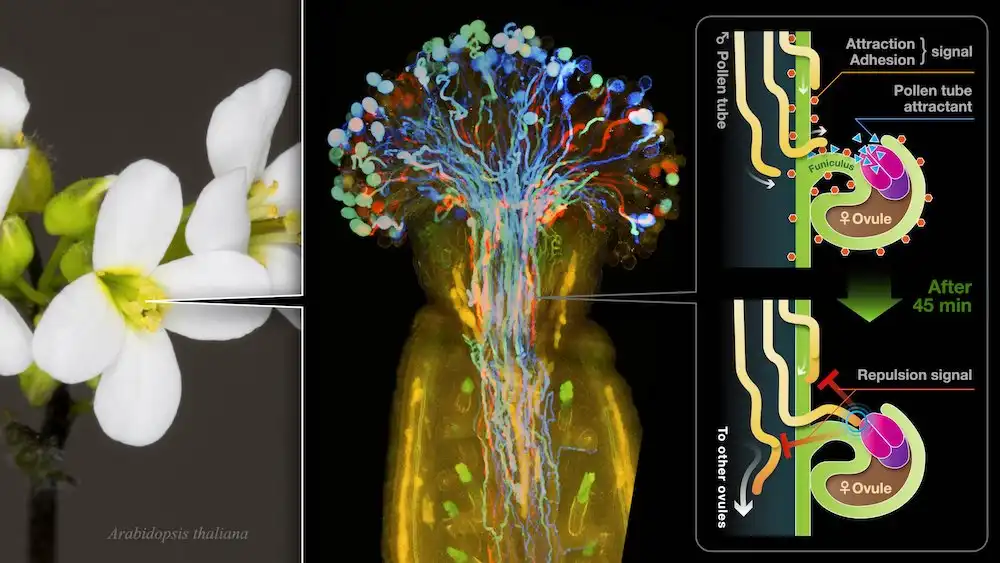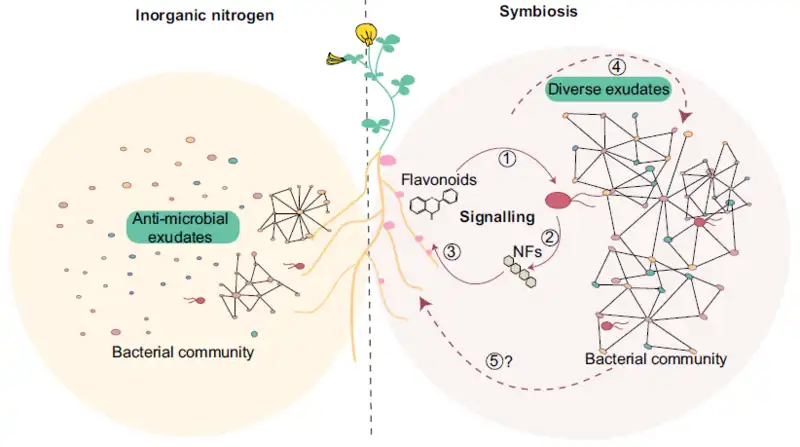
Researchers found that specific molecules enable symbiotic bacteria to communicate with legume plants, influencing bacterial growth near roots. This signaling fosters beneficial partnerships for nutrient uptake and resilience, crucial for sustainable agriculture. The study highlights the role of plant-bacteria communication…
Read More