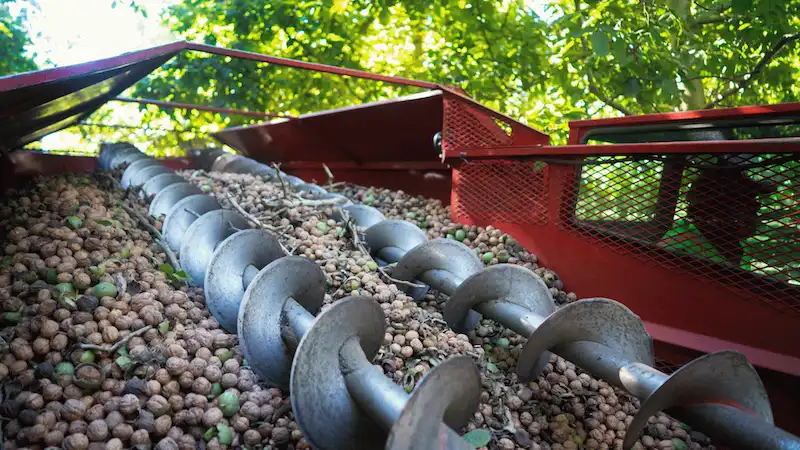
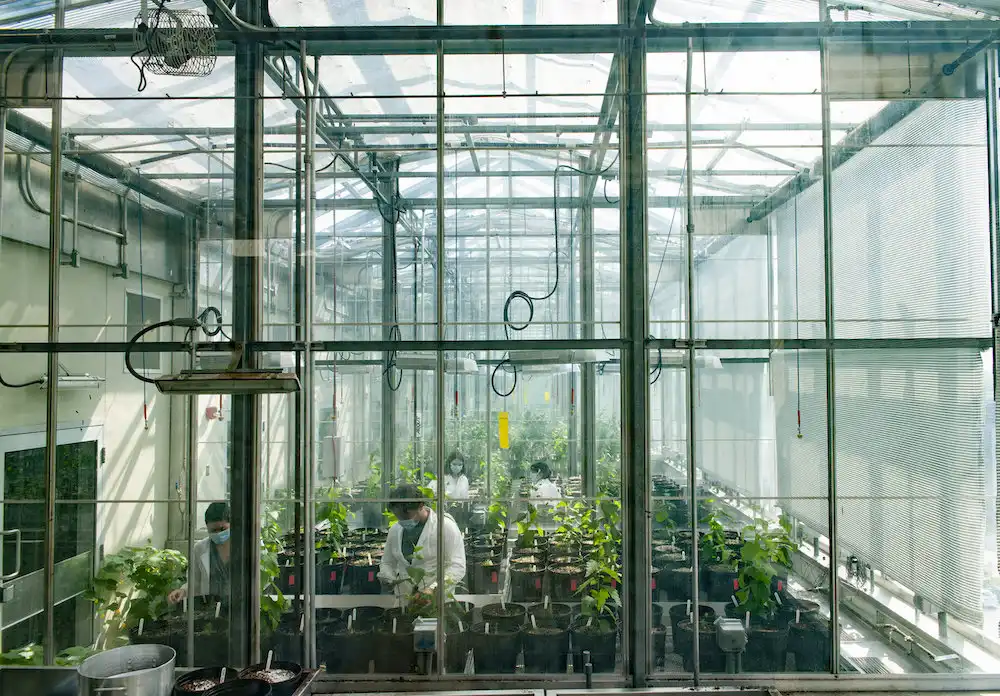
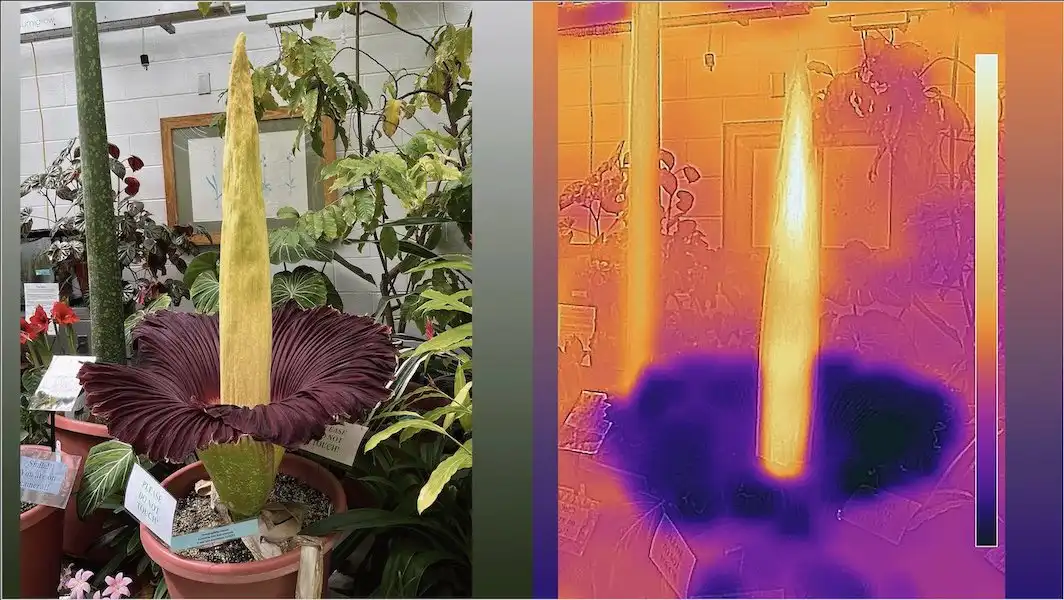
Scientists have uncovered a genetic mechanism in walnuts and their ancestors that has remained stable for 40 million years. Male-first or female-first flowering, balanced by a single genetic locus, parallels sex determination in animals. This evolutionary trait ensures genetic diversity,…
Read More