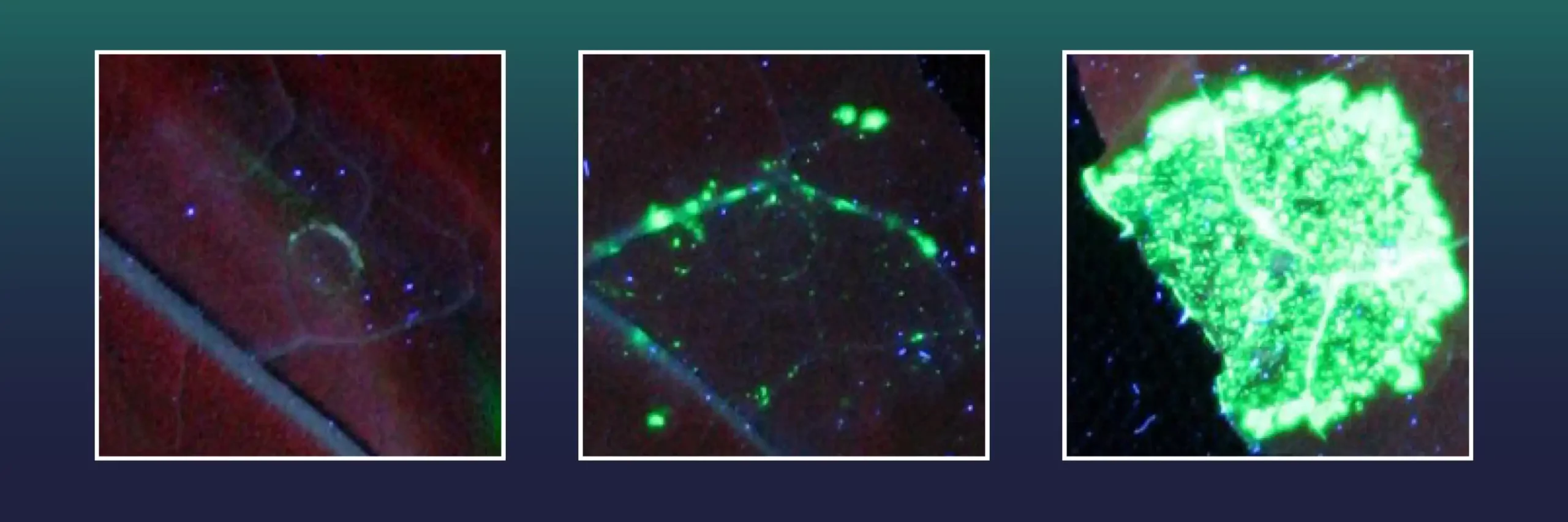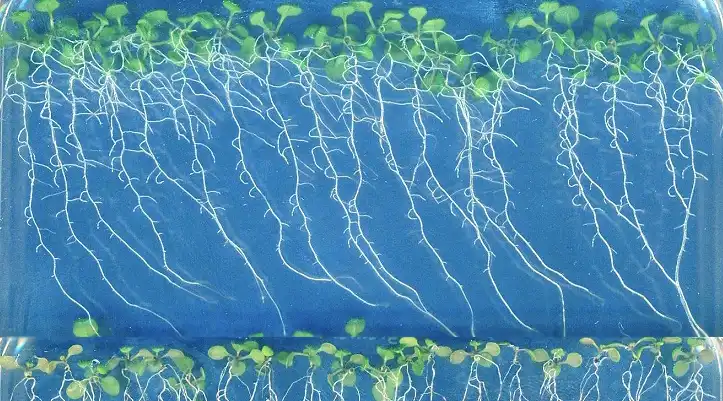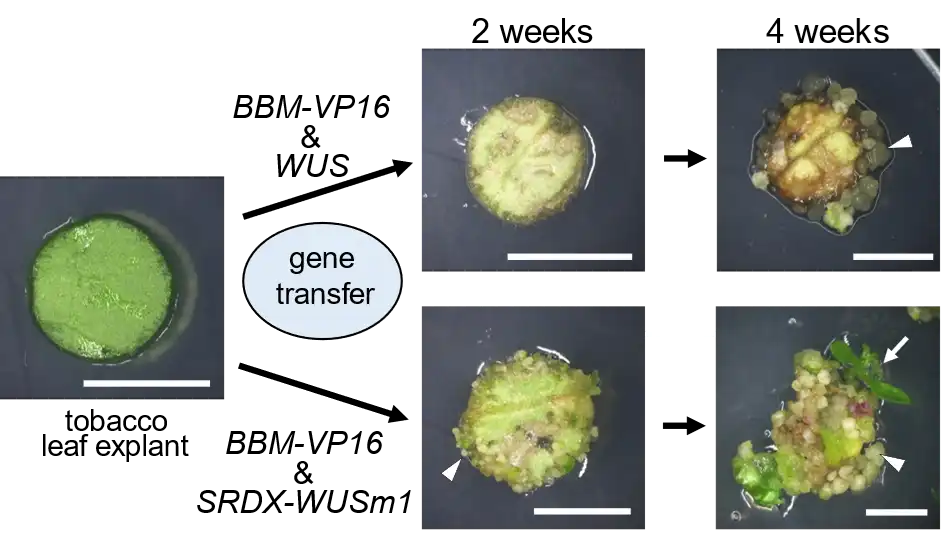
Researchers have devised a plant regeneration method by manipulating gene expression to control cell differentiation, eliminating the need for external growth regulators. This innovation promises simpler and more cost-effective development of genetically modified plants, potentially revolutionizing agriculture and biotechnology while…
Read More