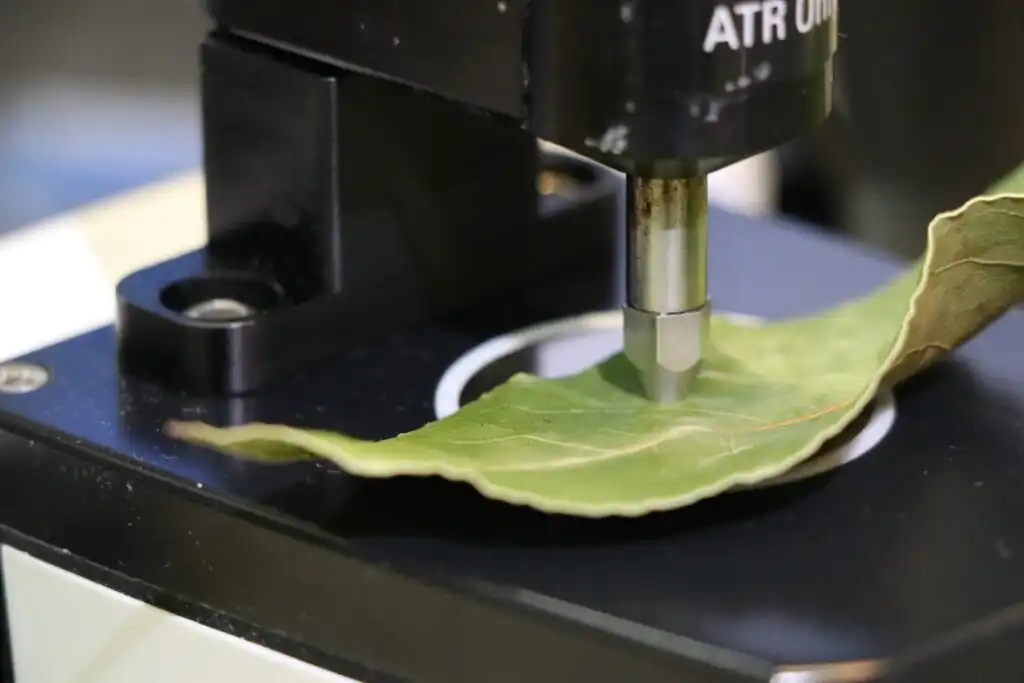
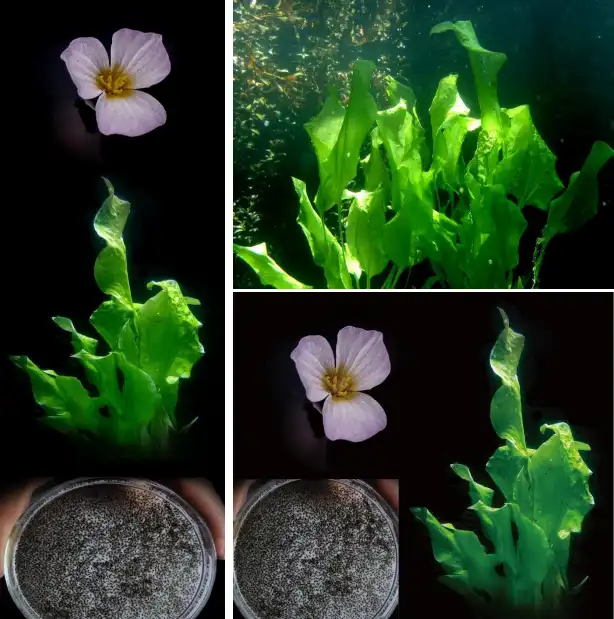
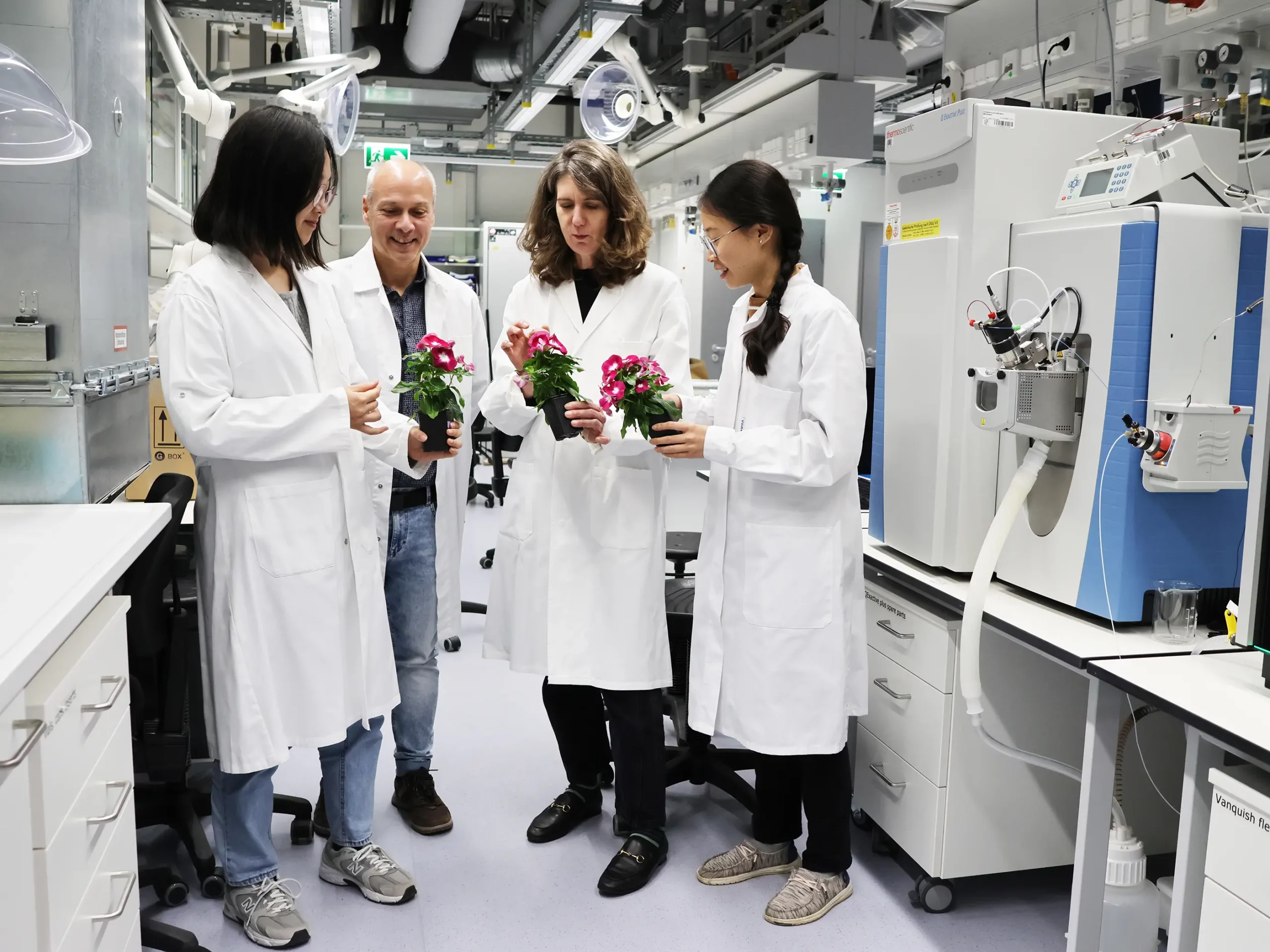
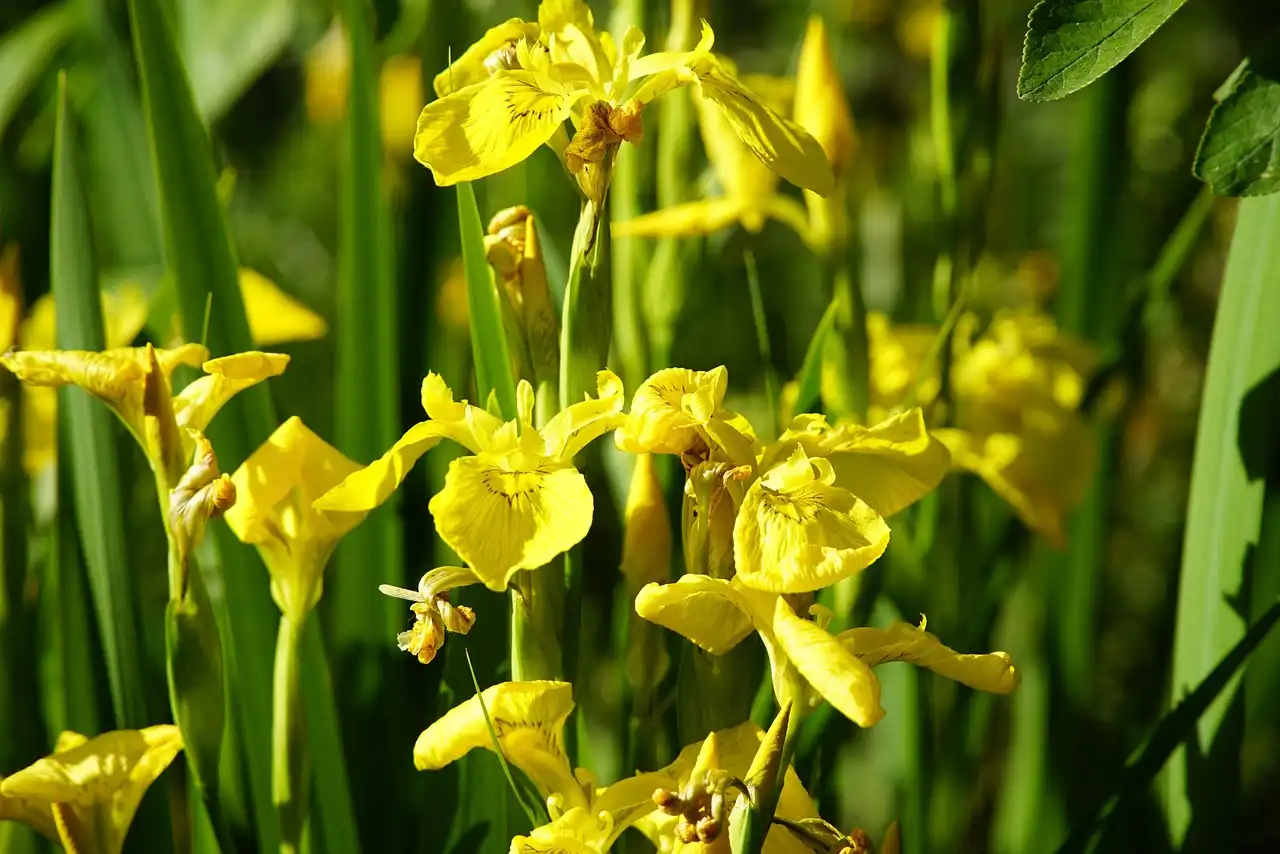
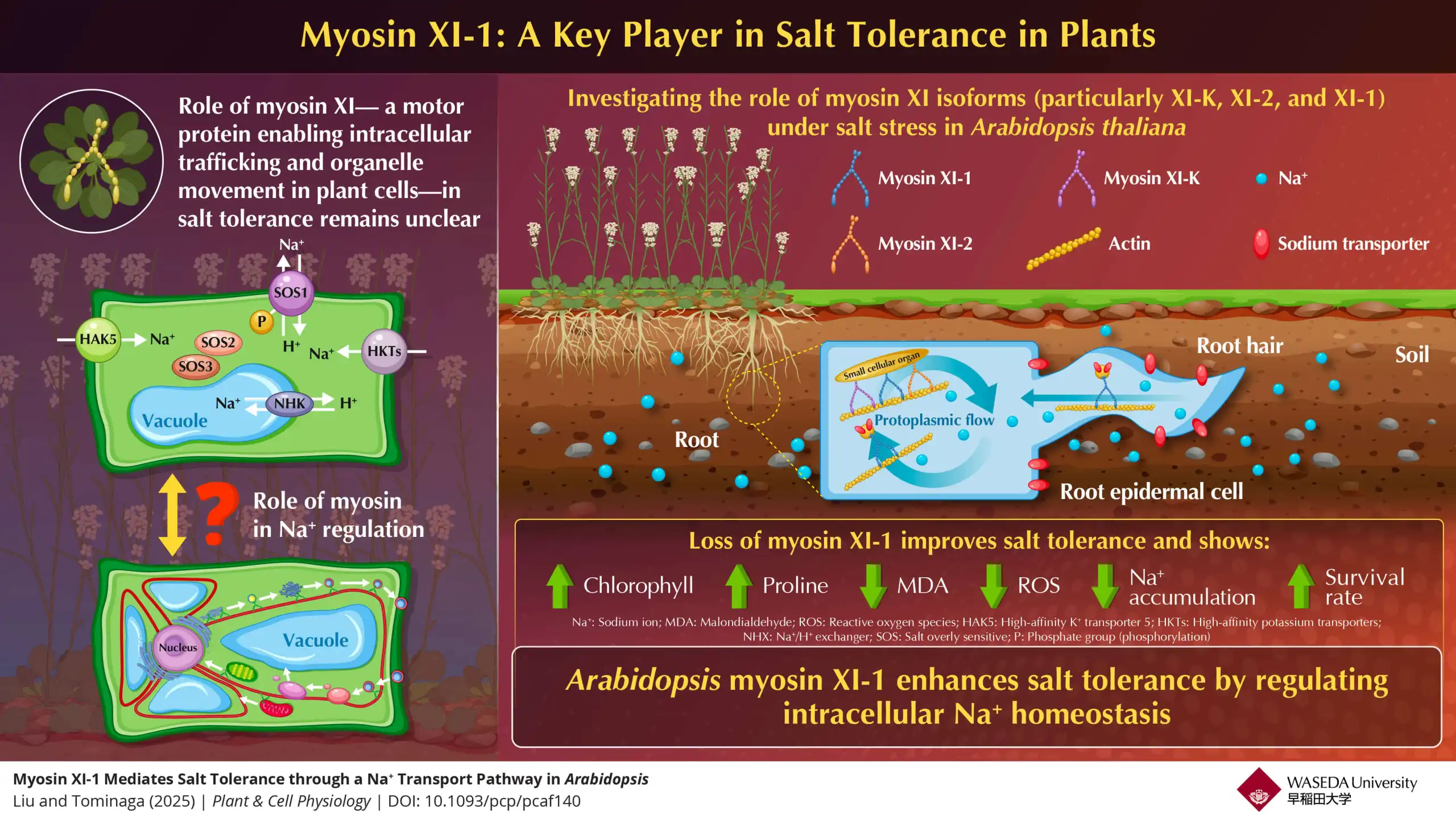
Wetlands function as biogeochemical filters, and new research suggests they may also help tackle PFAS contamination. In a recent greenhouse study, researchers showed that yellow flag iris plants, working in symbiosis with fungi on their roots, can take up and…
Read More