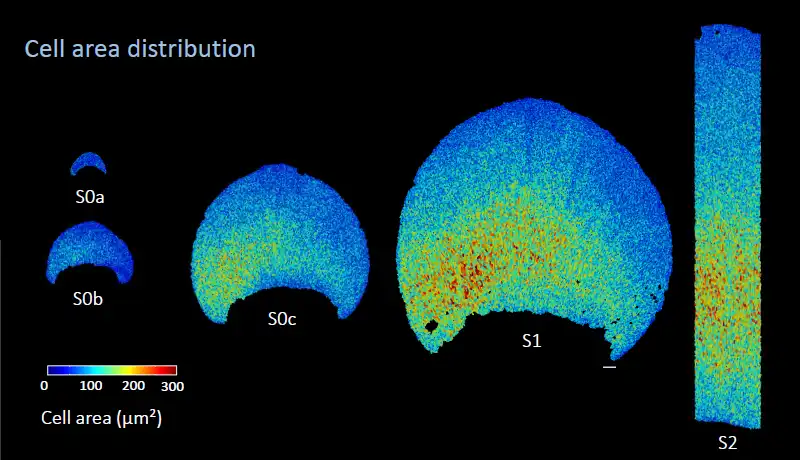
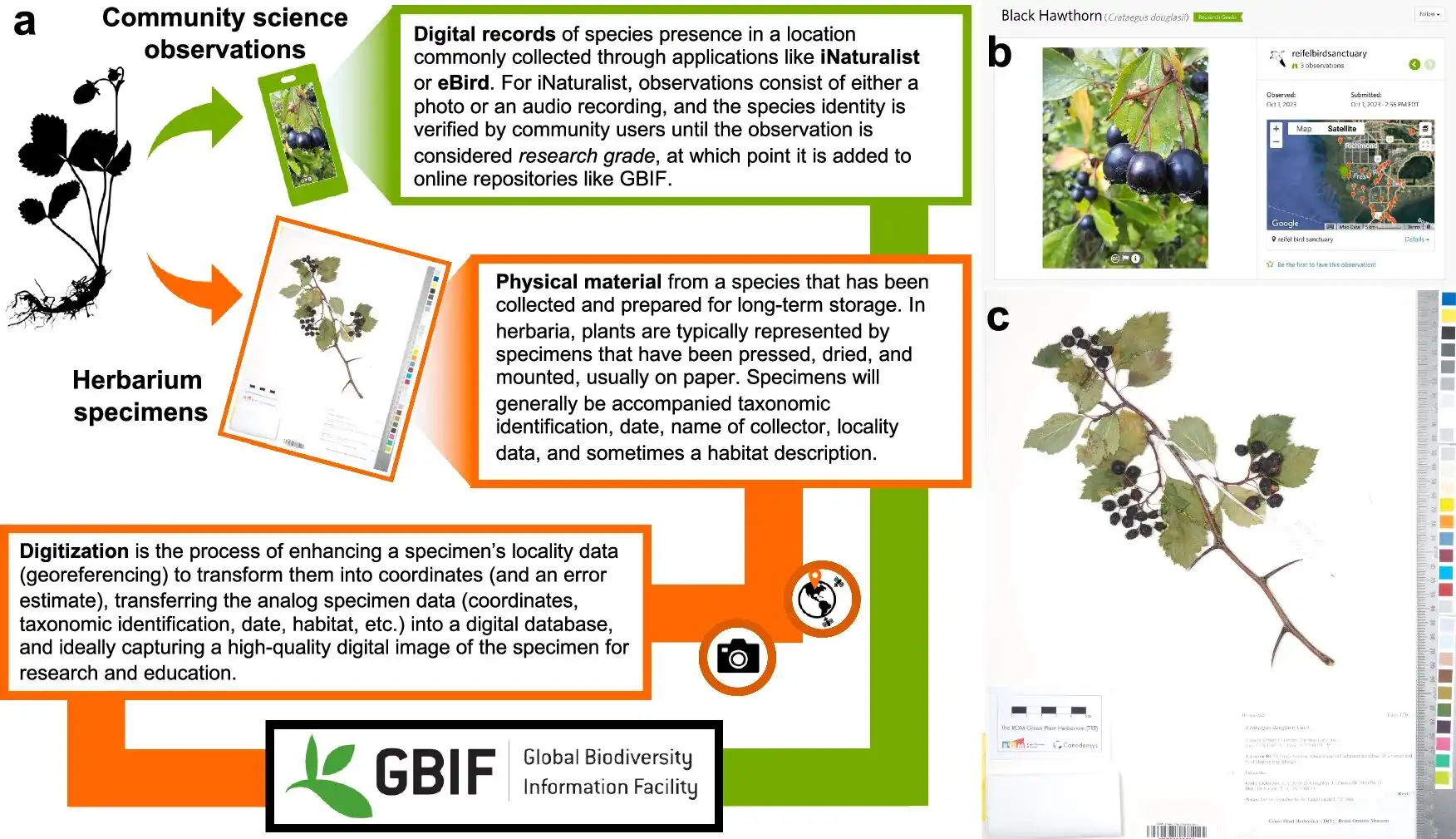
Nitrogen-fixing plants like clover and alder, crucial for enriching nutrient-poor soils, are declining in temperate forests due to human-driven nitrogen deposition, a new study shows. Using decades of data from Europe and the USA, researchers found this decline is independent…
Read More