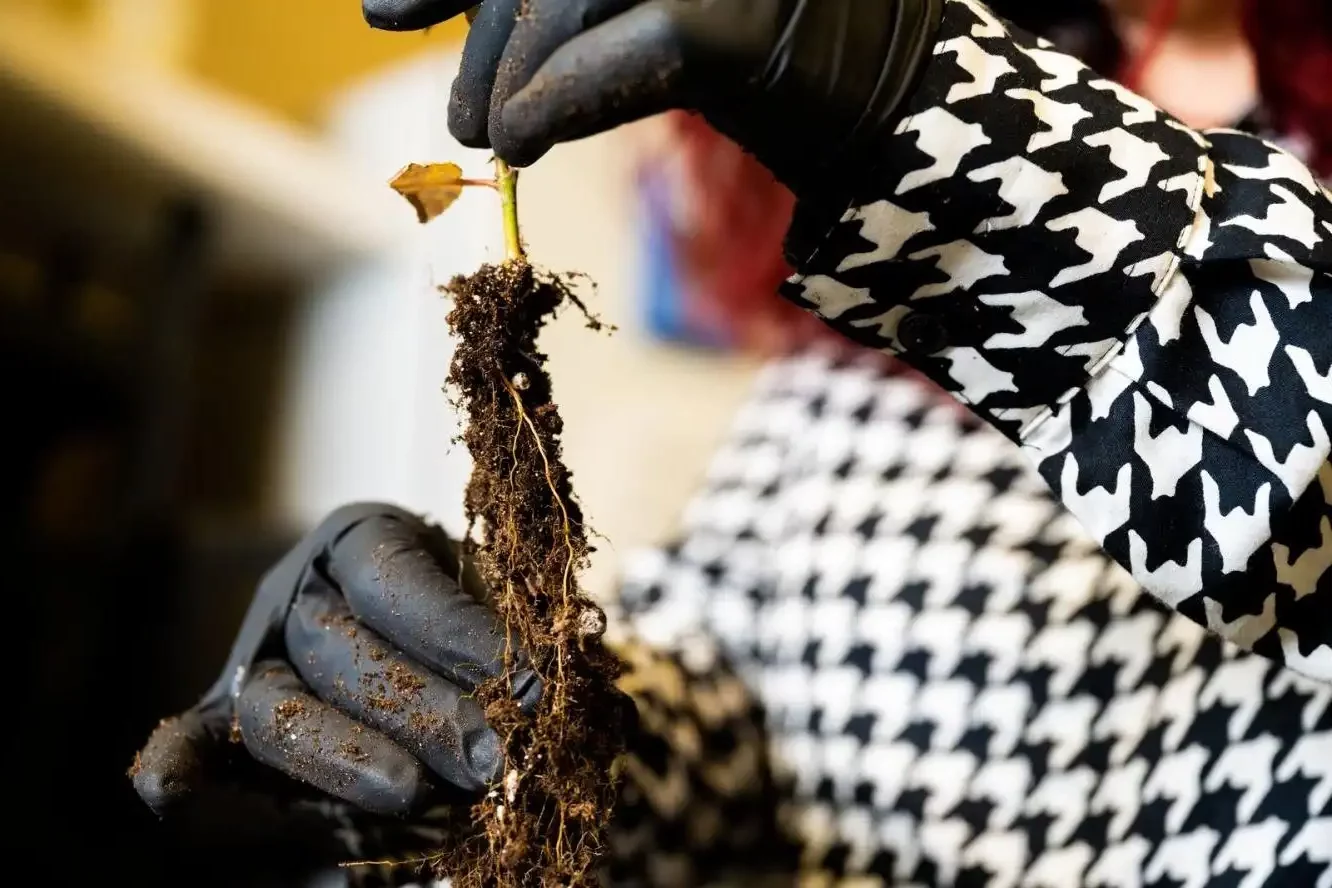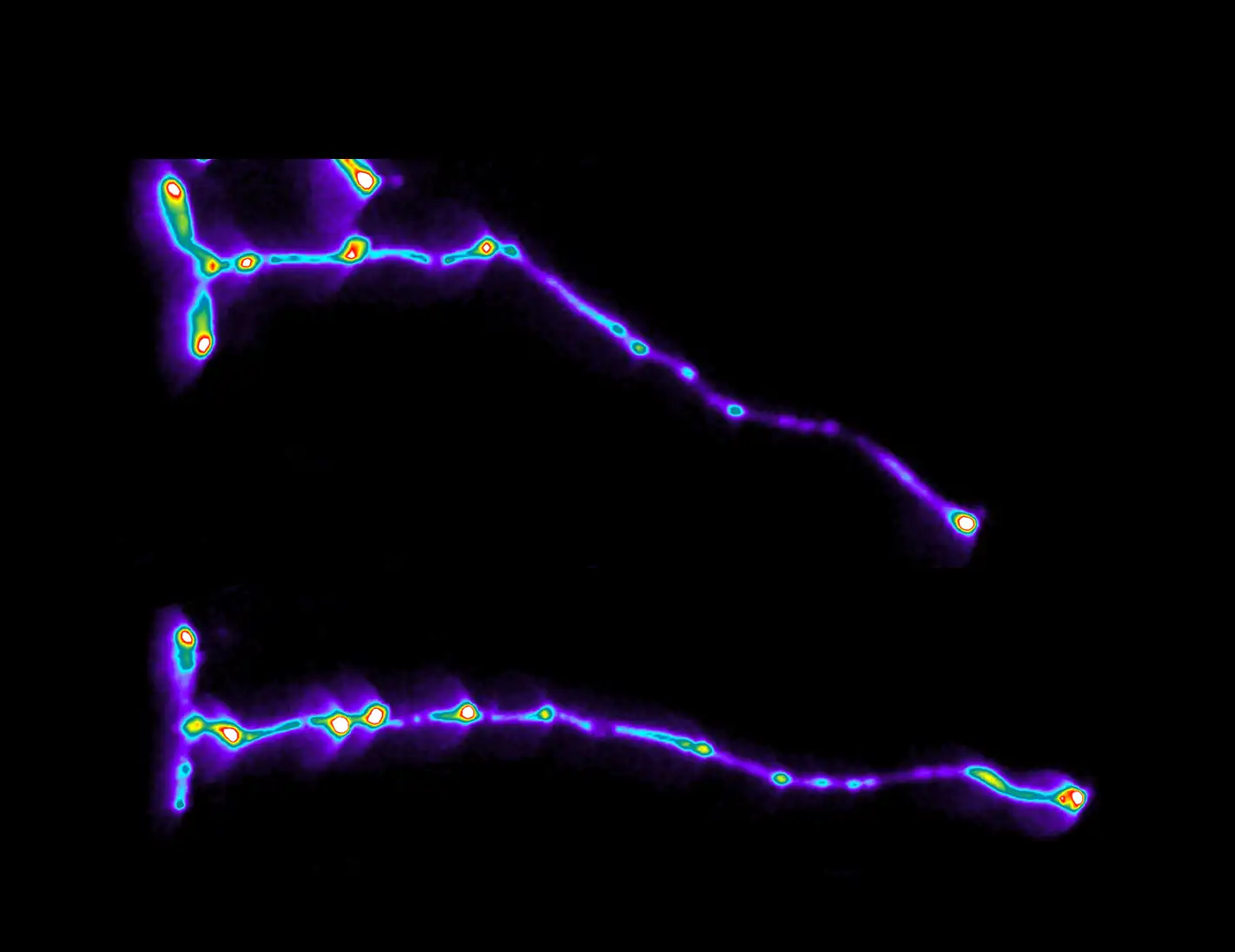
Scientists discovered that autophagy, a cellular clean-up process, is crucial for plant root growth. This mechanism, also found in fasting humans, optimizes the "heartbeat" of root tips, aiding water and nutrient absorption. Better understanding this process could enhance crop resilience…
Read More