Approaches to biofortification
Biofortification is the improvement of the nutritional value of our crops through both traditional breeding and genetic engineering. Alongside DivSeek and Stress Resilience, biofortification is one of the Global Plant Council’s three main initiatives and will be central to addressing many of the challenges facing world health. However, biofortification doesn’t always involve changing our crops in some way. Often the nutrients we are lacking are present in pre-existing crops. We can biofortify our diets simply by identifying what’s missing and altering our life style accordingly.
Tackling undernourishment
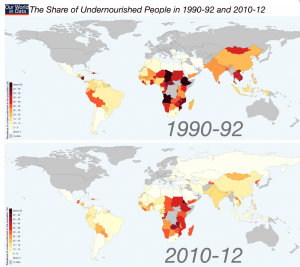
The share (%) of undernourished people per country. From: Max Roser (2015) -‘Hunger and Undernourishment’. Published online at www.OurWorldInData.org
More often that not we intuitively link biofortification with tackling undernourishment in the developing world, and indeed improvements in the diets of deprived communities would be of enormous benefit to global health.
To do this, a key challenge is to increase the nutrient content of staple food crops such as rice in Asia and maize in sub-Saharan Africa. We need to do this in a sustainable and affordable way; ensuring foods are accessible to those who need it. Alongside the fortification of staple crops we need to identify economical crop species that will grow in harsh environments and provide nutrients currently absent from the diet.
Addressing obesity
It is easy to forget that malnutrition is also a problem in developed countries. Worldwide, at least 2.8 million people per year die from obesity-related illnesses, and in 2011 more than 40 million children under the age of five were overweight. Obesity and related health problems such as diabetes, heart disease and certain cancers, place enormous strain on health services, and are partly a function of poor diet lacking in fibre and key phytonutrients. Addressing this is as important as tackling undernourishment, and many of the same principles apply.
Simple lifestyle changes, such as encouraging the consumption of more fruits and vegetables, are clearly a priority. In addition to this dietary change, if we are going to biofortify foods, there should be an emphasis on crops that are already widely consumed.
Purple tomatoes

Professor Cathie Martin works at the John Innes Centre researching the link between diet and health, and how crops could be fortified to improve our diets and global health.
Tomatoes, are one crop plant already eaten widely in the West, commonly found in fast and convenience foods. For this reason they became the focus of the work of Professor Cathie Martin at the John Innes Centre in Norwich, UK. Cathie’s lab has developed a genetically modified tomato that is rich in anthocyanins, making them purple in colour. Anthocyanins are an important dietary component that can have numerous health benefits, including a potentially significant role in the prevention of diseases such as cancer and diabetes. They are the compounds that give some foods, such as blueberries or eggplant, their distinctive blue or purple colouring. Consuming higher quantities could be highly beneficial to health.
“We focused on anthocyanins because of their huge potential health benefits. Pre-clinical studies show that introducing our purple tomatoes into the diet could be an incredibly effective way to protect against diseases such as cancer. Our next steps will be to confirm these findings in human trials,” says Cathie.
However, naturally occurring tomato varieties containing anthocyanins already exist. Wouldn’t it be better to increase consumption of these rather than creating new ones?
“Indeed purple tomatoes do occur naturally. However, these have anthocyanins only in the skin, in quantities too small to make a significant impact on health. Our genetically modified tomatoes have anthocyanins in all tissues,” explains Cathie.
Since developing the purple tomatoes, Cathie, in collaboration with Professor Jonathan Jones, has set up Norfolk Plant Sciences, the UK’s first GM crop company. However, resistance and uncertainty in Europe surrounding GM technology means that progress has been slow.
“The company was founded in 2007 and we are currently working towards the approval of our purple tomato juice in the USA. Producing just the juice rather than the entire fruit means there are no seeds in the final product. This eliminates environmental challenges without compromising health benefits. If the juice proves successful in the USA we may then work towards approval in the UK and Europe.”
It’s not all about Genetic Modification
Of course if we want to make drastic changes to our foods, such as increase anthocyanins in our tomatoes or carotenoids in our rice, GM technology will be a necessity. However, we can go some way to biofortifying our diets without the use of GM.

Golden rice, shown on the left, is a biofortified crop that accumulates high quantities of provitamin A in the grain. This could help tackle Vitamin A Deficiency in developing countries, from which 500,000 children become blind every year, and nine million will die of malnutrition. Photo credit: IRRI photos used under Creative Commons 2.0
Primarily we really need to focus on changing diet and lifestyle. Promoting plants rich in the nutritional components we need is essential, in addition to encouraging traditional diets such as the Mediterranean diet rich in fish, fruits and vegetables. However, changing people’s behavior and relationship with food is a huge challenge. Cathie cites the UK 5-A-Day governmental campaign as an example.
“This campaign was aimed at encouraging people to eat five portions of fruit or vegetables a day. At the end of this 25-year campaign only 3% more of the UK population was getting their five a day.”
In addition to dietary change, we could biofortify our crops through traditional breeding. For example, one answer to increasing anthocyanins in the diet could be red wheat. Red wheat is rich in anthocyanins, and furthermore less susceptible to pre-harvest sprouting, which causes large crop losses every year for farmers. However, we have so far resisted selecting for this trait in wheat breeding programs as it is not considered esthetically pleasing. To improve our diets we may need to change our expectations of what we want our plates to look like.
Next steps
Plant scientists alone cannot tackle biofortification of our diets! Cathie believes the key to a healthier future is interdisciplinary research:
“Everyone needs to come together: nutritionists, epidemiologists, plant breeders, and plant scientists. However, with such a diverse group of people it is hard to reach agreement on the next steps, and equally as difficult to secure funding for research projects. We really need to promote collaboration and interaction between all groups in order to move forwards.”





