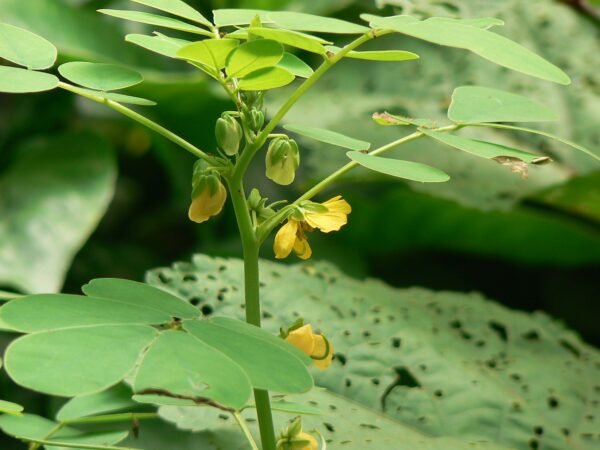
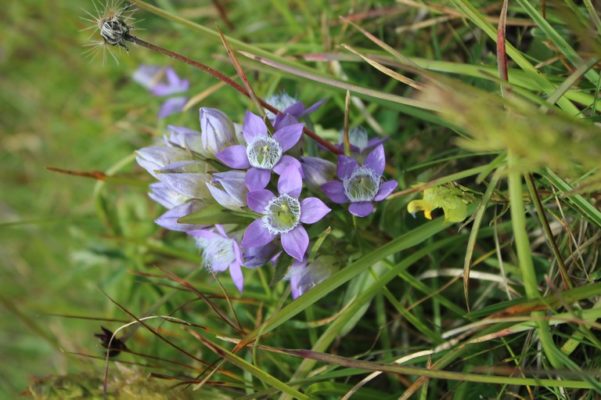
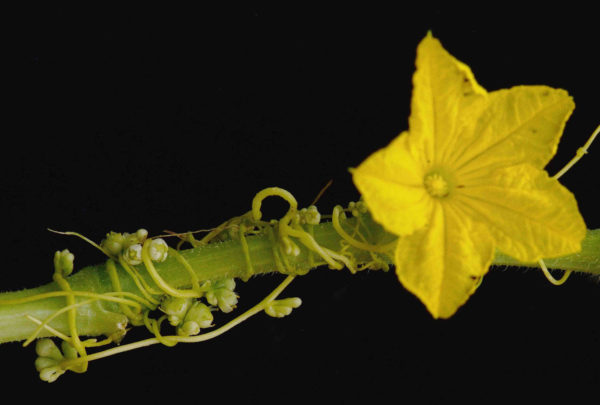
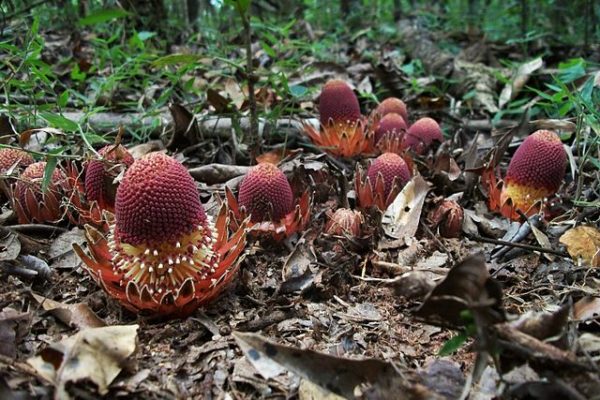
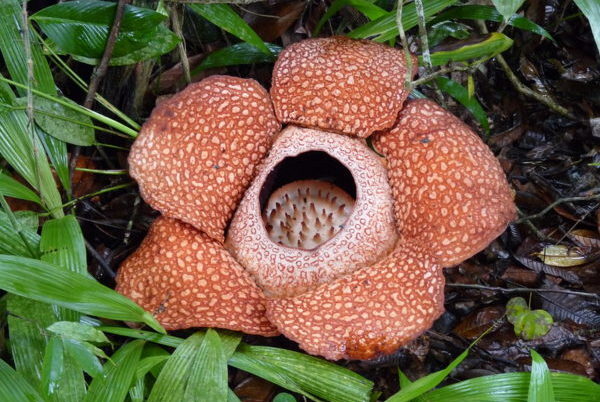
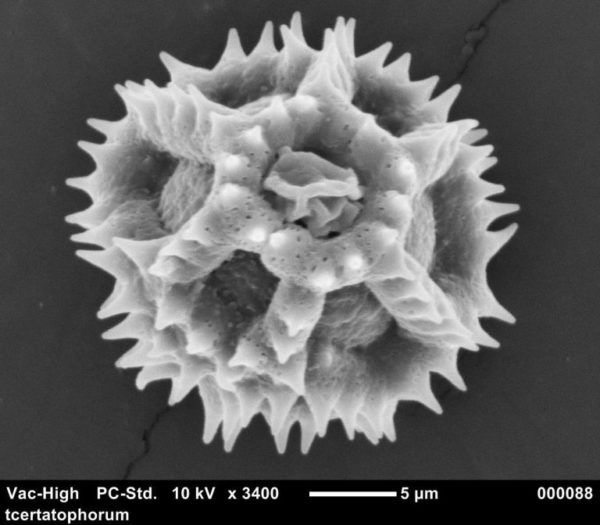
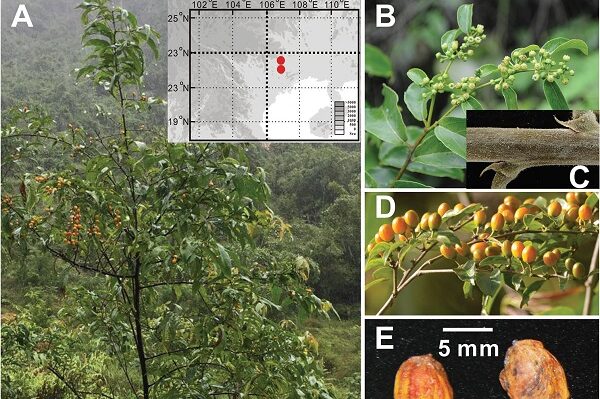
Anthraquinones are a class of naturally occurring compounds prized for their medicinal properties, as well as for other applications, including ecologically friendly dyes. Despite wide interest, the mechanism by which plants produce them has remained shrouded in mystery until now.
Read More