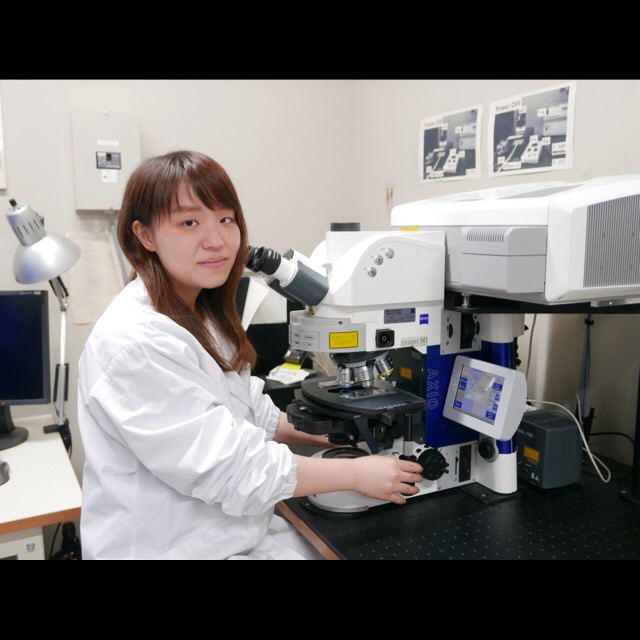
Akiko Nakazaki, PhD student at Kyoto University
Kon-nichiwa! (Hello!) I am Akiko Nakazaki, a PhD student studying plant molecular cell biology at Kyoto University in Japan.
I’m interested in plant defense – specifically the glucosinolate-myrosinase defense system, which is specific to Brassicales such as Arabidopsis thaliana. Glucosinolates are a group of secondary metabolites stored in separate cells to myrosinases, the enzymes that break them down. Upon tissue damage, the glucosinolates and myrosinases are released from their cells and combine. The glucosinolates are hydrolyzed to volatile repellent compounds such as isothiocyanates and nitriles.
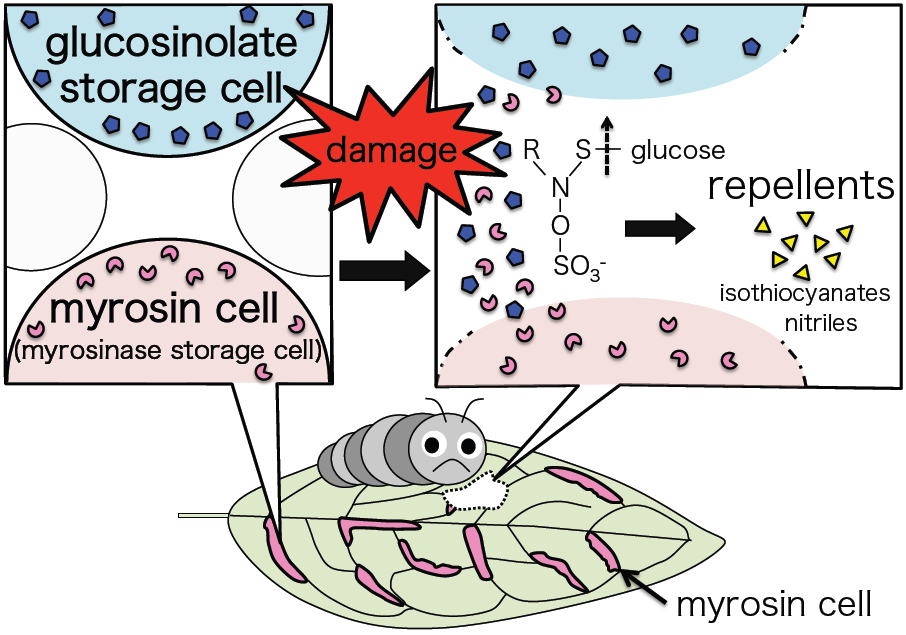
When damaged, cells containing glucosinolate and myrosinase are ruptured, releasing their contents. The glucosinolate is broken down by the myrosinase into volatile compounds that repel herbivores
I was impressed by this ingenious and rational survival strategy! I want to reveal this defense system at the cellular level, and am researching it in Arabidopsis thaliana by performing microscopic observations, bioassays with insects, and so on.
A day in the lab
Are you interested in how PhD students from other countries spend their day in the laboratory? I am! Let me tell you about my typical day in the lab.
I wake up at 8:30am, and have morning coffee and toast for breakfast while reading a newspaper. Then, I get dressed and ride on my bicycle to the University. During the ride (about 10 minutes), I remind myself of the day’s schedule. I get to the lab at 10am and take my seat. All the members of the lab have their own desk and workbench. I turn on my computer and check my emails.
In the daylight, I basically do experiments and read papers. I start doing microscopic observations and lose track of time until I hear my stomach growling and realize that it is almost 2pm. I have lunch at the eating space in lab. In this room, there are always some lab members who are eating, discussing their research, playing social games, etc. After lunch, I report the result of my microscopic observations to my boss and we have a brief discussion about it.
Then, I return to my seat and realize the primers I ordered yesterday have arrived. I perform a PCR and prepare an agarose gel for electrophoresis. While I am waiting for the PCR to end, I search PubMed and Google Scholar for new papers to read. I load the PCR products to the gel and check that the PCR worked. In the evening, I allocate myself free time for doing more experiments, reading more papers, preparing research presentations, discussions, etc.
I’ve sought a more effective way to advance my research through trial and error. For example, when I started researching in the lab I was a little too ambitious, and planned my schedule too tightly. I sometimes felt tired and depressed when my research was not right on schedule, as is often the case. In these negative moods I couldn’t enjoy my work, so I adopted a schedule with more free time. Because of this change, I’ve come to be able to work flexibly and keep a positive frame of mind.
I’m home between 10pm and midnight. At home, I have a late dinner and take a good long soak in the bath (my favorite time of day!). I go to bed at 2am.
Free weekends!
On weekends I enjoy playing badminton, learning traditional Japanese dance and shopping. I try to make plans without lab work as much as I can, however I’m not able to do avoid it sometimes when I am struggling to get new data before academic conferences and progress reports. Leaving the lab allows me to get rid of stress and feel refreshed for a healthy next week. Furthermore, I devise ways to work more efficiently on weekdays, because I am required to take time off at the weekends.
Treasure every encounter
My boss always says, “It is important to value encounters with people and things.” It wasn’t until recently that I finally understood that message! I have found that experiments may not always work well, but when I look at it from a different angle, even experiments that haven’t gone the way I’d wanted could make me aware of something new and interesting. This awareness could also be brought about through discussions with others.
I am grateful for being able to receive this opportunity. Thank you.
Akiko Nakazaki is in the first year of her doctoral program in the Department of Botany, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University, Japan.








