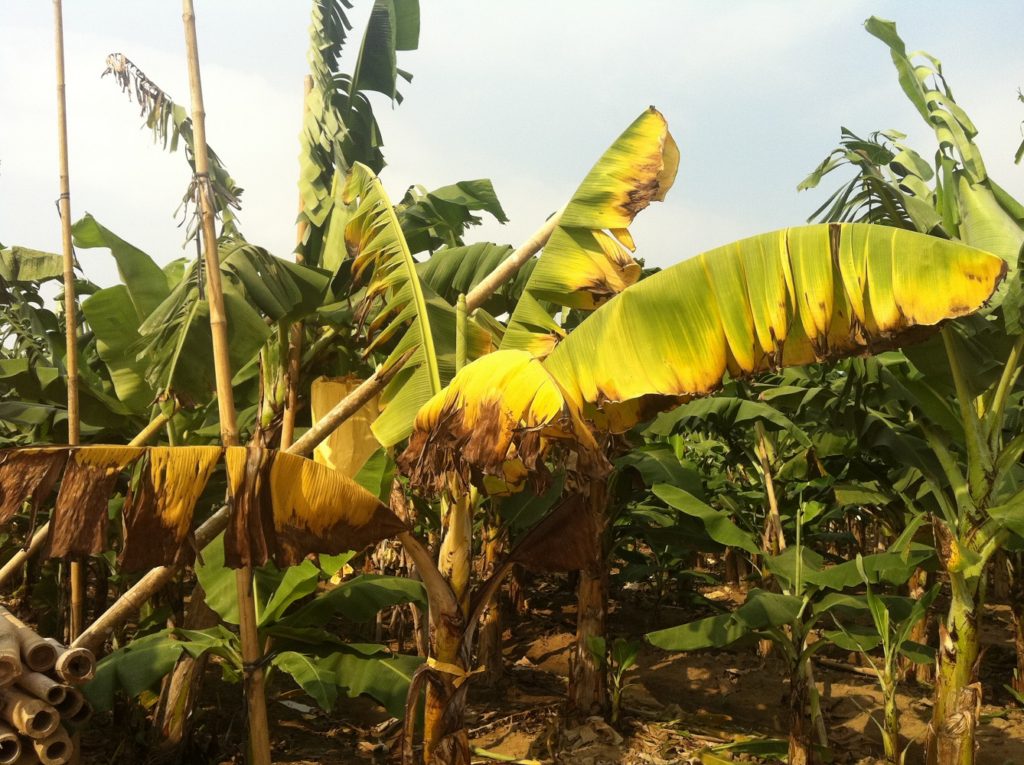
But when the researchers grew the plant under the more varied conditions it experiences in real life, it suffered serious damage, nearly dying.
“In nature, light and temperature quality change all the time, whether through the passing hours, or the presence of cloud cover or winds that blow through the leaves,” she says.
Plants slow photosynthesis for a reason!
Atsuko’s research now shows that the slowness of the ATP synthase is not an accident; it’s an important braking mechanism that prevents photosynthesis from producing harmful chemicals, called reactive oxygen species, which can damage or kill the plant.
“It turns out that sunlight can be damaging to plants,” says Dave Kramer, Hannah Distinguished Professor and lead investigator in the Kramer lab.
“When plants cannot use the light energy they are capturing, photosynthesis backs up and toxic chemicals accumulate, potentially destroying parts of the photosynthetic system. It is especially dangerous when light and other conditions, like temperature, change rapidly.”
“We need to figure out how the plant presses on the brakes and tune it so that it responds faster…”
The ATP synthase senses these changes and slows down light capture to prevent damage. In that light, the cfqmutant’s fast ATP is a bad idea for the plant’s well-being.
“It’s as if I promised to make your car run faster by removing the brakes. In fact, it would work, but only for a short while. Then things go very wrong!” Dave says.
“In order to improve photosynthesis, what we need is not to remove the brakes completely, like in cfq, but to control them better,” Dave says. “Specifically, we need to figure out how the plant presses on the brakes and tune it so that it responds faster and more efficiently,” David says.
Atsuko adds: “Scientists are trying different methods to improve photosynthesis. Ultimately, we all want to tackle some long-term problems. Crucially, we need to continue feeding the Earth’s population, which is exploding in size.”
The study is published in the journal, Frontiers in Plant Science.