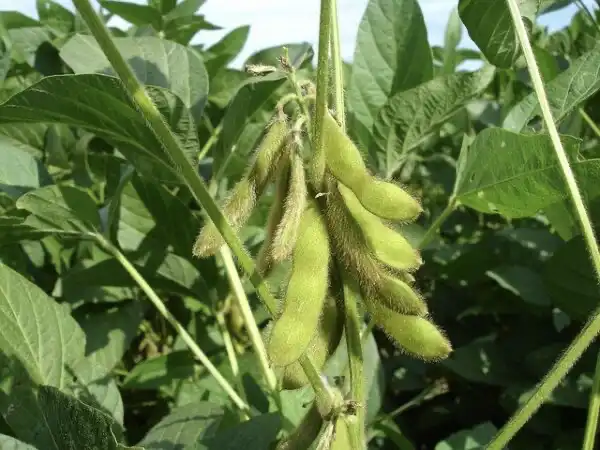
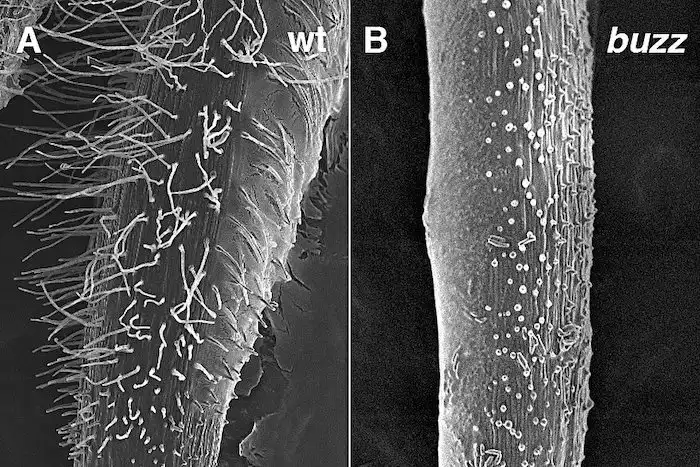
In the field of agricultural science, understanding the intricacies of soybean resilience holds profound significance. Soybeans (Glycine max) are a pivotal crop species, highly regarded for their versatility and their substantial contribution to global food and feed supplies, as well…
Read More