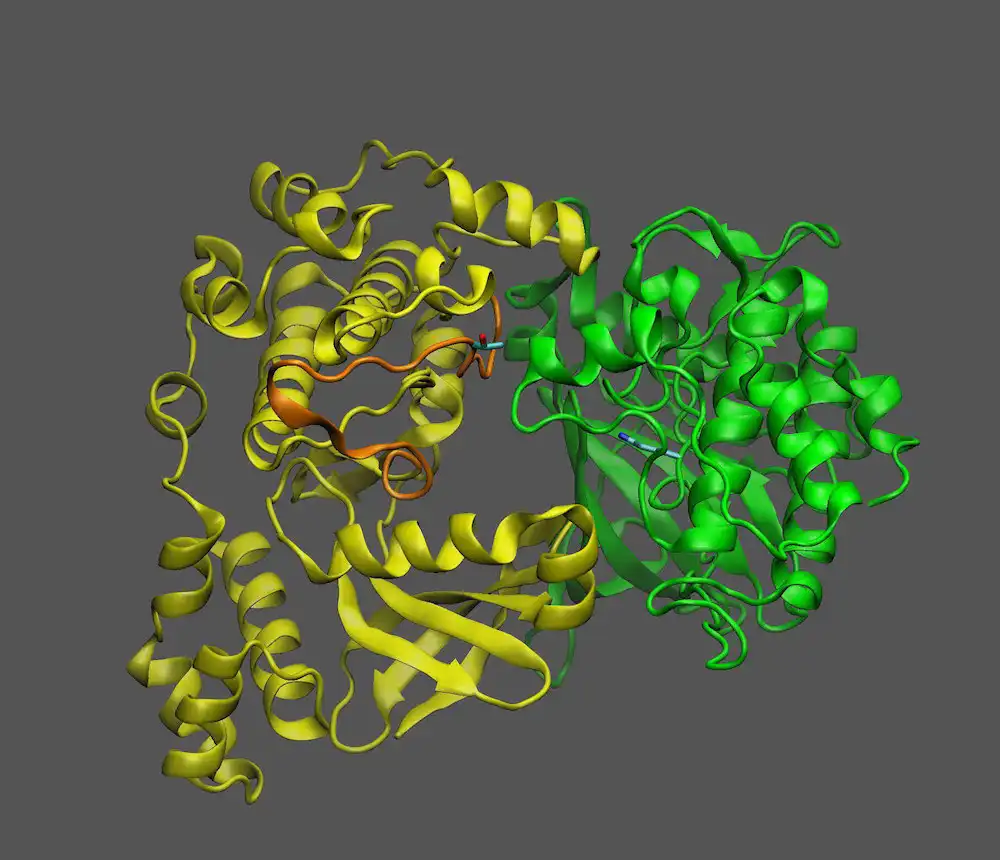
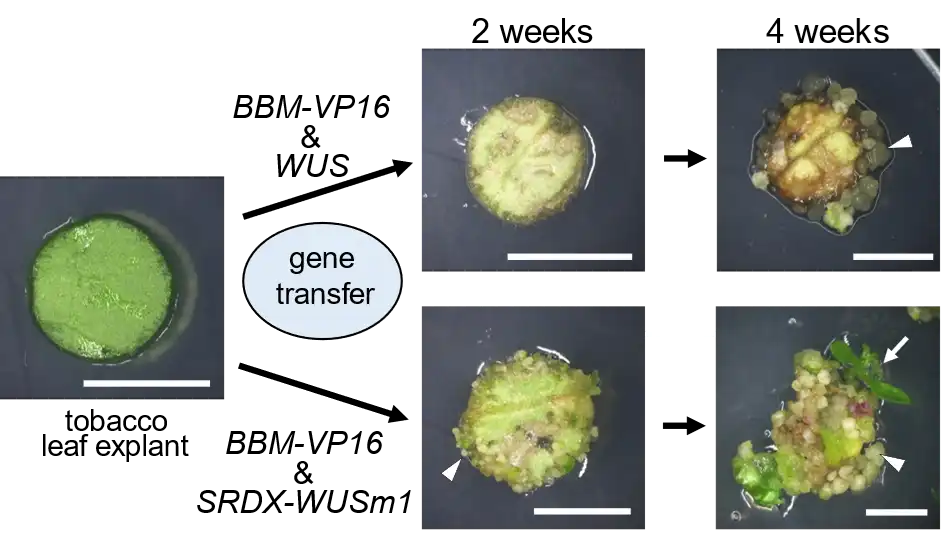
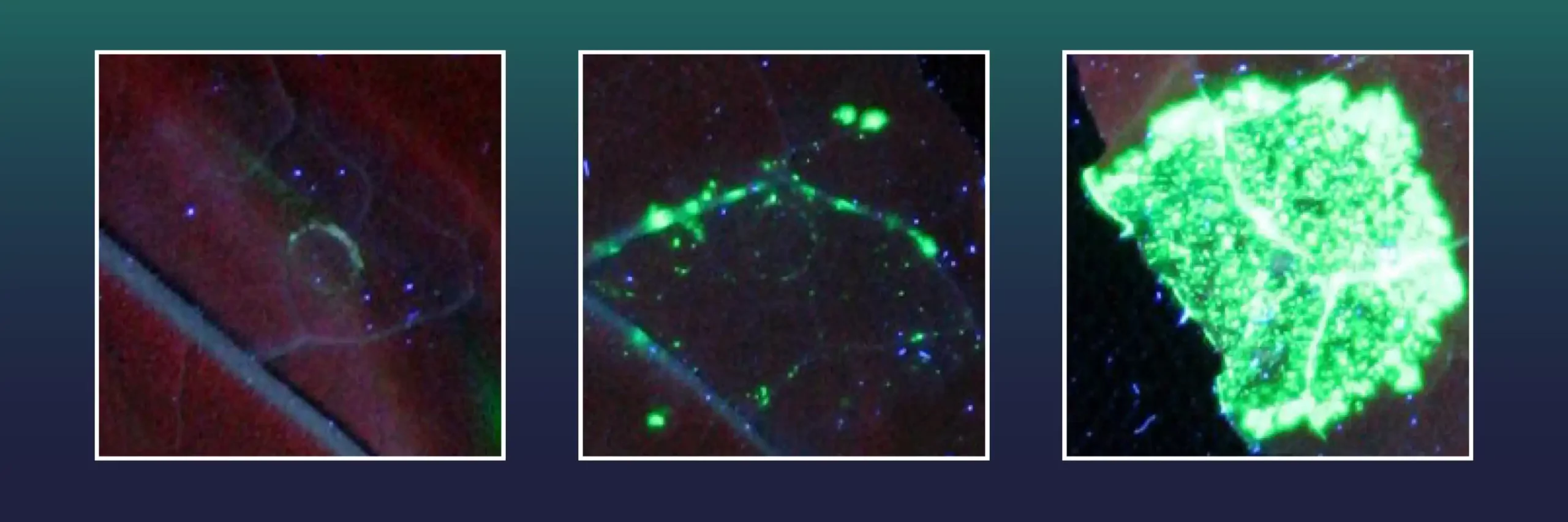
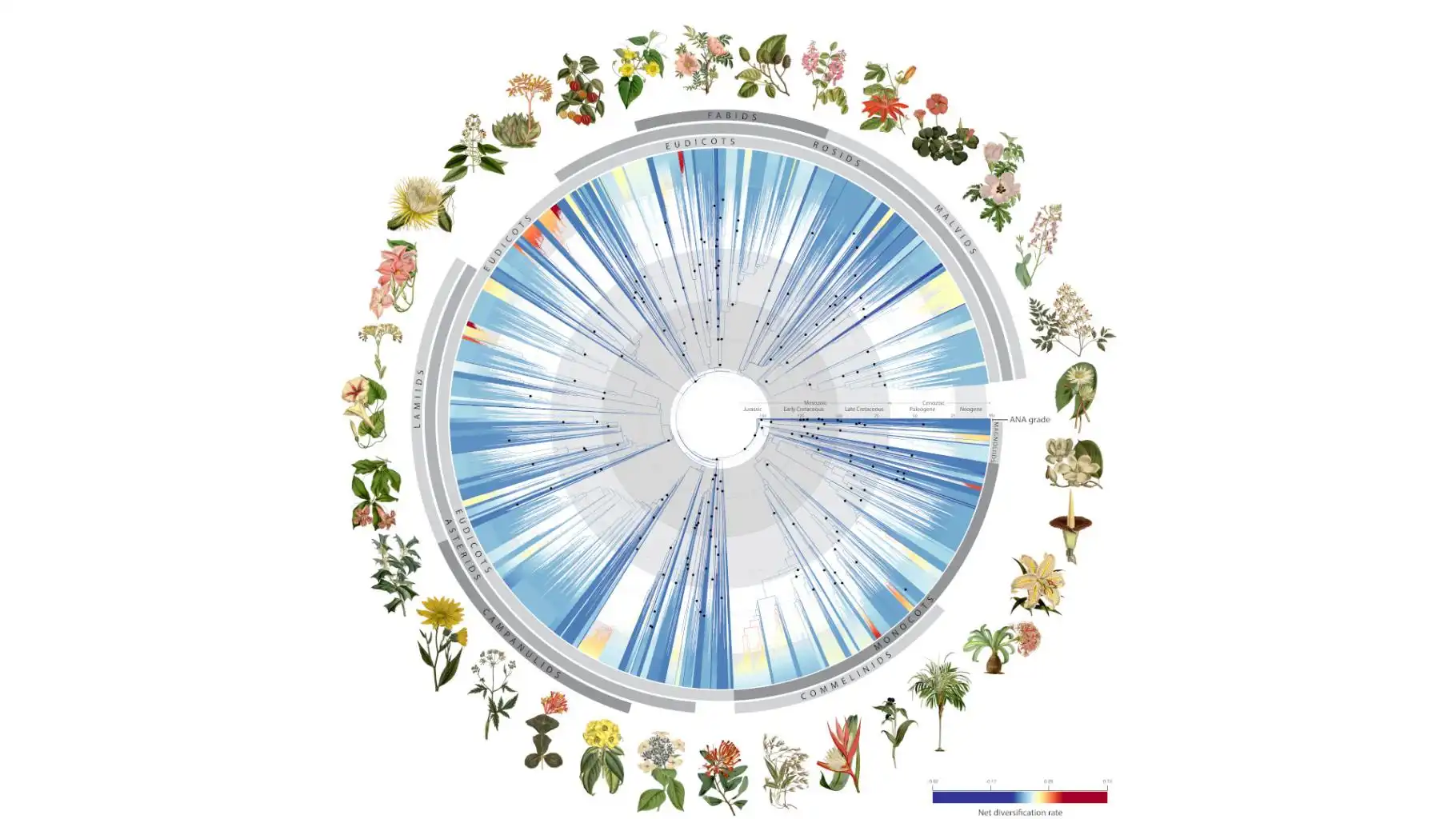
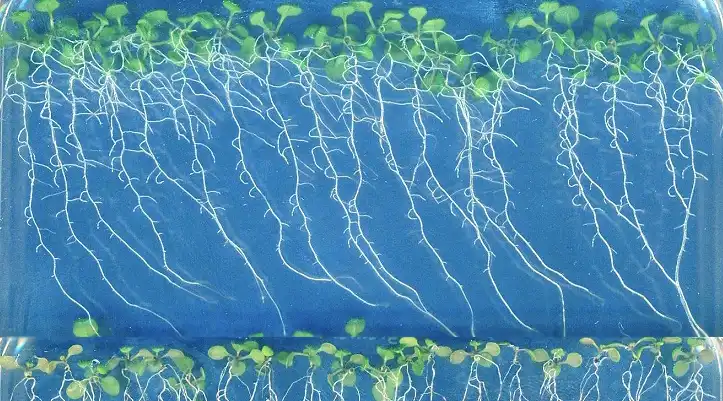
An international team has sequenced the genomes of Zygnema algae, the closest relatives of land plants. This breakthrough illuminates how early plants adapted to terrestrial environments 550 million years ago, paving the way for all land-based life, including humans. The…
Read More