Understanding the role of a key protein in plant immunity could inform the development of crops that are resistant to multiple pathogens.
Up to 30 per cent of crop yields worldwide each year are lost to pathogenic infection. Understanding how to make plants more resilient to infection is vital for future food security. Now researchers have uncovered the critical role of a linker histone protein, called H1, during plant immune responses to bacterial and fungal infections.
“Previous studies on Arabidopsis plants revealed that H1 is important for healthy growth and development,” says Arsheed Sheikh, who worked on the project with Heribert Hirt and co-workers. “Linker histones are known to regulate infection in animals, but their role in plant infection and immunity has never been explored.”
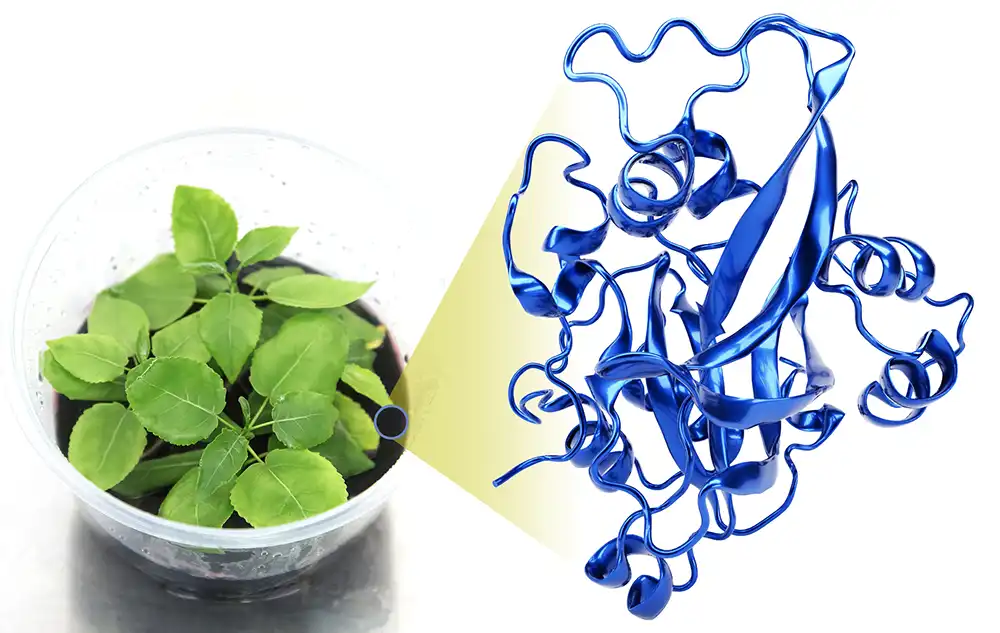
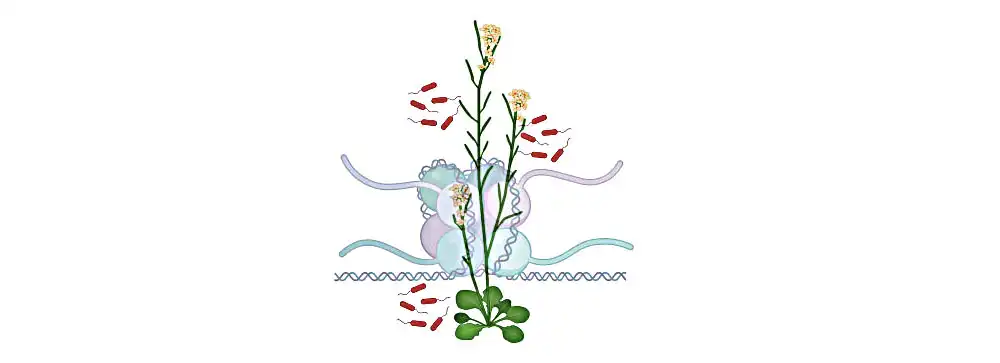
In animal and plant cells, fundamental units called nucleosomes contain DNA wrapped around a protein complex, and are critical for regulating genetic information. The individual nucleosomes are connected by linker DNA. Linker histone H1 holds the exit/entry site of linker DNA like a clip, thus regulating the unwinding and flexibility of nucleosomes.
“In plants like Arabidopsis, we find three isoforms of H1,” says Sheikh. “Normally, H1 suppresses gene expression — this includes the defense genes of the immune system.”
The team explored mutant Arabidopsis plants with all three H1 isoforms knocked out. They grew wild-type and mutant plants under controlled conditions and then infected them with either the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae or the fungal pathogen Botrytis cinerea. After three days, they compared the severity of infection between the different groups of plants.
“The mutant plants were resistant to both bacterial and fungal infection when compared to wild-type plants,” says Sheikh. “The knockout mutant had higher levels of defense gene expression and the immune response hormone salicylic acid.”
Probing H1’s role further, however, the team were surprised to find that the mutant plants lacked defense-priming ability. In other words, when subjected to a small dose of a pathogen some time after initial infection, the plants showed no enhanced immune response. Like vaccination, priming a plant with a small pathogen dose can boost its immunity. The lack of defense priming in the mutant plants suggests H1 plays a critical role in priming.
“This fundamental knowledge could help generate smart crops that are resistant to multiple infectious agents simultaneously,” says Hirt. “However, this study also serves as a cautionary warning that it is important to study both the direct and indirect effects of a given mutation in genetically modified plants.”
Read the paper: Nucleic Acid Research
Article source: KAUST
Image: Illustration of the model plant Arabidopsis. The genetic material is present as chromatin, which consists of DNA wrapped around a histone protein complex in cells. The linker histone H1 modulates the plant’s immunity against pathogens. Credit 2023 KAUST; Arsheed Sheikh.