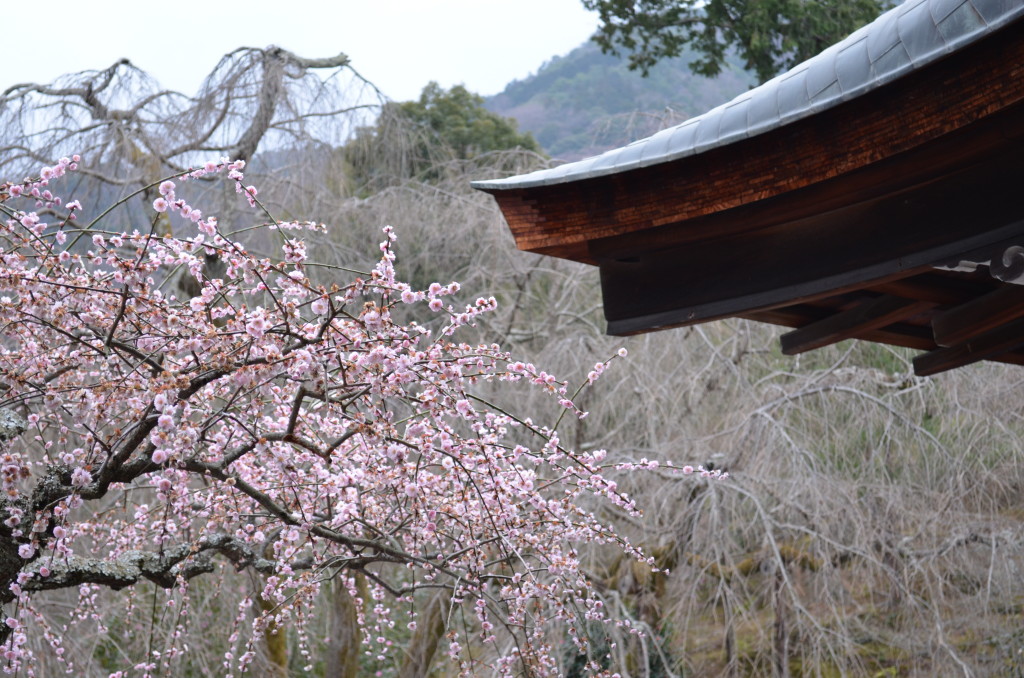
Image credit: Tom Paxton
It felt particularly fitting to travel to a plant science workshop in Japan, home of hanami, the ancient celebration of the beauty of flowers. Researchers from Heidelberg University, Germany; Kyoto University, Japan; and the University of Bristol, UK, met to discuss their cutting edge research in a meeting aptly titled ‘Novel Frontiers in Botany’.
Plant science at all three of these universities is enhanced by their botanic gardens. Heidelberg’s sounded especially impressive: established in 1593, it boasts over 10,000 species! As a former employee of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew (UK), which was recently threatened with a £5 million cut in government spending, I started thinking how important botanic gardens such as these are as vital tools for research, conservation, education and recreation.
Research
Botanic gardens are focused pools of amazing expertise in horticulture, taxonomy and ethnobotany, and this knowledge is constantly growing. Plant collections at Kyoto, Heidelberg and Bristol botanic gardens are continuously being visited by researchers studying almost all aspects of plant science. Some of the rarest species in the world can be cultivated and studied in botanic gardens without damaging wild populations; others are investigated for potential medicinal properties, evolution is studied by building banks of DNA, and we can get a fantastic overview of the diversity of life, from the microscopic structures of pollen to the architecture of trees.
Ex situ conservation
In the same way that zoos protect endangered species, botanic gardens around the world host and preserve at least a third of all known species of flowering plants.

Wollemi pine pollen cone. Image credit: Velella. Used under license: CC BY-SA 3.0.
One of my favorite examples is the wollemi pine (Wollemia nobilis). Plant nerds like me will know that the wollemi pine was only known from 2 million-year-old fossils until field officer David Noble discovered around 100 plants growing at Wollemi National Park, Australia. These living fossils were propagated by botanic gardens in Australia and internationally, and are now a popular tree in cultivation around the world.
Another important facet of ex situ conservation is the creation of seed banks. The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, established the Millennium Seed Bank in 1996, which aims to provide an ‘insurance policy’ against extinction by storing the seeds of 25% of all seed-bearing plants. The majority of the stored 75,000 species will be rare or threatened with extinction.
In situ conservation
As well as bolstering plant species on their own sites, many botanic gardens are involved in restoration projects of damaged ecosystems around the world. Botanic Gardens Conservation International, a global network for botanic gardens, describes many such efforts including the restoration of Brazil’s Atlantic Forest by the Rio de Janeiro Botanic Garden, the restoration of local upland forest by Kenya’s Brackenhurst Botanic Garden, and Hawaiian beach and coastal restoration by the US National Tropical Botanic Garden. In each case, rare and endemic species of plant replaced invasive species and increased the biodiversity of the entire ecosystem.
Education and recreation

Botanic gardens often hold events, like the Easter sculpture festival at the University of Bristol Botanic Gardens. Image credit: Sarah Jose
Botanic gardens are a great place for an afternoon stroll with the family, which plays nicely into their ulterior motive: education. Plants are amazing but they are often overlooked. By displaying the most wonderful and fascinating species from around the world, botanic gardens kindle an interest in plants from the general public, as well as potentially teaching children where food comes from, or fostering a love of nature and the environment.
It doesn’t stop there though. As well as restoration projects, which often include local people who learn about the economic importance of preserving their native ecosystems, the gardens can be involved in broader efforts. For example, the National Museums of Kenya are looking to develop a botanic garden. The garden will facilitate the transfer and accumulation of ethnobotanical knowledge surrounding the relationships between the Kenyan people and their local plant species; useful information that will also promote the importance of conserving their local flora.
In conclusion
Botanic gardens are integral to the study and appreciation of a wide range of plant taxa, and their importance should not be underestimated. Too many people view them as outdated and push to cut their funding, but we need to show that dynamic and cutting edge research, as well as public appreciation for plants and the environment, relies on their continuation both now and in the future.














 ob is to find answers to big questions, then communicate them clearly to the public they serve. His current big problem is trying to understand why many crop plants are only able to use 2% of the sun’s energy to grow and what we might be able to do to improve that percentage. He investigates this problem using a combination of physiological measurements and modeling both in the lab and in the field. To improve science communication, Berkley founded the
ob is to find answers to big questions, then communicate them clearly to the public they serve. His current big problem is trying to understand why many crop plants are only able to use 2% of the sun’s energy to grow and what we might be able to do to improve that percentage. He investigates this problem using a combination of physiological measurements and modeling both in the lab and in the field. To improve science communication, Berkley founded the