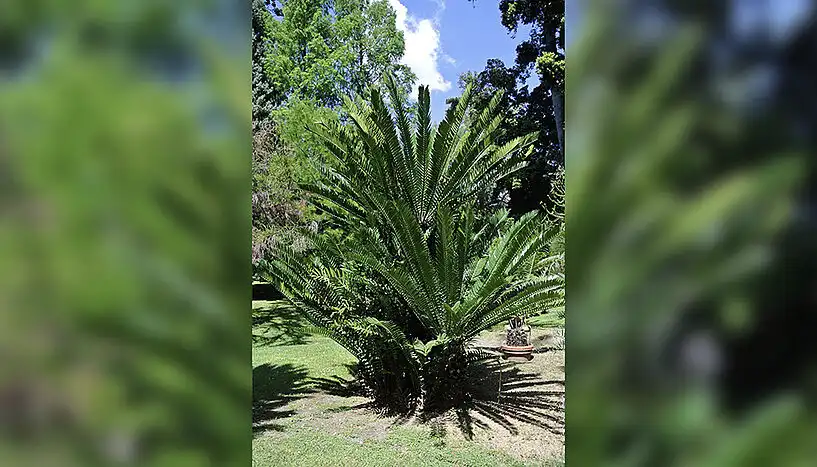
Paleobotanists have made an important breakthrough in understanding the origin and geographic distribution of cycads. By combining genetic data with leaf morphological data from both fossil and living species for the first time, the researchers created a phylogenetic tree of…
Read More