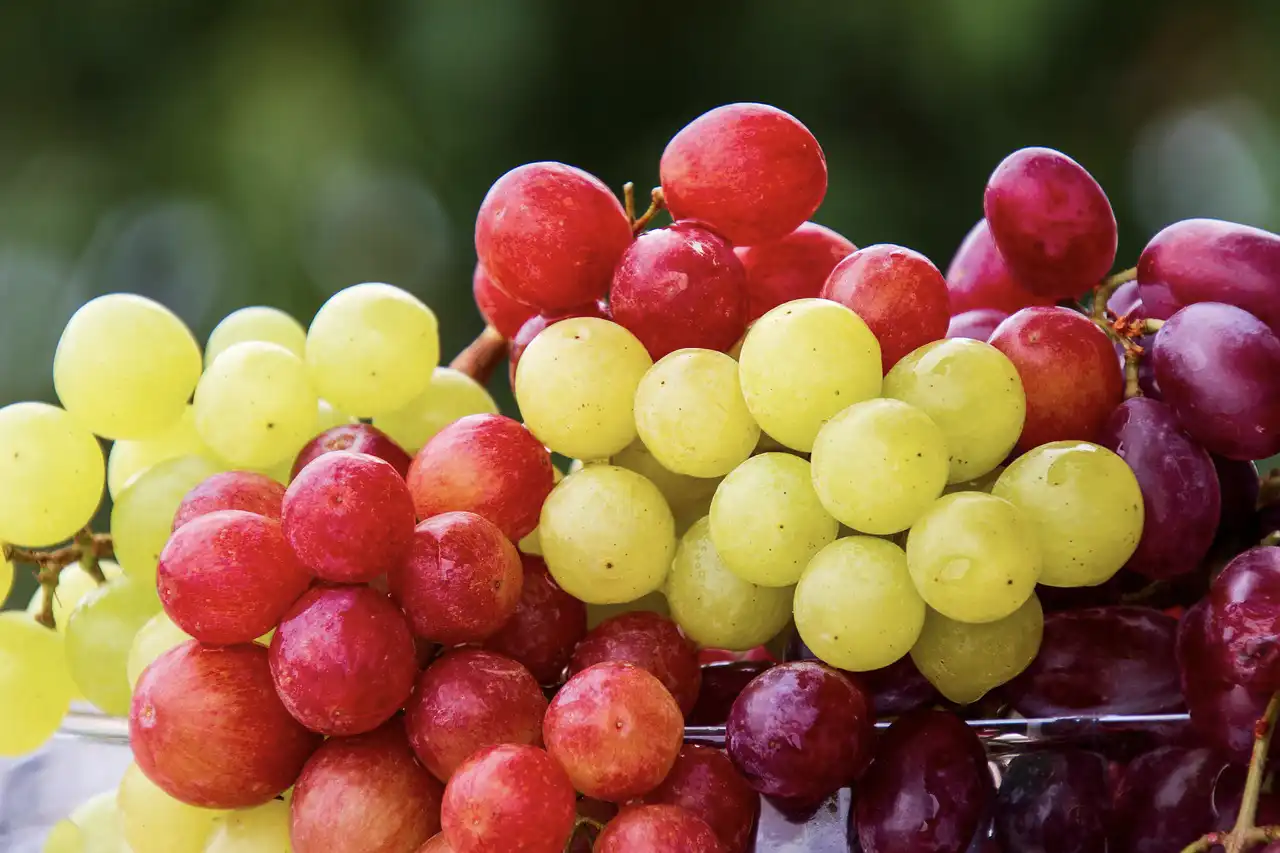
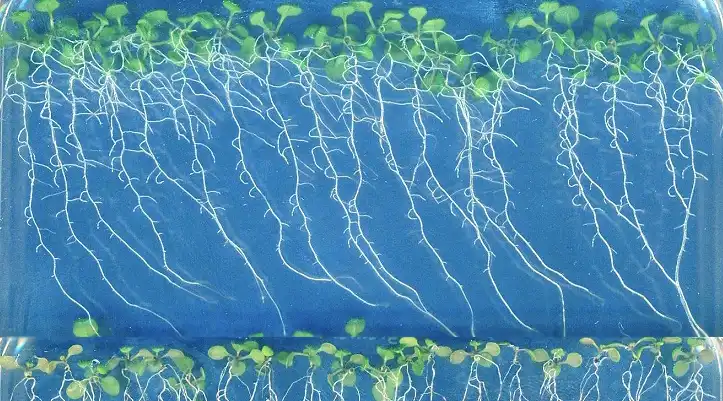
Researchers surveyed more than 2,800 people to assess how accepting they might be of gene-edited table grapes, even though none are yet on the market. Most participants cared more about the grapes’ taste, followed by their appearance, than how the…
Read More