





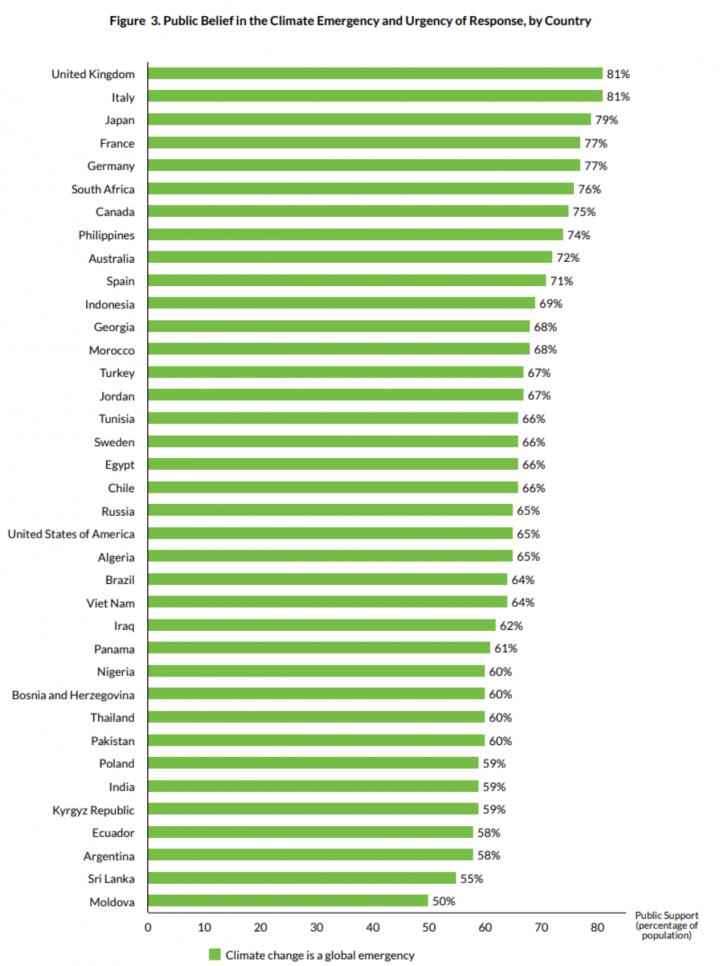
The results of the Peoples’ Climate Vote, the world’s biggest ever survey of public opinion on climate change are published in January. Covering 50 countries with over half of the world’s population, the survey includes over half a million people under the age of 18, a key constituency on climate change that is typically unable to vote yet in regular elections.
Detailed results broken down by age, gender, and education level will be shared with governments around the world by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), which organized the innovative poll with the University of Oxford. In many participating countries, it is the first time that large-scale polling of public opinion has ever been conducted on the topic of climate change. 2021 is a pivotal year for countries’ climate action commitments, with a key round of negotiations set to take place at the UN Climate Summit in November in Glasgow, UK.
In the survey, respondents were asked if climate change was a global emergency and whether they supported eighteen key climate policies across six action areas: economy, energy, transport, food & farms, nature and protecting people.
Results show that people often want broad climate policies beyond the current state of play. For example, in eight of the ten survey countries with the highest emissions from the power sector, majorities backed more renewable energy. In four out of the five countries with the highest emissions from land-use change and enough data on policy preferences, there was majority support for conserving forests and land. Nine out of ten of the countries with the most urbanized populations backed more use of clean electric cars and buses, or bicycles.
UNDP Administrator Achim Steiner said: “The results of the survey clearly illustrate that urgent climate action has broad support amongst people around the globe, across nationalities, age, gender and education level. But more than that, the poll reveals how people want their policymakers to tackle the crisis. From climate-friendly farming to protecting nature and investing in a green recovery from COVID-19, the survey brings the voice of the people to the forefront of the climate debate. It signals ways in which countries can move forward with public support as we work together to tackle this enormous challenge.”
The innovative survey was distributed across mobile gaming networks in order to include hard-to-reach audiences in traditional polling, like youth under the age of 18. Polling experts at the University of Oxford weighted the huge sample to make it representative of the age, gender, and education population profiles of the countries in the survey, resulting in small margins of error of +/- 2%.
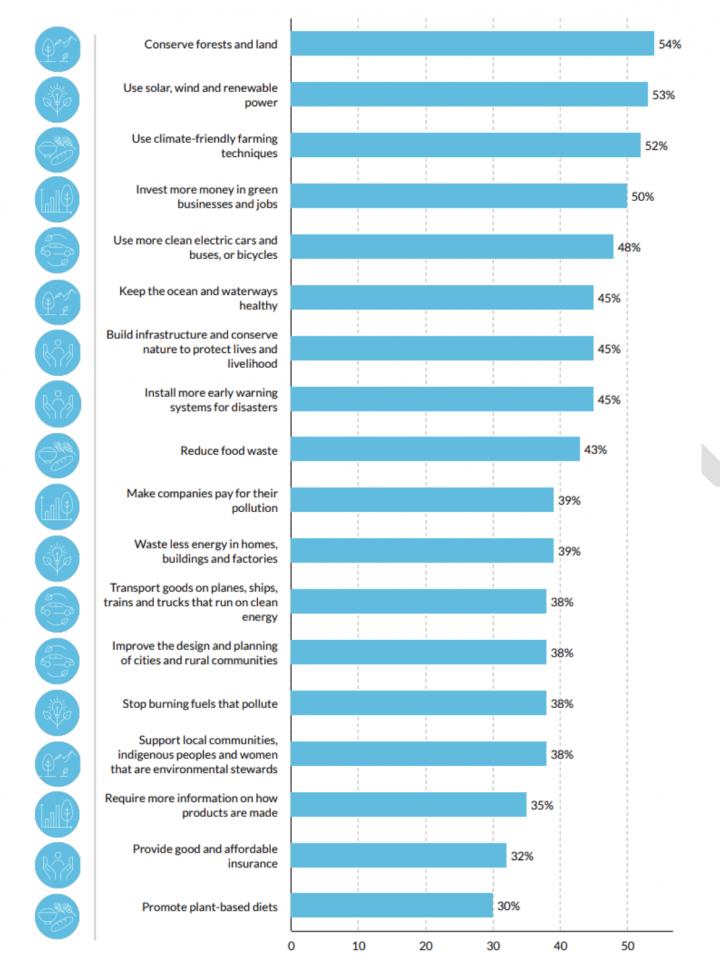
Policies had wide-ranging support, with the most popular being conserving forests and land (54% public support), more solar, wind and renewable power (53%), adopting climate-friendly farming techniques (52%) and investing more in green businesses and jobs (50%).
Prof. Stephen Fisher, Department of Sociology, University of Oxford, said: “The survey – the biggest ever survey of public opinion on climate change – has shown us that mobile gaming networks can not only reach a lot of people, they can engage different kinds of people in a diverse group of countries. The Peoples’ Climate Vote has delivered a treasure trove of data on public opinion that we’ve never seen before. Recognition of the climate emergency is much more widespread than previously thought. We’ve also found that most people clearly want a strong and wide-raging policy response.”
The survey shows a direct link between a person’s level of education and their desire for climate action. There was very high recognition of the climate emergency among those who had attended university or college in all countries, from lower-income countries such as Bhutan (82%) and Democratic Republic of the Congo (82%), to wealthy countries like France (87%) and Japan (82%).
Note:
The percentage of a population estimated to support a particular policy does not indicate that those who did not are against the same policy, since not endorsing a policy could also be due to indifference to it. The country results present what people think who are physically in a particular country. They are not representative of what nationals of a particular country think. So for example, they are representative not of what French people think, but of people in France.
Read the report: United Nations Development Programme
Article source: United Nations Development Programme via Eurekalert
Image credit: UNDP




The mutually beneficial relationship between legumes and rhizobia, the nitrogen-fixing soil bacteria that make their home in legume root nodules and create nutrient-rich fertilizer for them, is one of the most well-known and agronomically important examples of symbiosis. New research from Dr. Kenjiro Quides, a Postdoctoral Teaching and Research Fellow in the Grand Challenges Initiative at Chapman University, tested the boundaries of this relationship — and found that it’s not always as perfectly harmonious as previously thought.
The results are reported in a new paper in the journal Evolution.
Legumes provide carbohydrates for rhizobial bacteria that live in root nodules, while the rhizobia fix atmospheric nitrogen into a form that’s usable for the legume (nitrogen is often a limiting nutrient for plants). In theory, if legumes have greater root nodule growth, they should be able to host more rhizobia, which should produce more nitrogen and enable larger plant growth in general.
The research, carried out by Quides and colleagues at UC Riverside during his doctorate, tested the relationship between root nodule growth and rhizobia using a smaller relative of Soybeans, named Lotus japonicus. By using multiple genetic variants that formed a low, medium, and high number of nodules, the study showed that legumes grew to maximum size when a low and medium number of nodules formed, but legumes that formed a high number of nodules had drastically reduced growth.
The investigation then turned to the rhizobia. The size of the rhizobial population, a standard measure of bacterial growth, was found to continue to increase as the number of nodules formed increased. This suggests a hidden conflict in the symbiotic relationship. It seems that the legume and rhizobia interests are only aligned until the host optimum is reached, a point at which their interests diverge. This provides support for the conclusion that in the symbiotic relationship, rhizobia have an evolutionary advantage.
The results demonstrate that to avoid conflict in symbiotic relationships, hosts must tightly regulate their investment into symbiotic organs (like legumes’ root nodules) to maximize their own benefit-to-cost ratio of associating with their symbiotic partner.
“Legumes seem to play a balancing act to maximize their growth, but rhizobia continue to grow and that is a really exciting result,” Dr. Quides said.
He noted that this study opens the door to more research. “Although we found diminishing returns for the host from nodulation, the fact that rhizobia population size continued to increase is promising. We found the costs outweigh the benefits at high nodule numbers. However, if we can increase the number of nodules and therefore the rhizobia population size while minimizing the cost to the plant, we have the potential to increase the productivity of legume crops in the future.”
Read the paper: Evolution
Article source: Chapman University
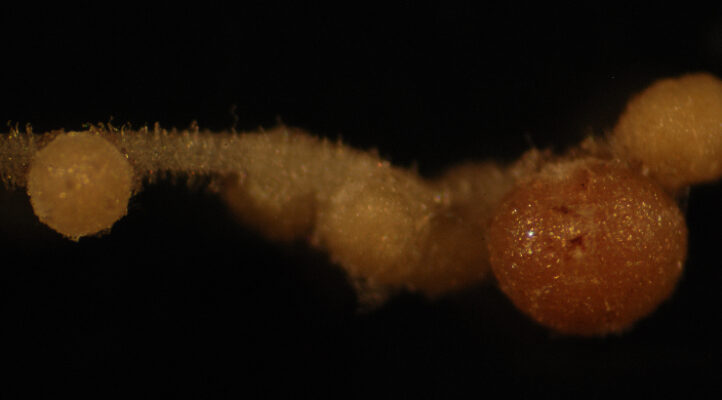
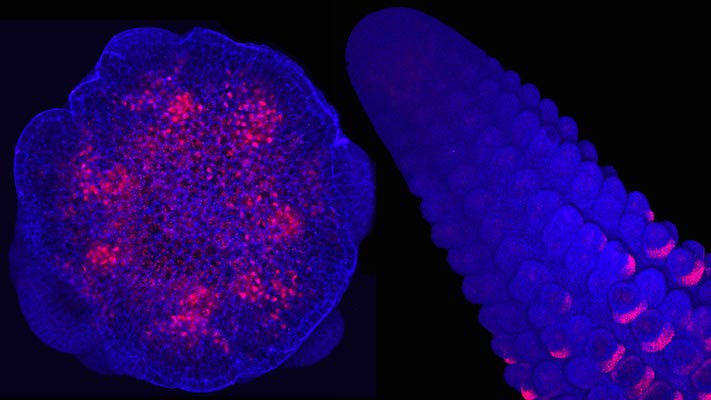
Image: A cluster of nodules on the roots of the plant Lotus japonicus. Bacterial rhizobia are housed within root nodules and supplied with carbohydrates from the host plant. The carbohydrates are used by rhizobia in exchange for the fixation of nitrogen then used by the plant. Credit: K. Quides
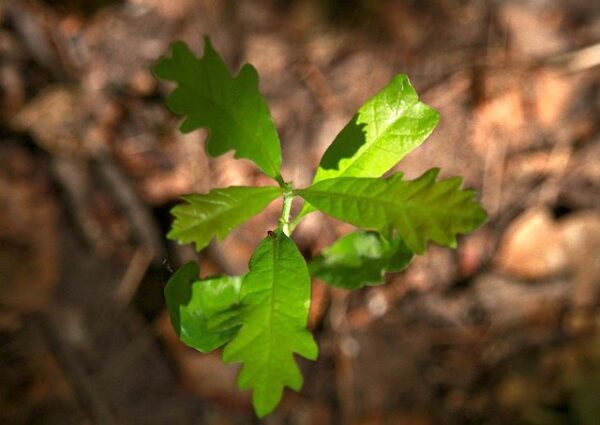

Scientists have been pondering if the microbiome of plants is due to nature or nurture. Research at Stockholm University, published in Environmental Microbiology, showed that oak acorns contain a large diversity of microbes, and that oak seedlings inherit their microbiome from these acorns.
“The idea that seeds can be the link between the microbes in the mother tree and its offspring has frequently been discussed, but this is the first time someone proves the transmission route from the seed to the leaves and roots of emerging plants”, says Ahmed Abdelfattah, researcher at the Department of Ecology Environment and Plant Sciences (DEEP) at Stockholm University.
The microorganisms found on the seed are often valuable for the plant, promoting its growth and protecting it against certain diseases. Each plant species harbours a distinct microbial community, with some of the microbes living on its surface and others inside the plant’s tissues.
The finding also means that since the microorganisms from the seed are there first, they can constitute a barrier which influences subsequent colonization by other microbes from the environment. The experiment was done in oaks, since it’s one of the most abundant tree species in the Swedish and European forests.
“The microorganisms from the seed are also expected to be very important for plant health and functioning”, says Ahmed Abdelfattah.
The fossil record indicates that plants have been associated with fungi and bacteria – constituting the microbiome – for more than 400 million years. Several species the scientists found on the oak seeds are already shown by other studies to be involved in the protection against several plant pathogens, growth-promotion, nitrogen-fixing, and the detoxification or biodegradation of toxic environmental pollutants.
Demonstrating inheritance under natural conditions is challenging since seeds are exposed to and dependent on their surrounding environment when they sprout, especially the soil, which is a microbially rich environment. Therefore, it’s nearly impossible to differentiate between which microorganism actually come from the seed or from the soil. The research team therefore used a novel culturing device, to grow oak seedlings in a microbe-free condition and keep the leaves separated from the roots. This allowed them to be certain that the microorganisms came from the seed, and that they could demonstrate that some seed microorganisms migrate to the roots, and some others to the leaves.
“Plant leaves and roots are already known to harbor distinct microbial communities, as shown by several recent studies. In this study however, we were surprised to see that it is also true at an early stage of the plant development, and that the seed could, at least partially, be responsible for these differences”, Says Ahmed Abdelfattah.
“Several breeding companies are taking into consideration the seed microbiome in their programs hoping to have super plants with better genes and better microbes. One technique used, is to treat seeds with beneficial microorganism with the aim that those microbes will eventually colonize the plant and exert their effects throughout the plant’s life”, says Ahmed Abdelfattah.
The next step for the research team is now to discern which is the major source of the of the microbiome – the environment or the seed.
Read the paper: Environmental Microbiology
Article source: Stockholm University
Author: Amanda Gonzalez Bengtsson
Image credit: Ирина Ирина / Pixabay