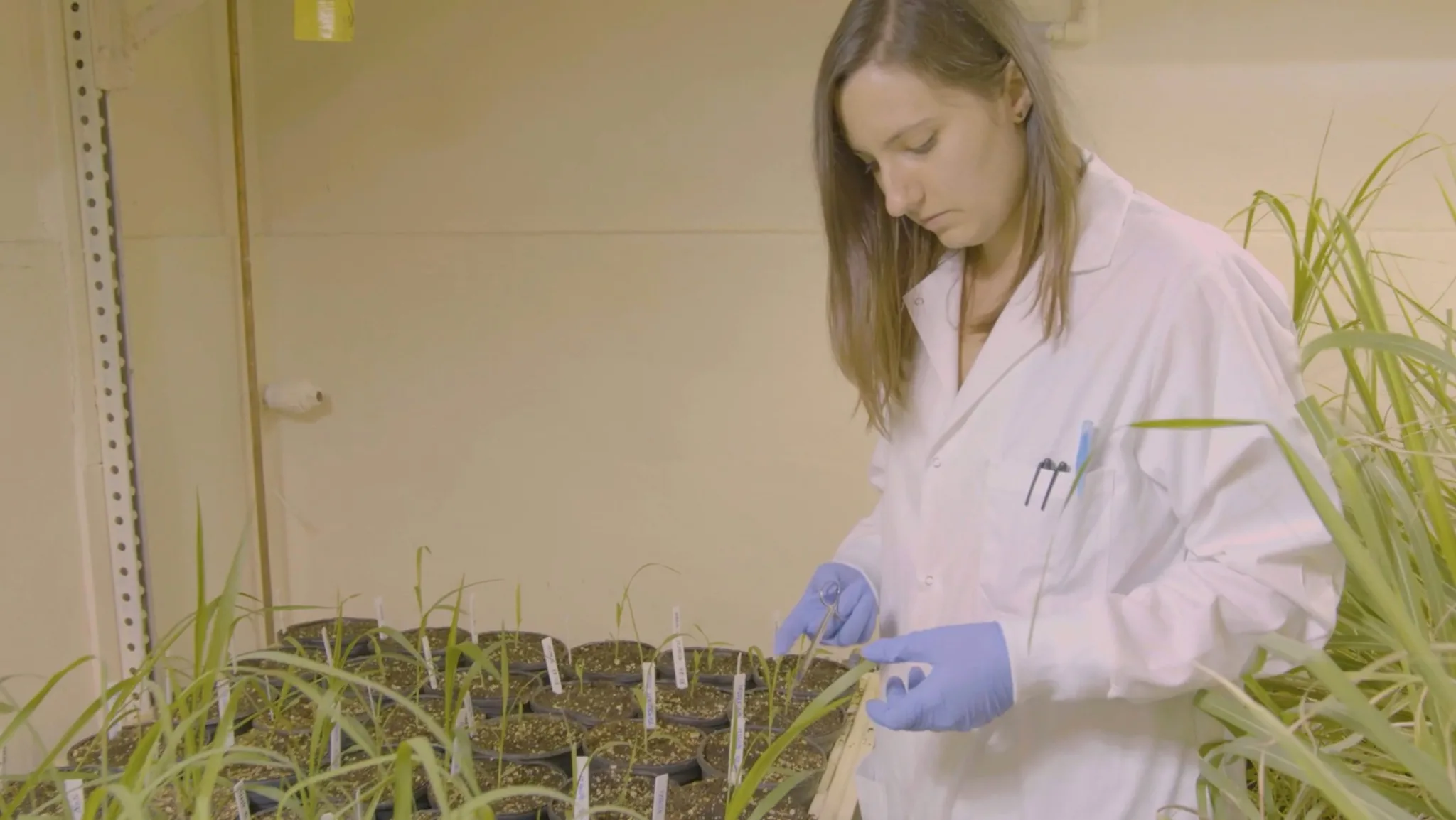
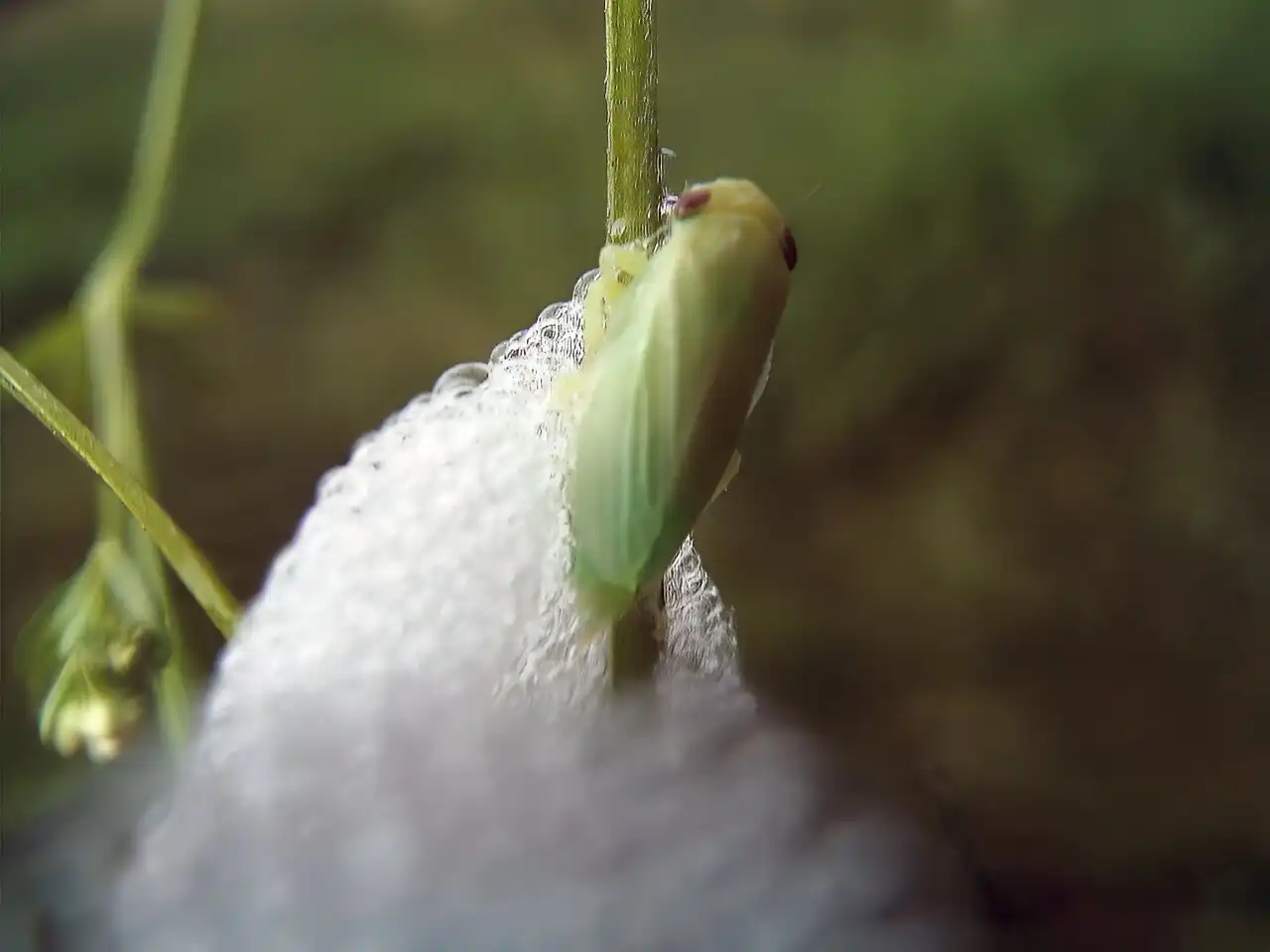
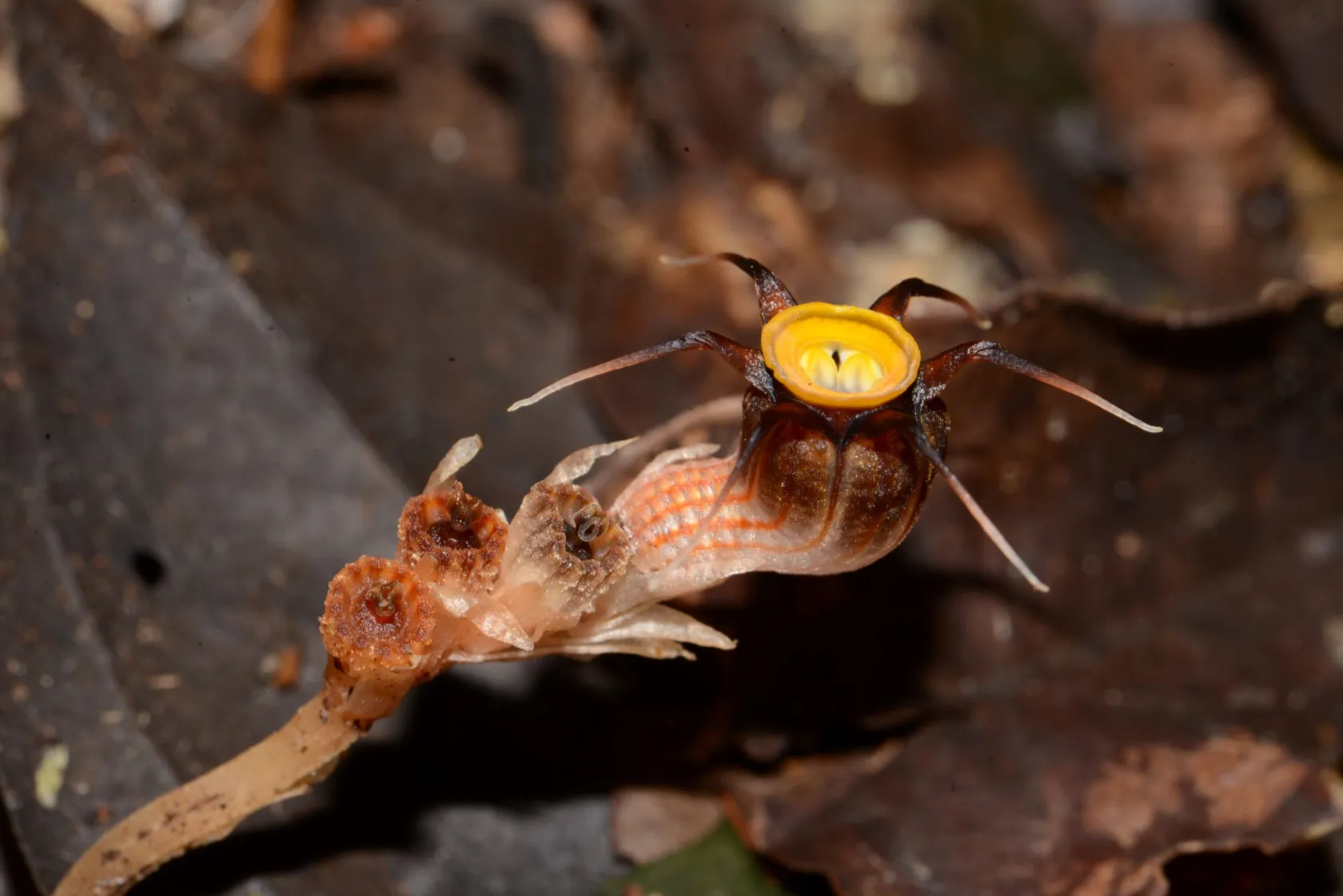
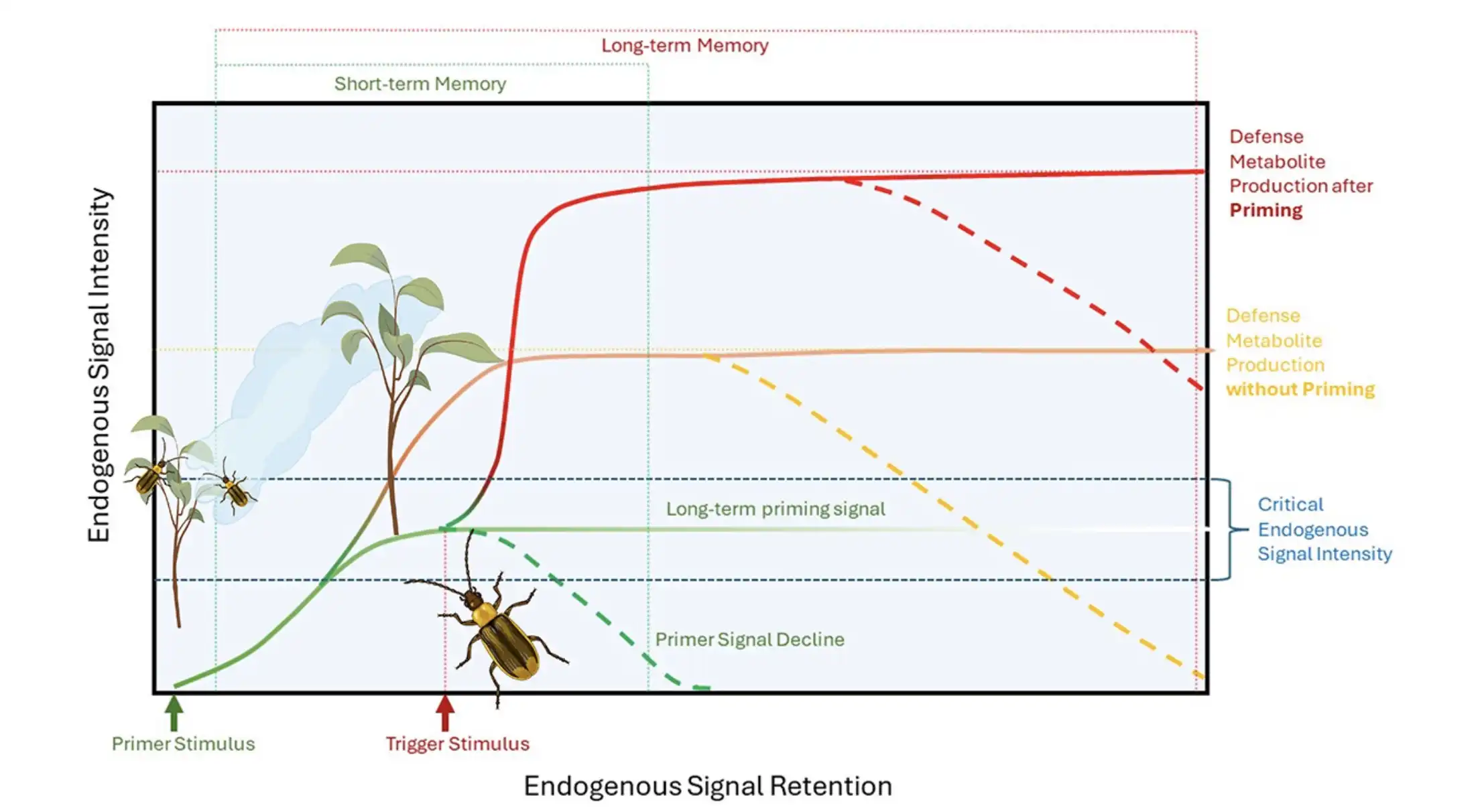
Researchers have created an improved family tree for Solanum plants, revealing that fruit color and size evolved together, challenging previous theories that fruit-eating animals were the primary drivers. This study offers insights for breeding better crops.
Read More