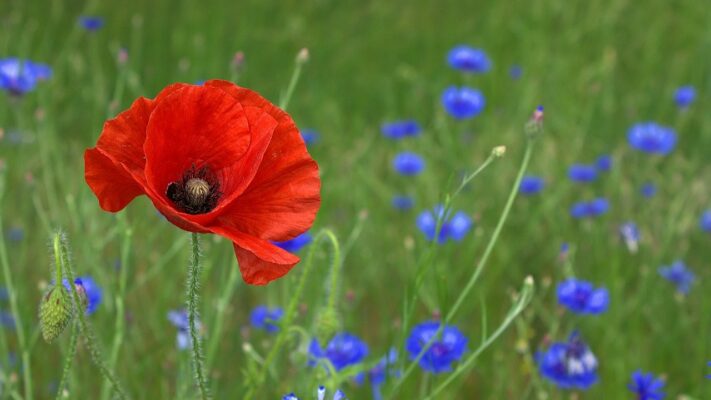
New research affirms a unique peptide found in an Australian plant can destroy the No. 1 killer of citrus trees worldwide and help prevent infection.
Huanglongbing, HLB, or citrus greening has multiple names, but one ultimate result: bitter and worthless citrus fruits. It has wiped out citrus orchards across the globe, causing billions in annual production losses.
All commercially important citrus varieties are susceptible to it, and there is no effective tool to treat HLB-positive trees, or to prevent new infections.
However, new UC Riverside research shows that a naturally occurring peptide found in HLB-tolerant citrus relatives, such as Australian finger lime, can not only kill the bacteria that causes the disease, it can also activate the plant’s own immune system to inhibit new HLB infection. Few treatments can do both.
Research demonstrating the effectiveness of the peptide in greenhouse experiments has just been published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The disease is caused by a bacterium called CLas that is transmitted to trees by a flying insect. One of the most effective ways to treat it may be through the use of this antimicrobial peptide found in Australian finger lime, a fruit that is a close relative of citrus plants.
“The peptide’s corkscrew-like helix structure can quickly puncture the bacterium, causing it to leak fluid and die within half an hour, much faster than antibiotics,” explained Hailing Jin, the UCR geneticist who led the research.
When the research team injected the peptide into plants already sick with HLB, the plants survived and grew healthy new shoots. Infected plants that went untreated became sicker and some eventually died.
“The treated trees had very low bacteria counts, and one had no detectable bacteria anymore,” Jin said. “This shows the peptide can rescue infected plants, which is important as so many trees are already positive.”
The team also tested applying the peptide by spraying it. For this experiment, researchers took healthy sweet orange trees and infected them with HLB-positive citrus psyllids — the insect that transmits CLas.
After spraying at regular intervals, only three of 10 treated trees tested positive for the disease, and none of them died. By comparison, nine of 10 untreated trees became positive, and four of them died.
In addition to its efficacy against the bacterium, the stable anti-microbial peptide, or SAMP, offers a number of benefits over current control methods. For one, as the name implies, it remains stable and active even when used in 130-degree heat, unlike most antibiotic sprays that are heat sensitive — an important attribute for citrus orchards in hot climates like Florida and parts of California.
In addition, the peptide is much safer for the environment than other synthetic treatments. “Because it’s in the finger lime fruit, people have eaten this peptide for hundreds of years,” Jin said.
Researchers also identified that one half of the peptide’s helix structure is responsible for most of its antimicrobial activity. Since it is only necessary to synthesize half the peptide, this is likely to reduce the cost of large-scale manufacturing.
The SAMP technology has already been licensed by Invaio Sciences, whose proprietary injection technology will further enhance the treatment.
Following the successful greenhouse experiments, the researchers have started field tests of the peptides in Florida. They are also studying whether the peptide can inhibit diseases caused by the same family of bacteria that affect other crops, such as potato and tomato.
“The potential for this discovery to solve such devastating problems with our food supply is extremely exciting,” Jin said.
Read the paper: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Article source: University of California – Riverside
Author: Jules Bernstein
Image: Untreated citrus plants on the left, as compared to treated ones on the right. Credit: Hailing Jin/UCR





New research has revealed how an invasion of the alien evergreen tree, Prosopis juliflora seriously diminishes water resources in the Afar Region of Ethiopia, consuming enough of this already scarce resource to irrigate cotton and sugarcane generating some US$ 320 million and US$ 470 million net benefits per year.
A team of Ethiopian, South African and Swiss scientists, including lead author Dr Hailu Shiferaw, Dr Tena Alamirew, and Dr Gete Zeleke from the Water and Land Resource Centre of Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia, and Dr Sebinasi Dzikiti from Stellenbosch University, South Africa, and Dr Urs Schaffner, Head Ecosystems Management, CABI, have been assessing water use of prosopis and its impacts on catchment water budget and rural livelihoods in the dry Afar Region of Ethiopia, since 2015 as part of a long-term collaboration in the framework of the CABI-led Woody Weeds project.
Their new study, published in Scientific Reports, provides evidence that this alien tree, which has invaded both the floodplains of the Awash River and the surrounding dryland habitats, uses excessive amounts of water by consuming approximately 3.1-3.3 billion m3/yr of water throughout the year in the Afar Region.
Dr Shiferaw said, “We found that single trees of the evergreen prosopis consume between 1-36 liters of water per day, depending on stem diameter and site conditions. Prosopis trees not only use water throughout the year, but even consume more water during the dry season, when almost all native plants have shed their leaves. The high sap flow of prosopis in the drylands throughout the year may be due to exceptionally deep roots that penetrate up to 50m below the surface, where they tap into groundwater that cannot be used by native trees with shorter roots.”
In the context of climate change and an increasing frequency of drought events in dry regions of Sub-Saharan Africa, the report concludes that this invasive tree is likely to have serious consequences for sustainable livelihoods in the region unless its spread is contained and its density reduced.
Dr Urs Schaffner, senior author and Head Ecosystems Management at CABI in Switzerland, said, “Since its introduction in the Afar Region in the 1980s, prosopis has invaded 1.2 million ha of land. Thus, unless the spread of prosopis is contained and the density reduced in areas where it has become established, this invasive tree is likely to have serious consequences for sustainable livelihoods in the region. The estimated net benefits from water savings alone would strongly justify the implementation of a coordinated control programme.”
The report clearly supports findings from work undertaken in South Africa on water use by invasive tree species. Prof Brian van Wilgen from Stellenbosch University, South Africa, previous scientific advisor to the ‘Working for Water’ programme in South Africa and partner of the Woody Weeds project, said, “In South Africa, invasive alien trees are estimated to reduce surface water runoff by between 1.5 and 2.5 billion m3 per year, and this could increase substantially as the invasions continue to spread. In addition, invasive trees in drier parts of the country have substantially reduced water in groundwater aquifers on which local farmers and towns are totally reliant.”
He further explained that, “These losses have serious consequences for a country where water scarcity limits economic activity and growth. The government in South Africa has responded by creating a multi-million dollar, national-scale programme, dubbed ‘Working for Water’, to control invasive alien trees, and has also passed legislation preventing further propagation of invasive alien trees and requiring landowners to control them.”
Read the paper: Scientific Reports
Article source: CABI
Image: Prosopis juliflora. Credit: CABI.