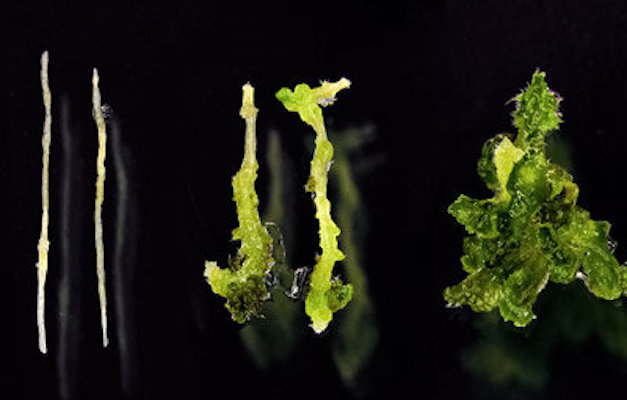
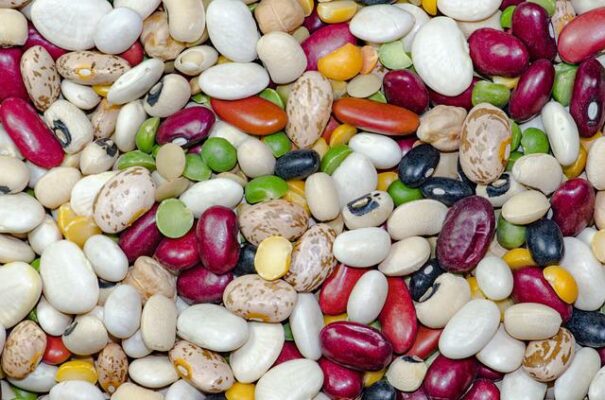
The researchers have evaluated the impact of the effects of climate change on vital parameters of bean varieties, such as their morphology, reproduction, production, and phenology. Thus, they have detected some very sensitive types to variations in their conditions of…
Read More