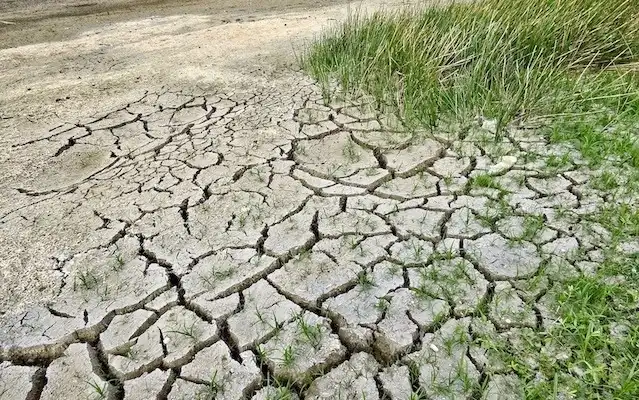
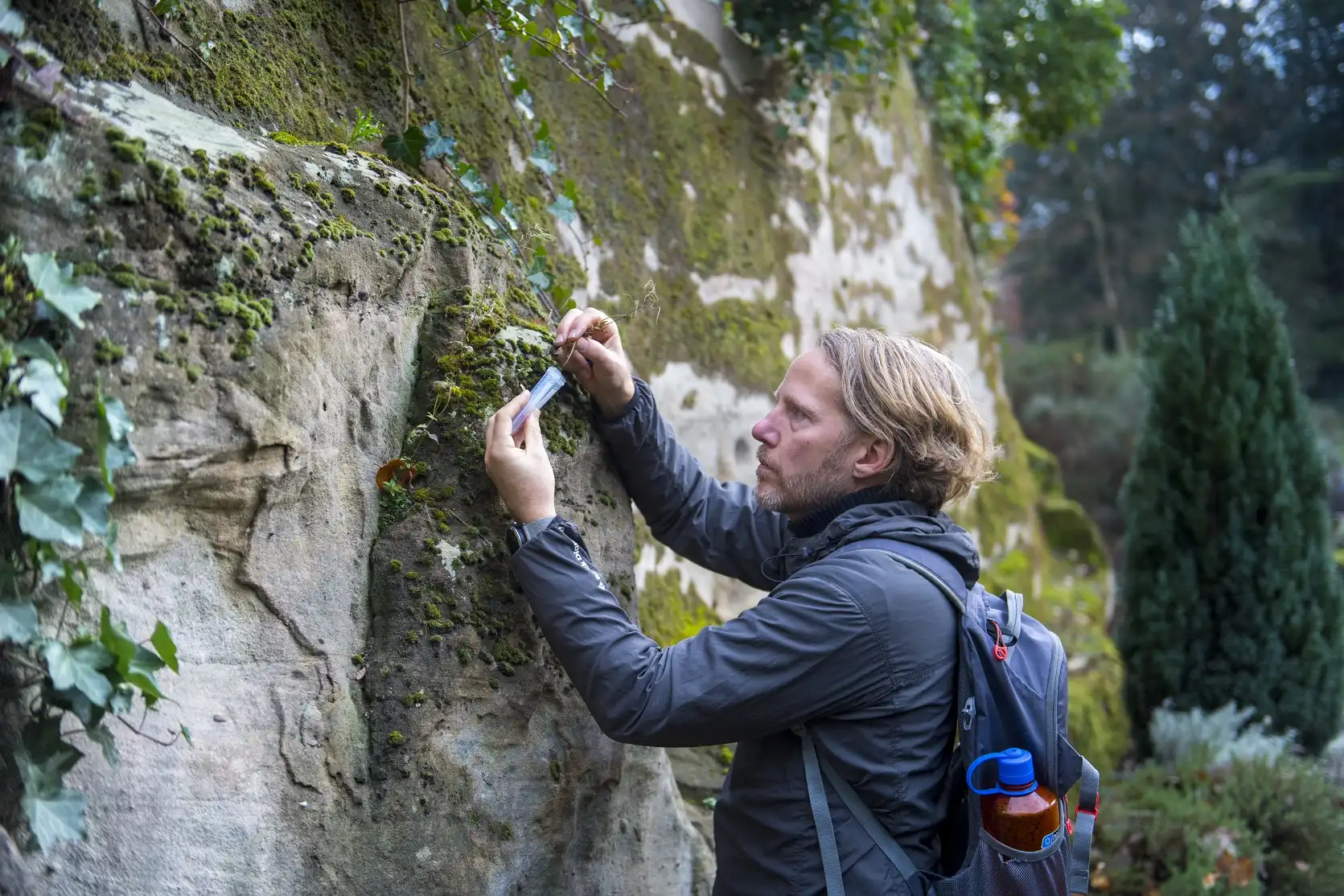
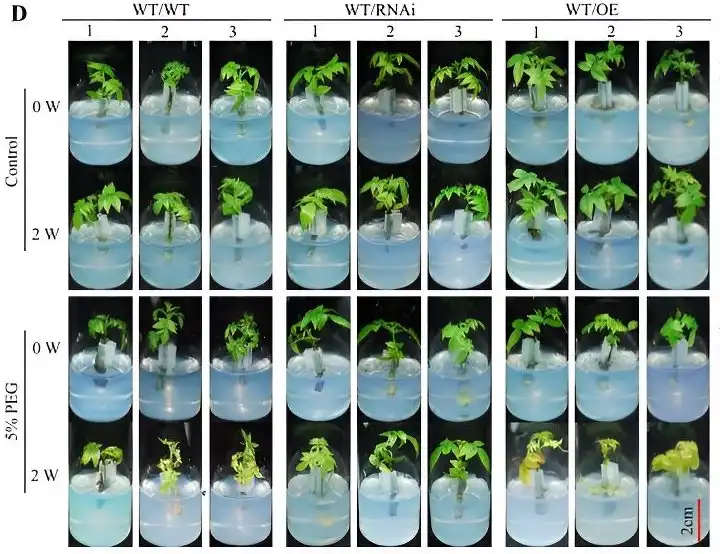
Researchershave developed optogenetic tobacco plants to study plant signaling pathways. Using light-activated ion channels, they discovered that membrane depolarization, not calcium influx, triggers key plant responses to stress, like drought. This breakthrough enables a deeper understanding of plant defense mechanisms,…
Read More