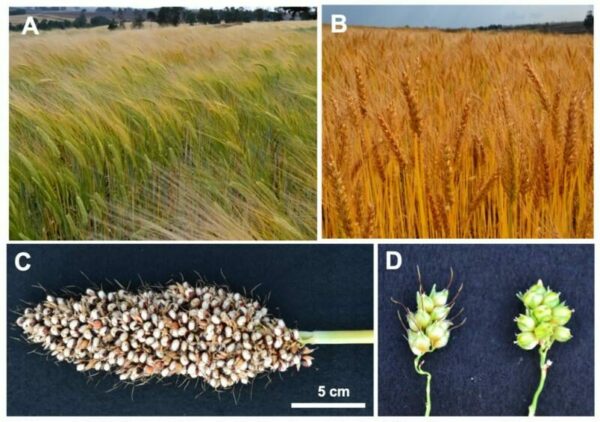
An international team of researchers conducting a long-term study has found that climate-friendly farming practices could lead to higher crop yields, reduced costs and improved local ecosystems. In their paper, the group describes 30 long-running farming experiments designed to improve…
Read More