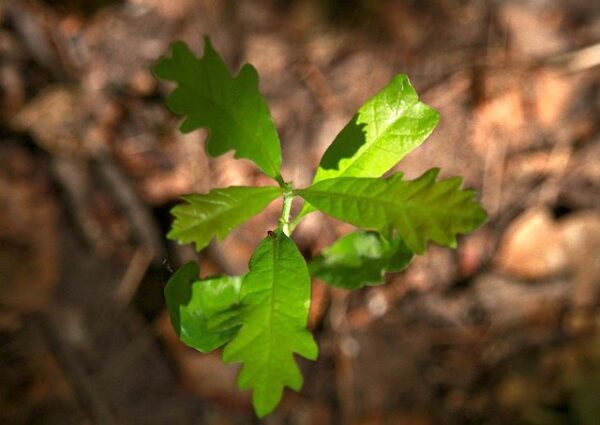
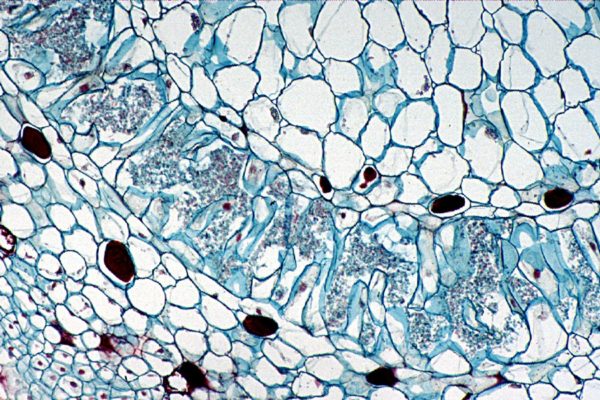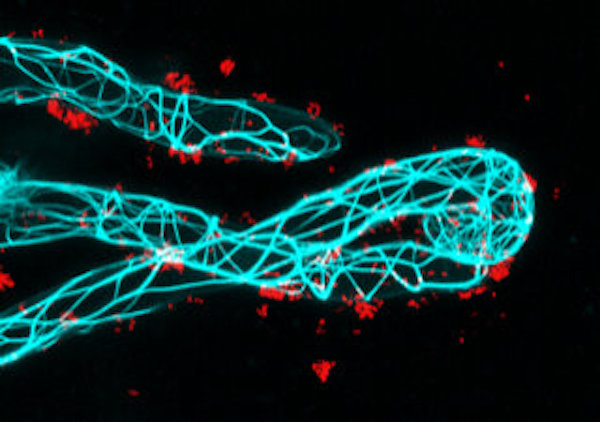

Scientists have been pondering if the microbiome of plants is due to nature or nurture. Research at Stockholm University, published in Environmental Microbiology, showed that oak acorns contain a large diversity of microbes, and that oak seedlings inherit their microbiome from these acorns.
“The idea that seeds can be the link between the microbes in the mother tree and its offspring has frequently been discussed, but this is the first time someone proves the transmission route from the seed to the leaves and roots of emerging plants”, says Ahmed Abdelfattah, researcher at the Department of Ecology Environment and Plant Sciences (DEEP) at Stockholm University.
The microorganisms found on the seed are often valuable for the plant, promoting its growth and protecting it against certain diseases. Each plant species harbours a distinct microbial community, with some of the microbes living on its surface and others inside the plant’s tissues.
The finding also means that since the microorganisms from the seed are there first, they can constitute a barrier which influences subsequent colonization by other microbes from the environment. The experiment was done in oaks, since it’s one of the most abundant tree species in the Swedish and European forests.
“The microorganisms from the seed are also expected to be very important for plant health and functioning”, says Ahmed Abdelfattah.
The fossil record indicates that plants have been associated with fungi and bacteria – constituting the microbiome – for more than 400 million years. Several species the scientists found on the oak seeds are already shown by other studies to be involved in the protection against several plant pathogens, growth-promotion, nitrogen-fixing, and the detoxification or biodegradation of toxic environmental pollutants.
Demonstrating inheritance under natural conditions is challenging since seeds are exposed to and dependent on their surrounding environment when they sprout, especially the soil, which is a microbially rich environment. Therefore, it’s nearly impossible to differentiate between which microorganism actually come from the seed or from the soil. The research team therefore used a novel culturing device, to grow oak seedlings in a microbe-free condition and keep the leaves separated from the roots. This allowed them to be certain that the microorganisms came from the seed, and that they could demonstrate that some seed microorganisms migrate to the roots, and some others to the leaves.
“Plant leaves and roots are already known to harbor distinct microbial communities, as shown by several recent studies. In this study however, we were surprised to see that it is also true at an early stage of the plant development, and that the seed could, at least partially, be responsible for these differences”, Says Ahmed Abdelfattah.
“Several breeding companies are taking into consideration the seed microbiome in their programs hoping to have super plants with better genes and better microbes. One technique used, is to treat seeds with beneficial microorganism with the aim that those microbes will eventually colonize the plant and exert their effects throughout the plant’s life”, says Ahmed Abdelfattah.
The next step for the research team is now to discern which is the major source of the of the microbiome – the environment or the seed.
Read the paper: Environmental Microbiology
Article source: Stockholm University
Author: Amanda Gonzalez Bengtsson
Image credit: Ирина Ирина / Pixabay