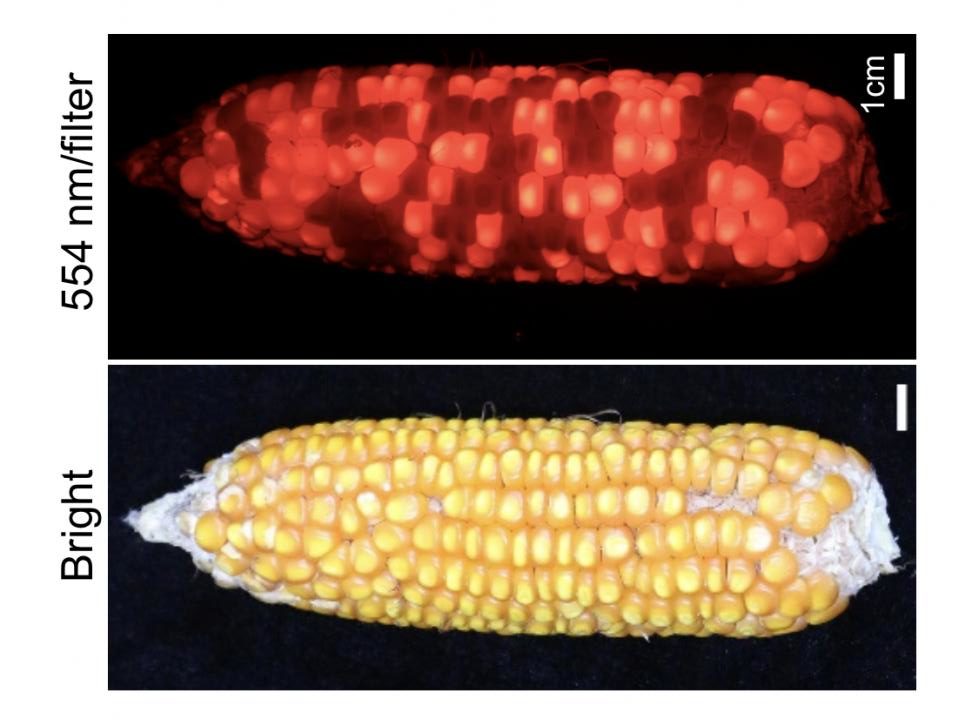
Crop hybrid technologies have contributed to the significant yield improvement worldwide in the past decades. However, designing and maintaining a hybrid production line has always been complex and laborious. Now, researchers have developed a new system combining CRISPR-mediated genome editing…
Read More