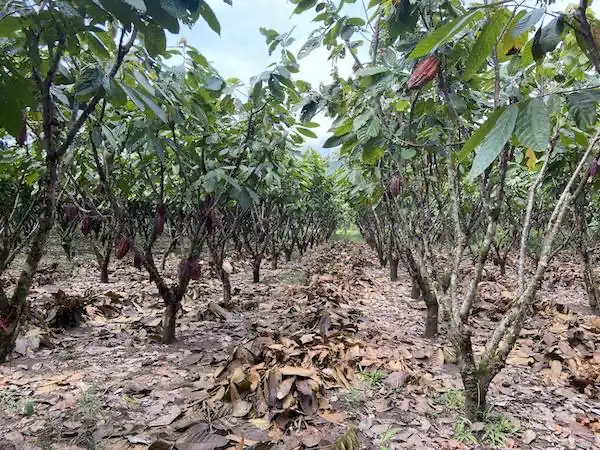
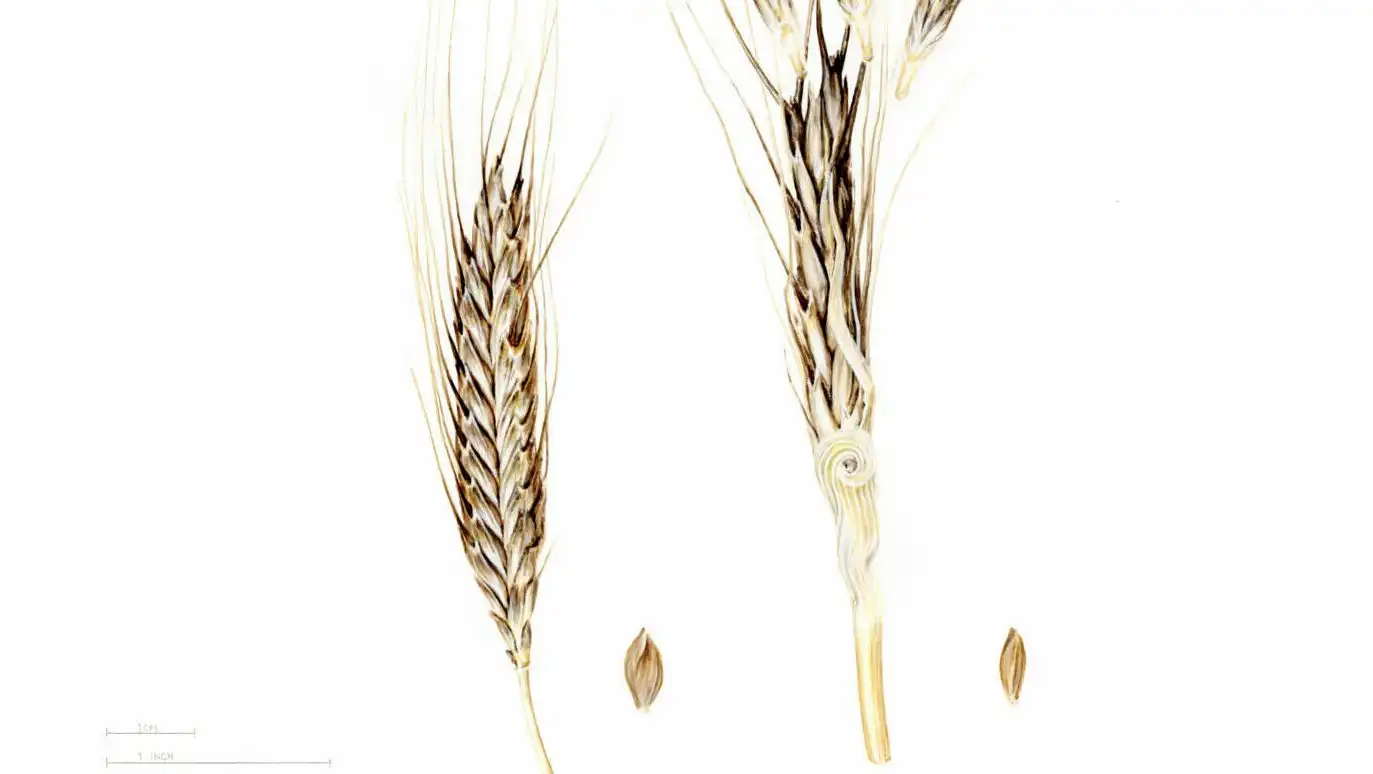
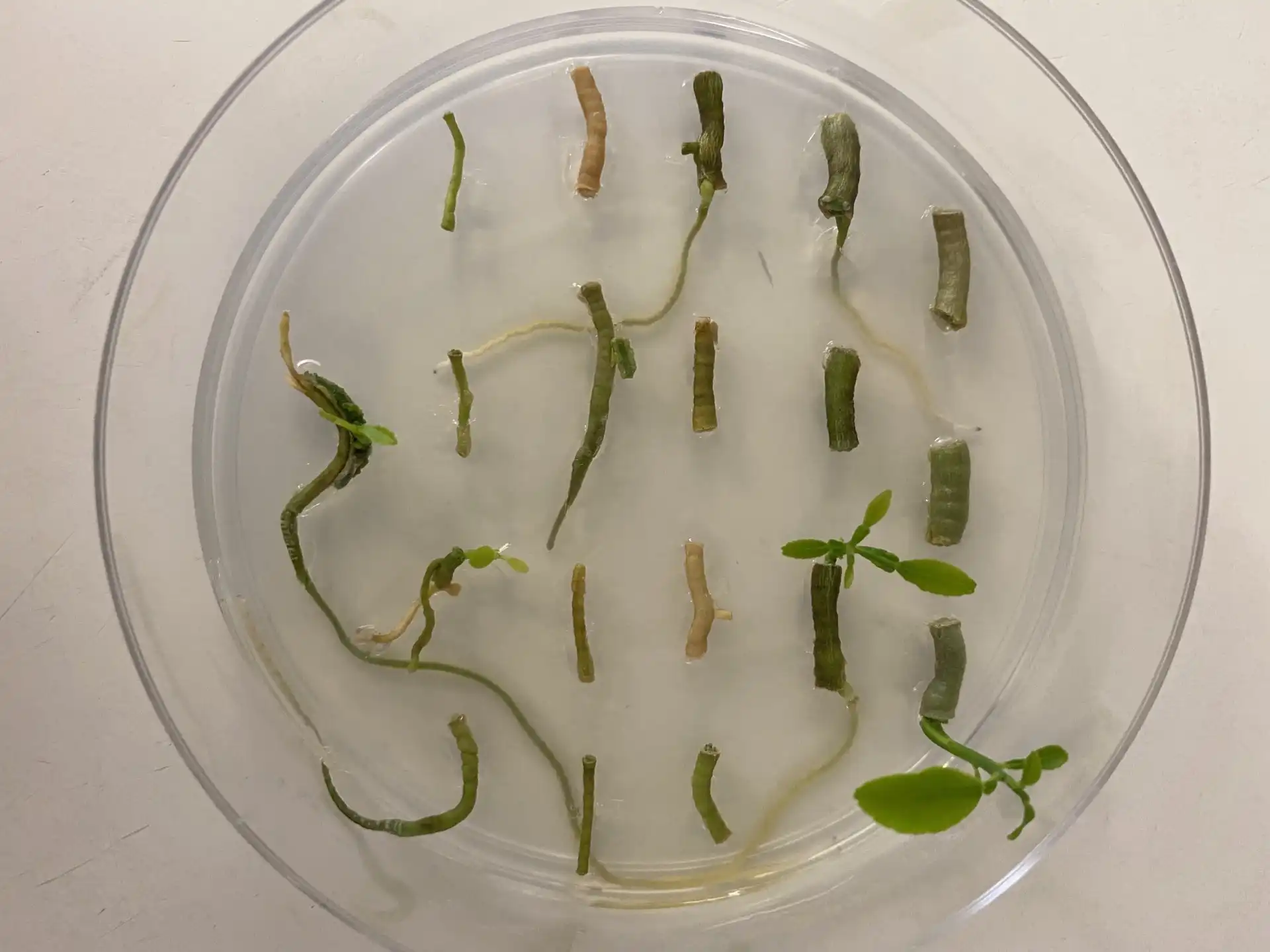
Maize roots secrete certain chemicals that affect the quality of soil. In some fields, this effect increases yields of wheat planted subsequent to maize in the same soil by more than 4%. While the findings from several field experiments show…
Read More