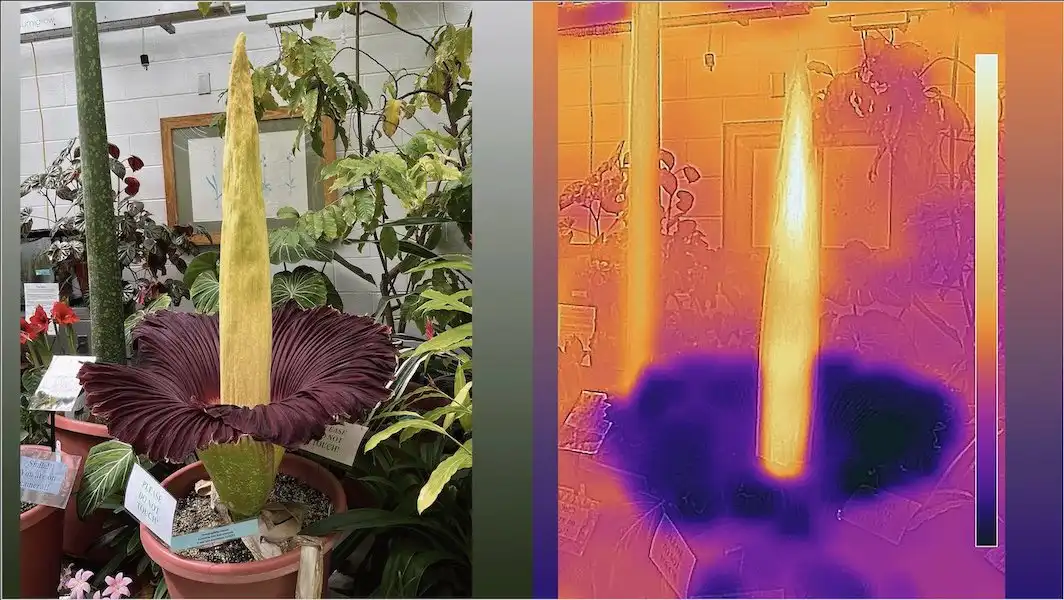
Scientists have developed PlantRNA-FM, an AI model that deciphers the genetic "language" of plants, analyzing RNA sequences and structures. Trained on data from 1,124 species, it predicts RNA functions and structural patterns. This breakthrough aids crop improvement, stress resilience, and…
Read More