Mycorrhizal symbiosis helps plants expand their root surface area, giving plants greater access to nutrients and water. Although the first and foremost role of mycorrhizal symbiosis is to facilitate plant nutrition, how mycorrhizal types mediate the nutrient acquisition and interactions of coexisting trees in forests has not been clear to scientists.
To address this issue, Prof. Liu Lingli‘s research team from the Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences investigated nutrient acquisition strategies of arbuscular mycorrhizae (AM) and ectomycorrhizal (EcM) trees in the Biodiversity–Ecosystem Functioning (BEF) experiment in a subtropical forest in China, where trees of the two mycorrhizal types were initially evenly planted in mixtures of two, four, eight or 16 tree species.
The researchers found that as species richness increased, the net primary production (NPP) of EcM trees rapidly decreased, but the NPP of AM trees progressively increased, leading to the sheer dominance (>90%) of AM trees in the highest diversity treatment.
The team’s analyses further revealed that differences in mycorrhizal nutrient-acquisition strategies, both nutrient acquisition from soil and nutrient resorption within the plant, contribute to the competitive edge of AM trees over EcM ones.
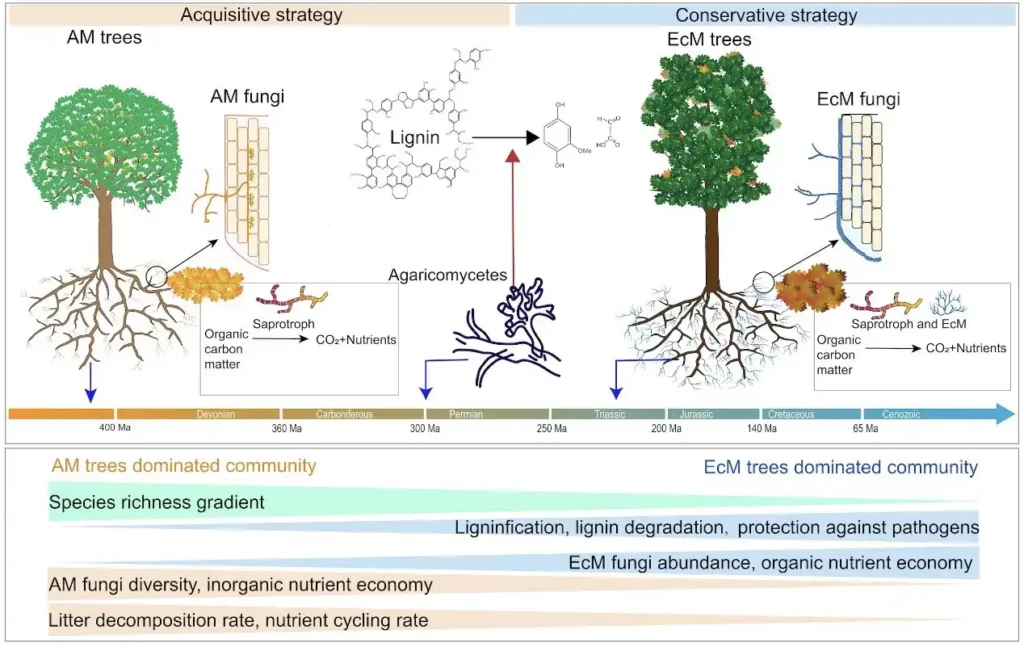
Image: Changes in nutrient acquisition strategies and soil microbial communities of AM and EcM trees as species diversity increases. Credit: Liu Lingli
In addition, analysis of soil microbial communities showed that EcM-tree monocultures have a high abundance of symbiotic fungi, whereas AM-tree monocultures were dominated by saprotrophic and pathogenic fungi.
According to the researchers, as tree richness increased, shifts in microbial communities, particularly a decrease in the relative abundance of Agaricomycetes (mainly EcM fungi), corresponded with a decrease in the NPP of EcM subcommunities, but had a relatively small impact on the NPP of AM subcommunities.
These findings suggest that more efficient nutrient-acquisition strategies, rather than microbial-mediated negative plant-soil feedback, drive the dominance of AM trees in high-diversity ecosystems.
This study, based on the world’s largest forest BEF experiment, provides novel data and an alternative mechanism for explaining why and how AM trees usually dominate in high-diversity subtropical forests.
These findings also have practical implications for species selection in tropical and subtropical reforestation—suggesting it is preferable to plant mixed AM trees, as they have a more efficient nutrient-acquisition strategy than EcM trees.
Read the paper: Science Advances
Article source: Institute of Botany, the Chinese Academy of Sciences
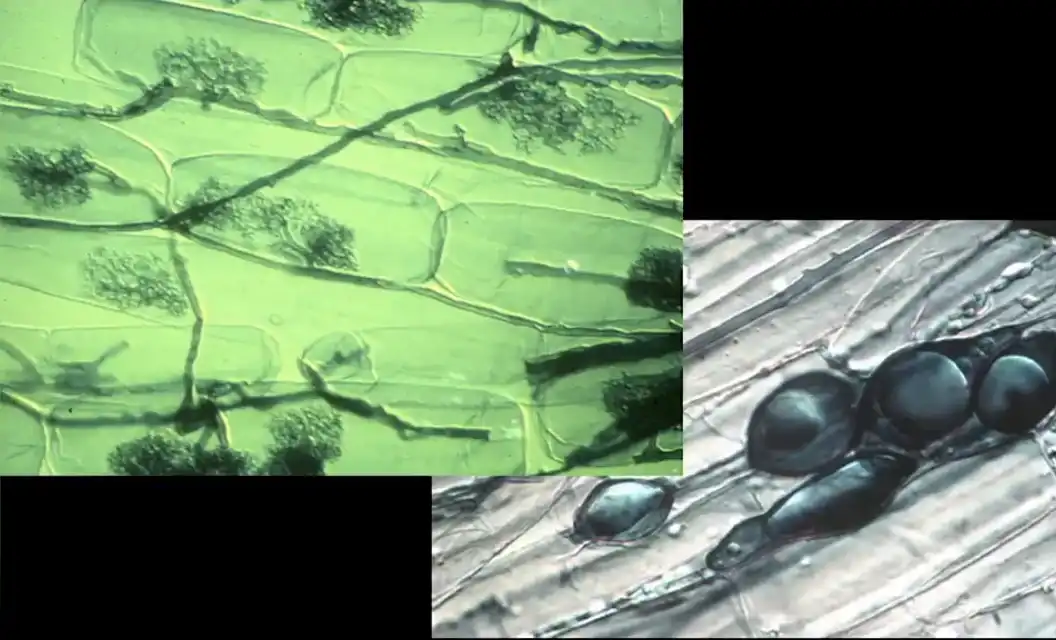
Image: Right: Arbuscular endomycorrhiza: Hyphae of Glomeromycetes along the cells of a root and ramifications inside them by penetrating the cell wall and pushing back the membrane. Left: Droplets of lipid stores. Source: Microbial diversity & mycorrhizae, by Marc-André Selosse, Ver de Terre production, May 29, 2020, 3 hours online video. Frame at 1 hour, 54 min, 40 sec, via Wikimedia. Credit: Marc-André Selosse