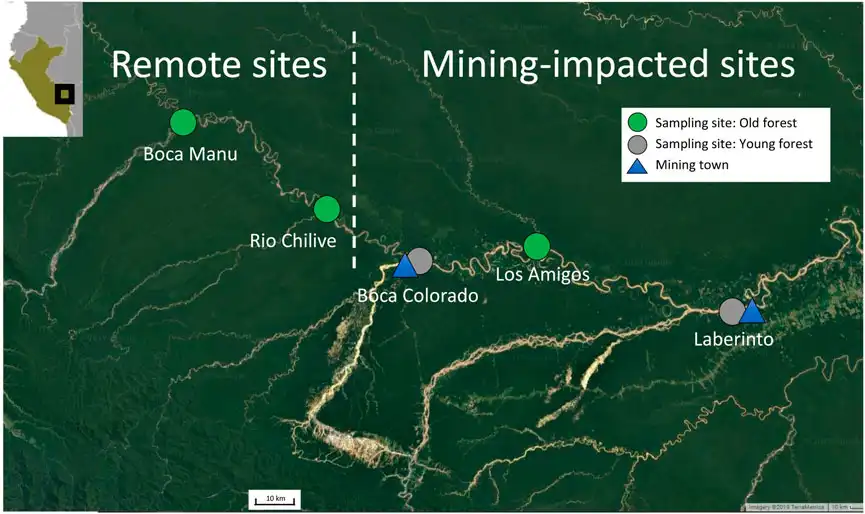
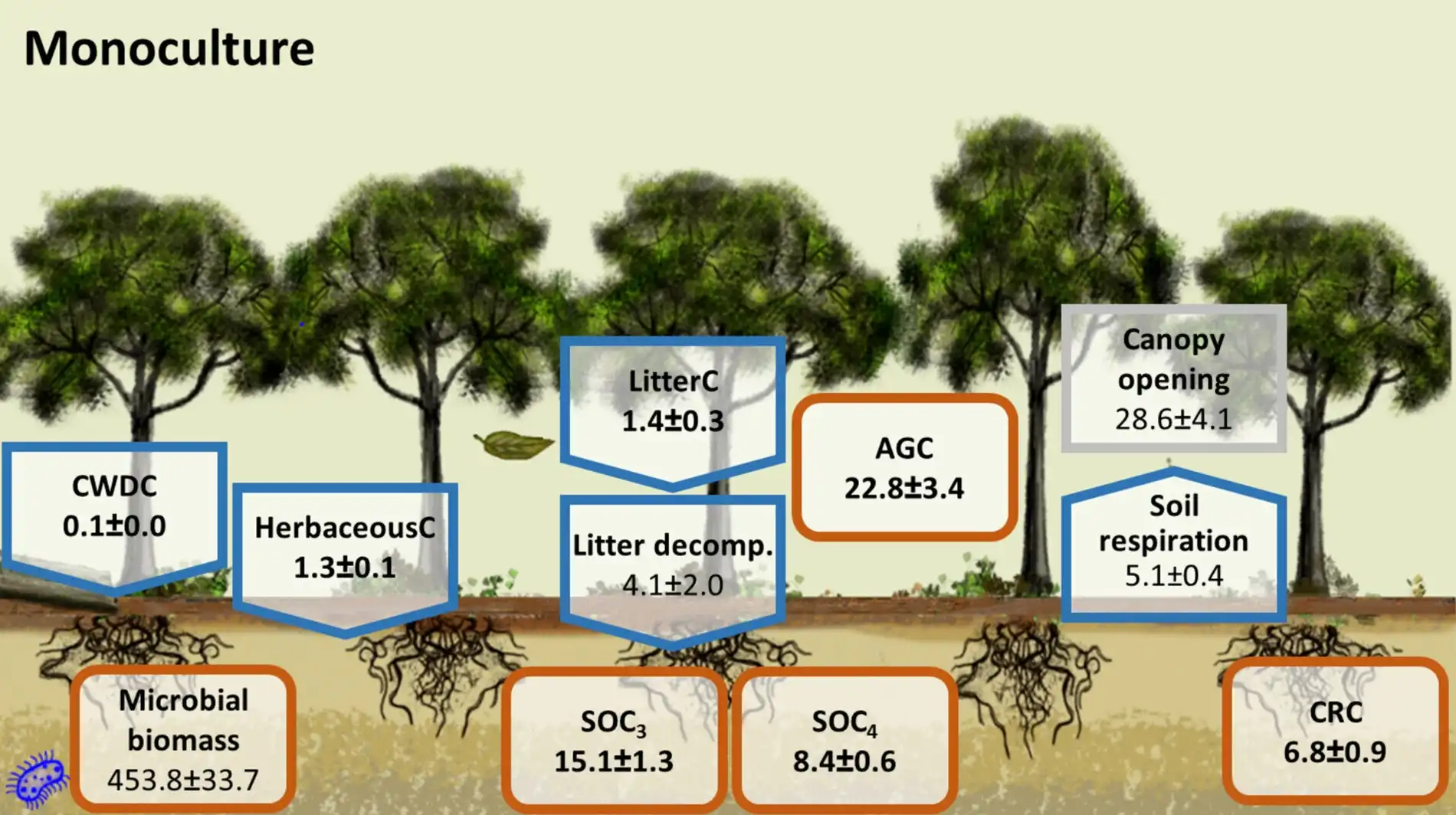
A new computational biology pipeline has mapped out over 13,000 groups of protein-coding genes conserved across grasses, offering a powerful tool for researchers investigating gene function in these economically and ecologically vital species.
Read More