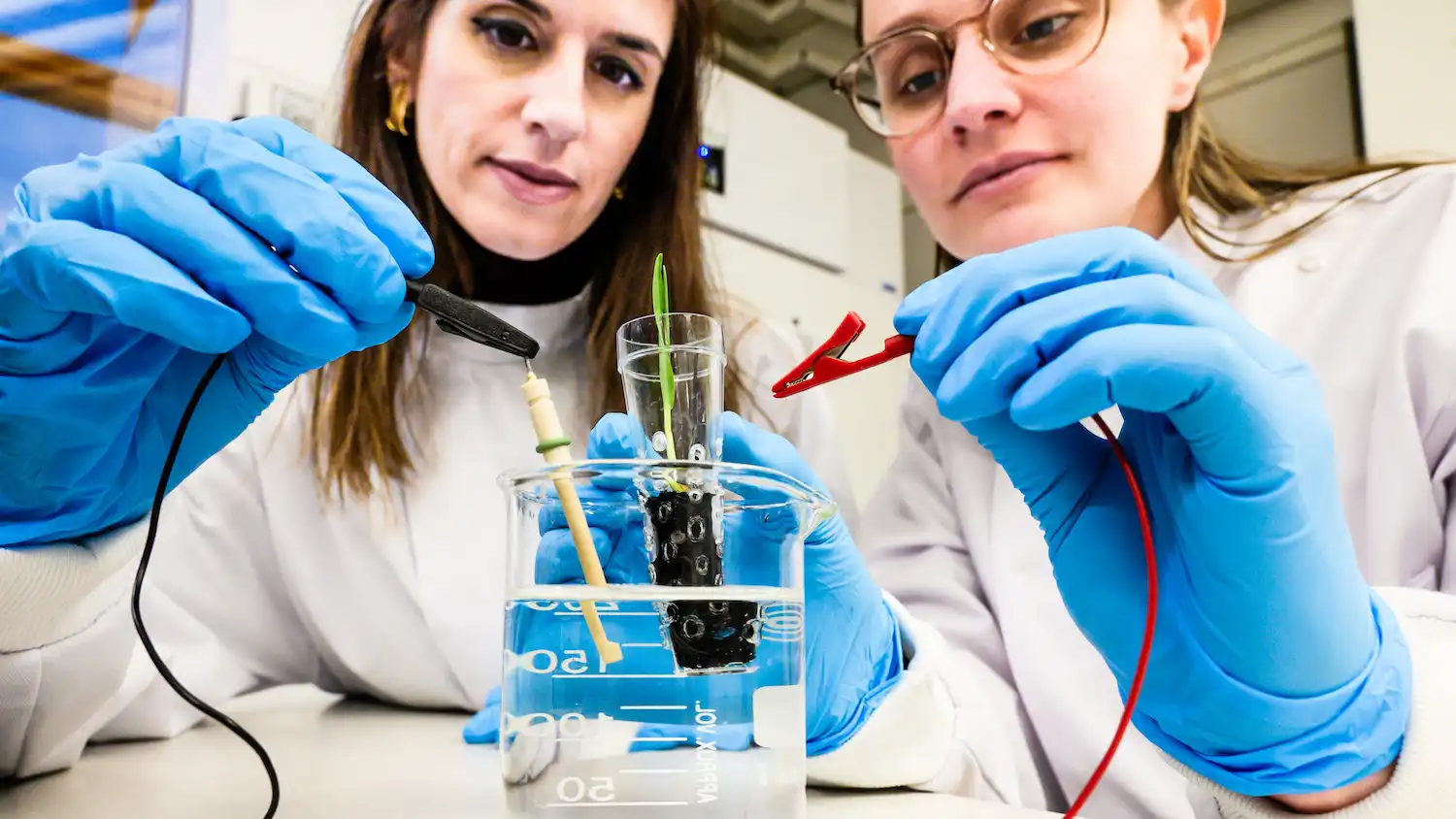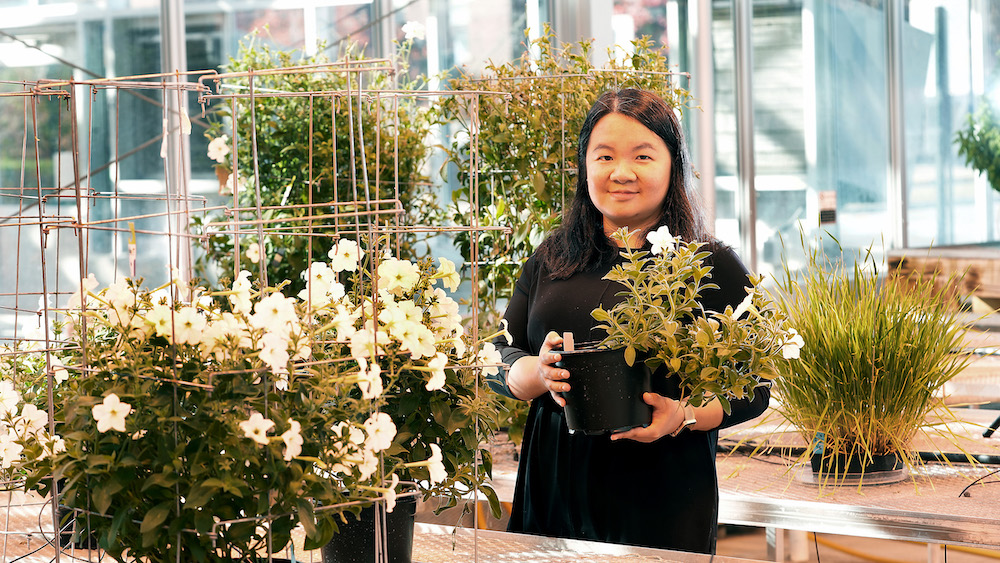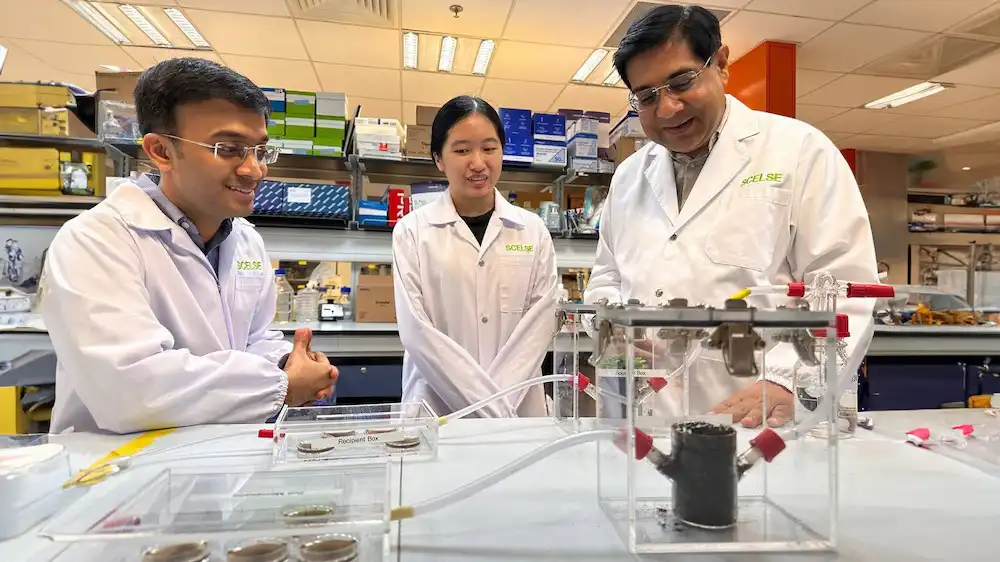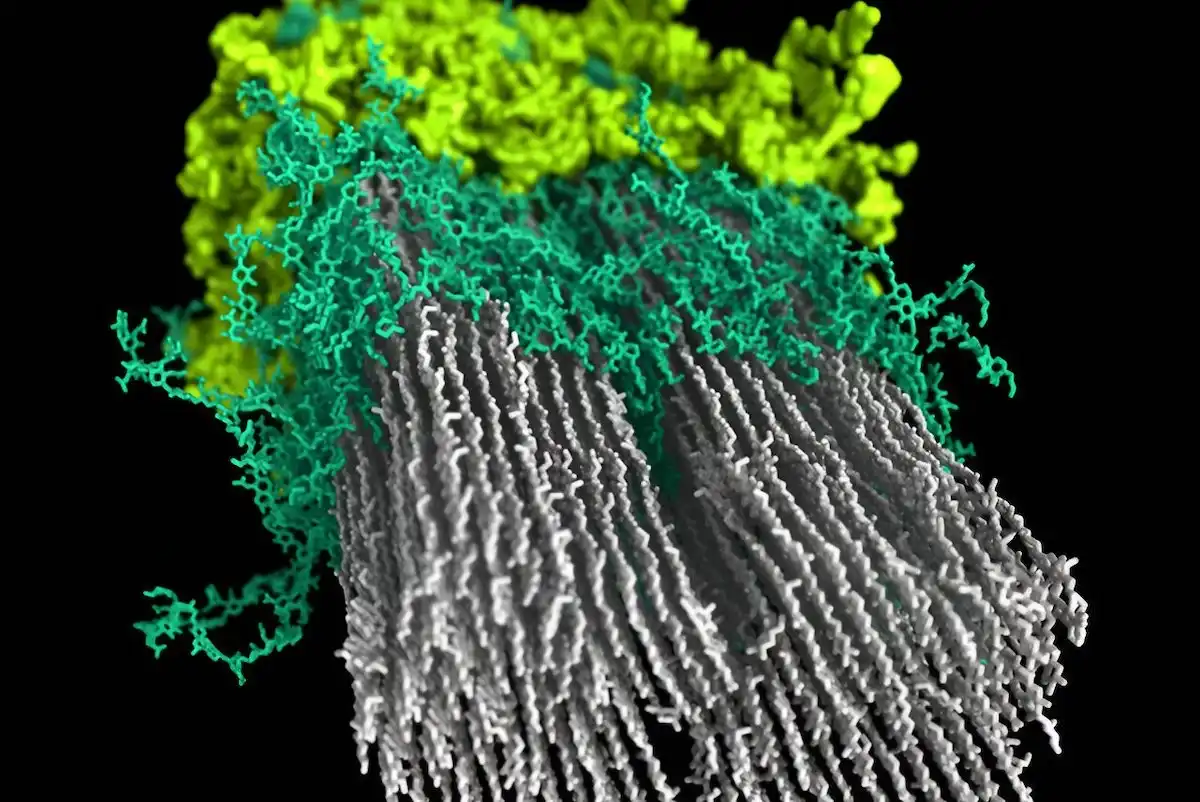
Researchers uncover biological circuit that offers a new avenue for creating drought-resistant crops
Climate change is already harming agricultural yields and may one day pose a significant threat to the world’s food supply. Engineering more resilient crops, including those able to thrive in the face of drought or high soil salinity levels, is an increasingly…
Read More