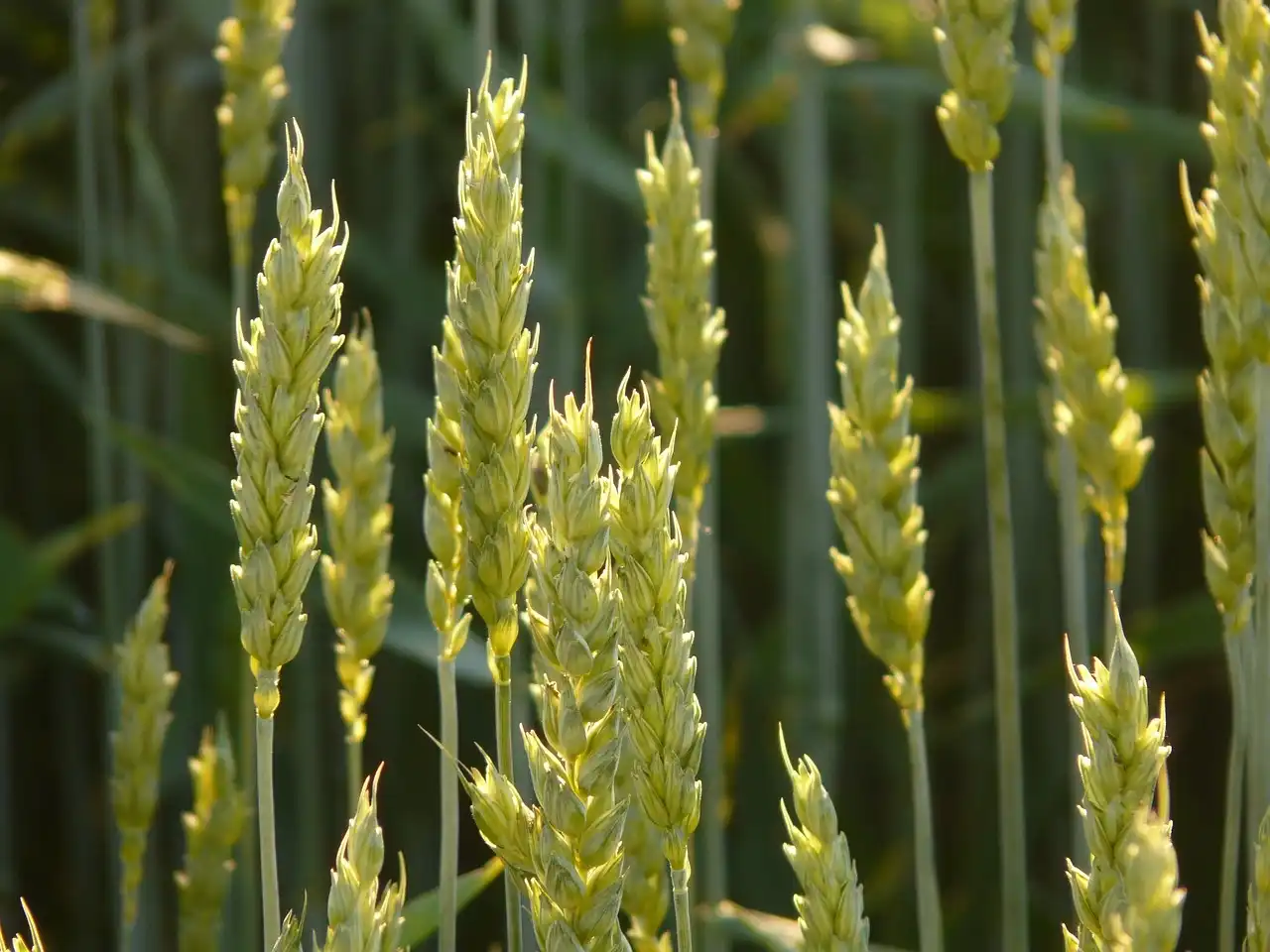
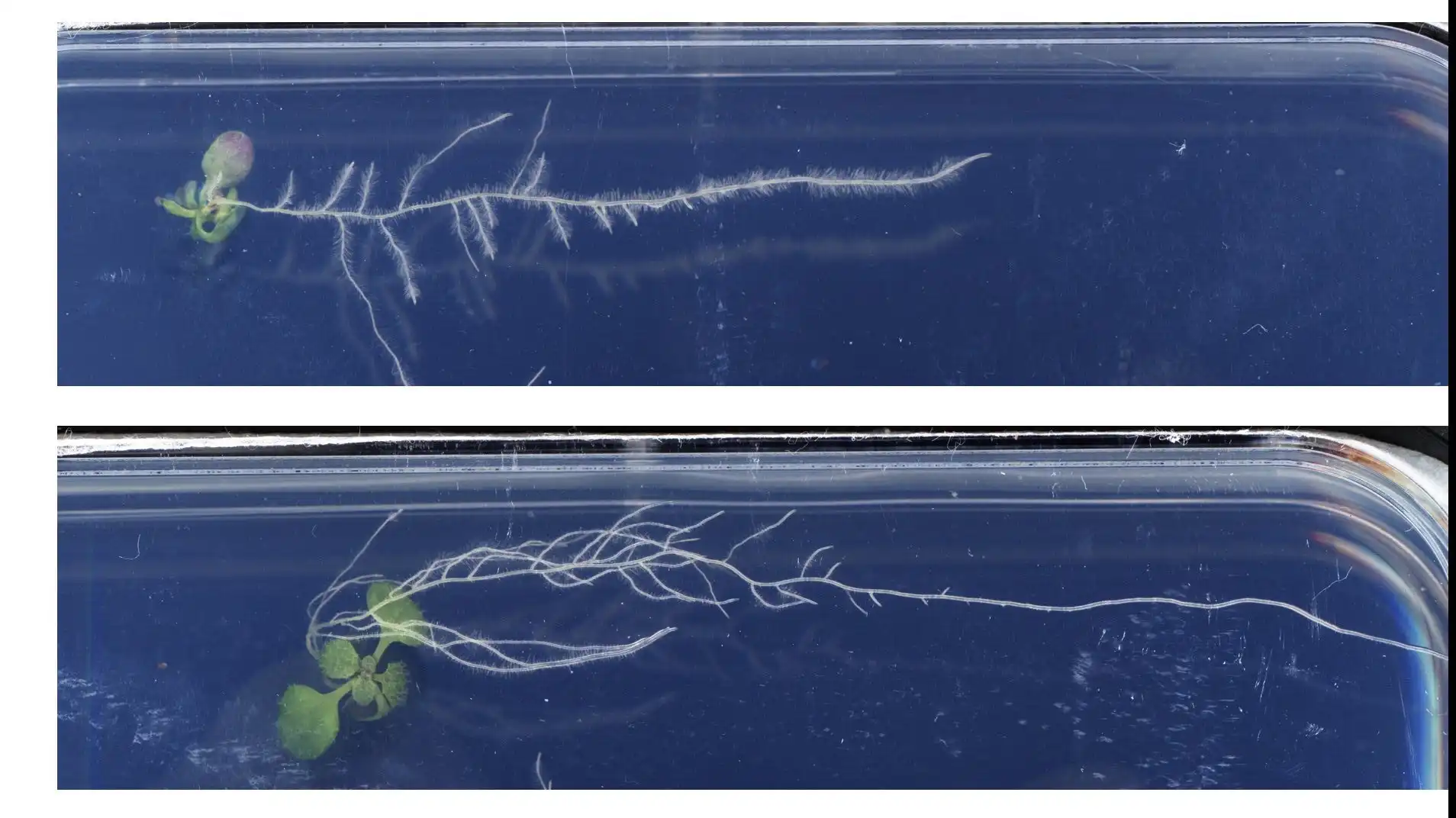
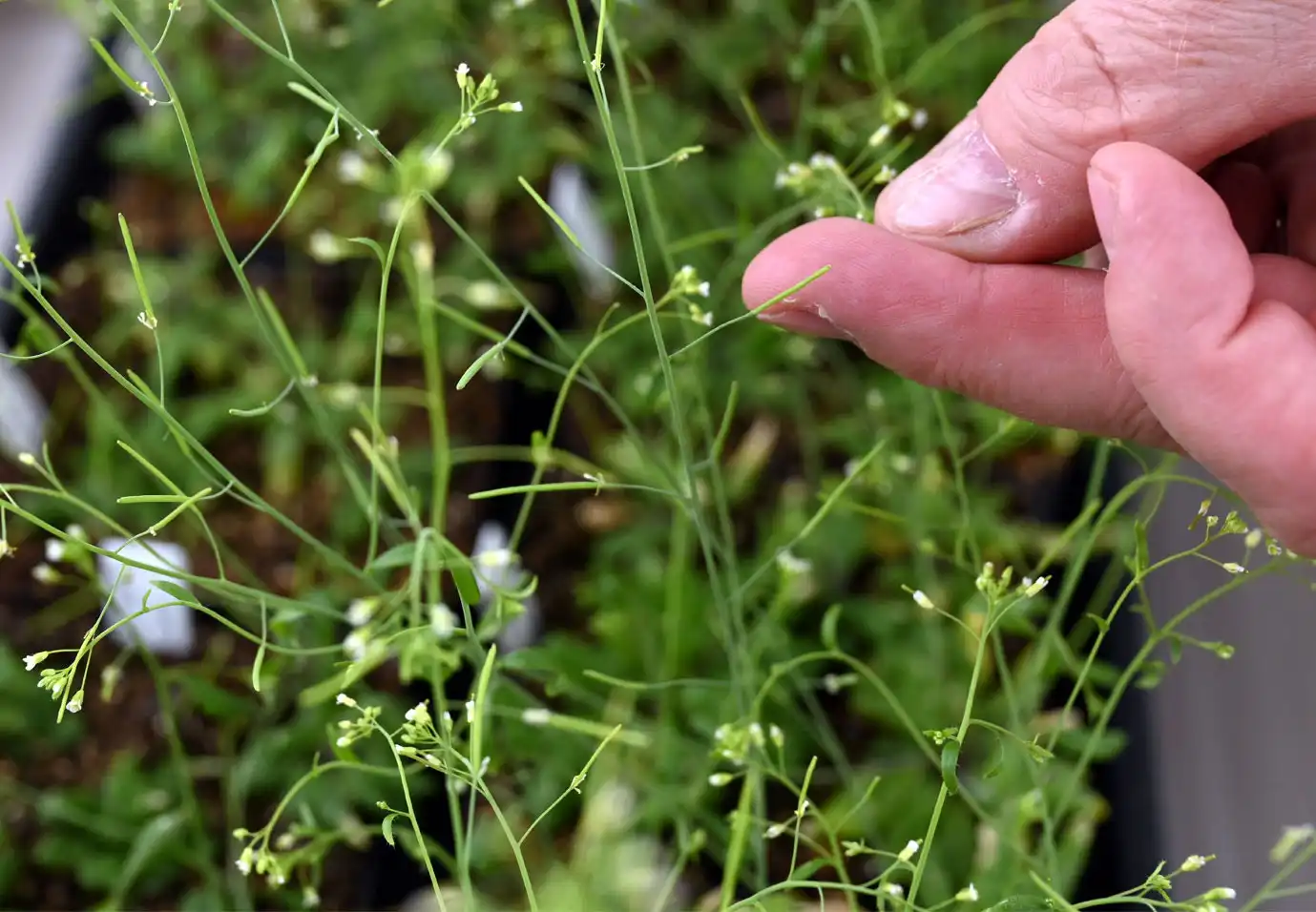
A study unveils a novel approach to identify pivotal regulators in wheat spike development. By integrating omics and population genetics, researchers pinpoint 227 potential factors. Phenotypic screening of 61 genes led to 36 mutations, validating the method’s efficacy.