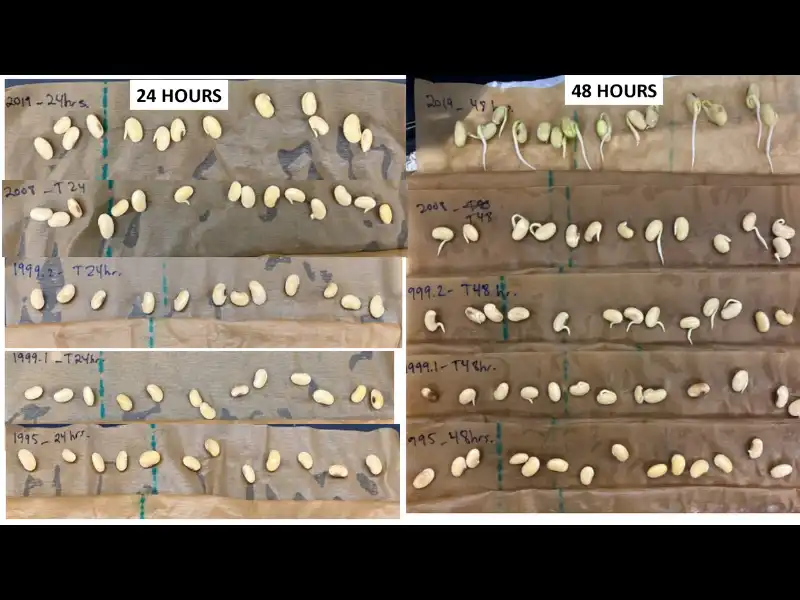
Study used video games to test ways of balancing agriculture and conservation—and found getting more women involved in decision-making may boost productivity and the planet’s health.
When a family of five-ton elephants stomps and chomps its way through your crops, there’s only one winner. And in the central African nation of Gabon, farmers are getting fed up with the giant animals trampling their fields—and their livelihoods.
In conservation terms, Gabon is a success story—protected areas and tough anti-poaching measures have allowed the numbers of critically endangered African forest elephants to stabilize. But with food prices rising, anti-elephant protests have been spiking too. “Some people cannot farm anymore—the elephants are eating so much of their crops,” Gabon’s environment minister Lee White told Reuters in 2022. “It has become a political issue and is eroding support for conservation and for the president (and) government.”
As Gabon’s leaders have learned, balancing conservation and agriculture isn’t easy: tilt policies in favor of farmers, and important habitats or species could be lost; tip efforts toward animals or land, and people may lose their livelihoods. Paying farmers to support the environment might seem like an easy answer—incentivizing them to conserve habitats. But a new study led by Andrew Reid Bell, a Boston University College of Arts & Sciences assistant professor of Earth & environment, has found payments don’t always reconcile the tension between agricultural production and the planet’s health.
With an international team of researchers, he used video games to test how farmers around the world react when faced with conservation dilemmas—like traipsing elephants in Gabon, hungry geese in Scotland, and crop pests in Cambodia. For the most part, payments designed to motivate eco-friendly behavior weren’t a reliable panacea: if they boosted pro-conservation work, they usually dented agricultural outputs. The study did, though, discover one seemingly surefire way of improving conservation andproduction: including more women in decision-making. Their involvement boosted cooperation between farmers on environmental issues and increased output. The results were published in Communications Earth & Environment.
“It informs this bigger story of finding ways to better empower women in agricultural contexts around the world,” says Bell.
To see how farmers and pastoralists behaved when confronted with a conservation predicament, Bell designed and built three games using the modeling tool NetLogo. Each game posed a different dilemma for players: GooseBump, decide to let wildlife damage crops, scare animals onto other farms, or use lethal control; NonCropShare, choose between using pesticides or natural pest control; and SharedSpace, balance growing crops while conserving forest and managing fallow land. The multiplayer games were played on tablets in seven countries, from the Orkney Islands off the northernmost tip of Scotland to Madagascar to Vietnam.
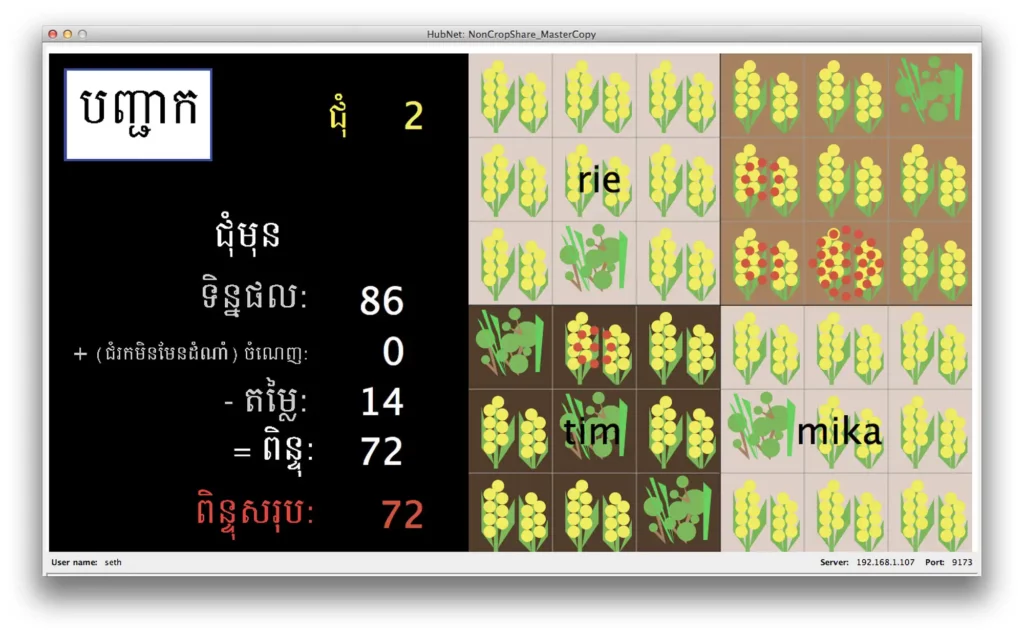
“We were looking at how players sharing a space will coordinate and any player has equal opportunity to lead the group, follow, or encourage a particular result,” says Bell, a resource ecology and management expert who specializes in building computer models and behavioral experiments to examine issues like agricultural development and water use.
It turned out that pro-environment payments can work in some situations—usually if there’s a clear agricultural benefit, such as when neighboring farmers coordinate on leaving areas fallow, boosting soil resiliency and, therefore, their overall crop yield. But when the benefits take time or don’t quickly improve output, payments aren’t effective: increased biodiversity might help society in the long term, but doesn’t change this year’s harvest, or next year’s.
“The challenge in many lower-income environments is that a lot of the payoffs to conservation agriculture emerge on four- to eight-year time horizons,” says Bell, “which is often beyond the planning horizon of farmers who are thinking two or three months ahead, meeting more immediate needs. It’s a mismatch.”
The first program the team created was NonCropShare, a pest control game that was played by farmers in Cambodia and Vietnam.
“You could do well by just spraying everything and avoiding pest damage,” says Bell, “but you could do equally well by coordinating on maintaining natural enemies—parasitic wasps, spiders, or dragonflies that would eat the pests. The challenge with that coordinated solution is that if anybody defected, everybody else would be worse off. The question was, how much do we have to incentivize that pro-environmental solution to tip the balance?”
The answer depended on the country. In Vietnam, payments nudged farmers into cooperation, while in Cambodia they just made things worse. “The approach to farming—in the game, at least—wasn’t a good match for the payments” in Cambodia, says Bell, “and the mix of strategies that people employed when we offered payments left the landscapes worse off than if we hadn’t offered anything.” The other two games reflected the overall trend.
It’s not the first time Bell has mixed video games and conservation studies. In one past paper, he drew lessons from Nintendo’s Mario Kart, looking at the way it gives better bonuses to dawdling players to keep races even. He says games are useful as an experimental tool, too, allowing researchers and policymakers to trial a theory or an approach to an issue when a field test is either impractical or too costly. And they help him dig into human behavior and decision-making in deeper ways than a survey or interview can: “It’s really common people can’t tell you what they’re thinking,” says Bell, who’s also affiliated with the BU Center on Forced Displacement, “or how they do something, or they don’t want to.”
And in conservation, some of the dilemmas faced by farmers aren’t exactly polite dinner table topics—not many people will admit to killing wildlife, but they might debate the action in an impersonal video game.
“Dynamic games like this can help desensitize illegal activities, such as lethal control or forest clearing, in a way conventional tools cannot,” says Sarobidy Rakotonarivo, an author on the paper and environmental socioeconomist based in Madagascar. “These are often criminalized activities that farmers are unwilling to talk about for fear of prosecution. The games provide a safer environment to get them to talk openly.”
When it comes to our changing planet, says Bell, we have a lot of big data—satellite images, gauges on land, sea, and air—but not nearly as much information on human decision-making.
“We can talk about sea surface temperature or rainfall anomalies, about deviation from a mean, but we don’t have that with social data—we don’t know much about what people do,” he says. With one exception: when disaster, like a famine, strikes. Then researchers descend and grab as much information as possible about what went wrong. “But we miss all these stories where things are going just fine, we miss our ability to explain why that is. So, we need ways to better engage with people to capture their decisions.”
Including women in farming groups was one human factor that made a lot of things go right, according to Bell’s study. Whenever a group had increased gender diversity, production and pro-environment outcomes improved. In their paper, the researchers write that “mixed gender groups may lead to better natural resource management.” They also showed that when the players built strong relationships and trusted each other, conservation efforts got a boost.
“We need to be better at empowering women in agricultural contexts,” says Bell. “It’s hard, because, in part, you see all these cases where people invest in a crop that’s traditionally a women’s crop, it succeeds, then becomes a men’s crop.”
The International Food Policy Research Institute—whose senior research fellow Wei Zhang was a coauthor on the latest study—has found protecting women’s rights to own land, improving their access to credit and financial services, and giving them more decision-making power can all help.
And, adds Rakotonarivo, an African Research Initiative for Scientific Excellence research fellow, we also need to step up when it comes to listening to—and trusting—the people most impacted by conservation policies.
“Small-scale rural farmers, although often portrayed as having low levels of education, are capable of wise choices,” she says. “They are not the key obstacles to conservation as often assumed. Obstacles may be simply broader social barriers, such as very low agricultural productivity, that need to be addressed by other types of programs.”
Rakotonarivo says that ignoring farmers when developing pro-environment interventions will only lead to failure; if their needs aren’t considered, programs “might fail to mitigate conservation conflicts through lack of engagement, uptake, and follow-through.” Although many problems—farmers killing pest animals or clearing forests—are “commonly framed as human-wildlife conflicts,” she says, the issues may be better addressed by looking at the “more complex social conflicts between different social groups.”
In their paper, the researchers recommend policymakers consider programs that have both conservation and production goals, rather than just one of those goals, or that include bonuses for cooperation among groups of farmers. They also highlight improved access to insurance programs that cover the risks of pro-environment efforts, ensuring payouts, for example, when tigers or lions raid livestock. But most of all, they write, rather than being prescriptive with program suggestions, “we only wish to highlight the challenges of aligning encouragements simultaneously with environment and livelihood goals.”
There is one innovative, nature-based solution in the paper though that might be of particular interest to the farmers of Gabon: bee fences. These makeshift, homespun barriers are hung with beehives every 10 meters or so. If an animal tries to crash through, the bees quickly give them a reason to turn around. And while popular culture might show elephants cowering when a mouse scuttles by, it’s bees they really don’t like. If the elephants, preoccupied by bees, don’t trample and gobble the crops, the farmers are more likely to help protect the animals.
“Conservation often comes at the cost of rural livelihoods,” says Rakotonarivo. “Policymakers, and especially the conservation community, need to be deliberate about the joint people and environment goals of an intervention.”
This study was primarily supported by the CGIAR Research Program on Water, Land, and Ecosystems; the CGIAR Research Program on Policies, Institutions, and Markets; and the European Research Council. The research team also included Apurva Bhargava, New York University; A. Bradley Duthie and Adams Kipchumba, University of Stirling, Scotland; Becca Sargent, Newcastle University, England; and Spike Lewis, Bangor University, Wales.
Read the paper: Communications Earth & Environment
Article source: Boston University
Author: Andrew Thurston
Image credit: Mikadago/Pixabay
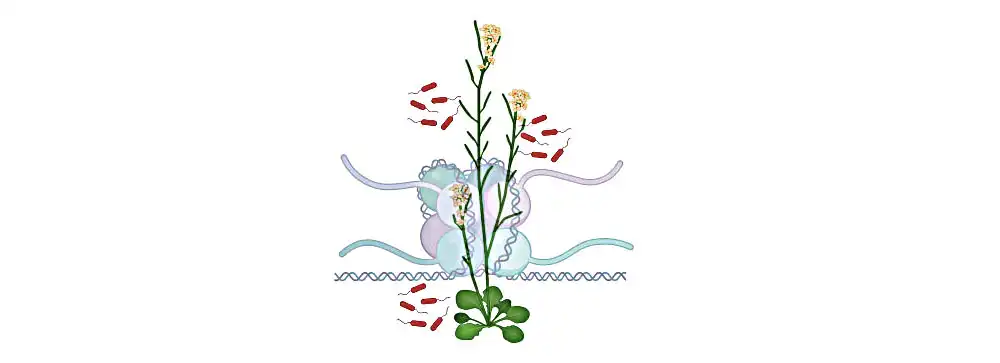
Understanding the role of a key protein in plant immunity could inform the development of crops that are resistant to multiple pathogens.
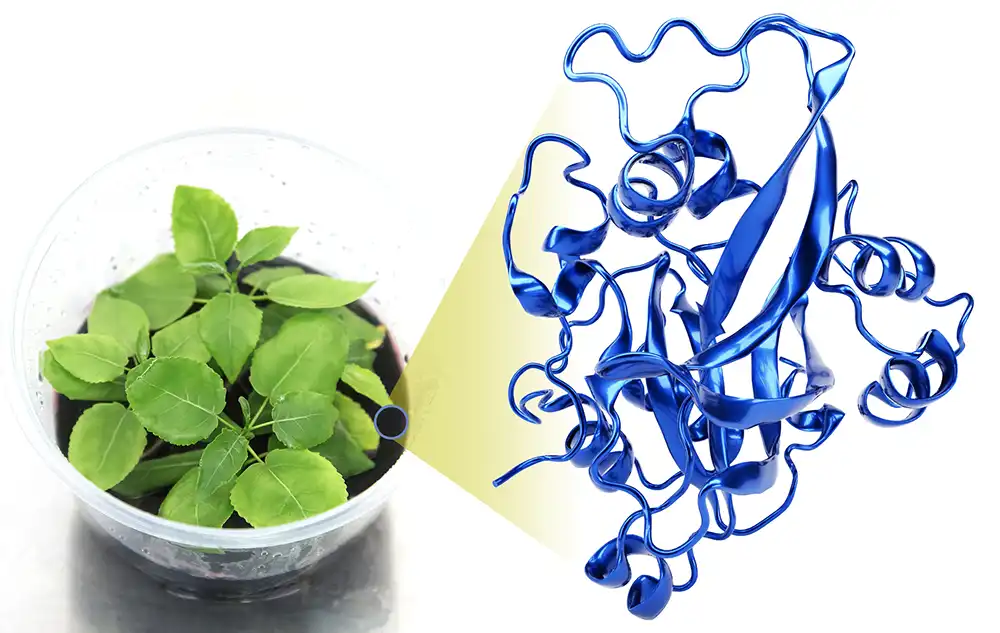
Up to 30 per cent of crop yields worldwide each year are lost to pathogenic infection. Understanding how to make plants more resilient to infection is vital for future food security. Now researchers have uncovered the critical role of a linker histone protein, called H1, during plant immune responses to bacterial and fungal infections.
“Previous studies on Arabidopsis plants revealed that H1 is important for healthy growth and development,” says Arsheed Sheikh, who worked on the project with Heribert Hirt and co-workers. “Linker histones are known to regulate infection in animals, but their role in plant infection and immunity has never been explored.”
In animal and plant cells, fundamental units called nucleosomes contain DNA wrapped around a protein complex, and are critical for regulating genetic information. The individual nucleosomes are connected by linker DNA. Linker histone H1 holds the exit/entry site of linker DNA like a clip, thus regulating the unwinding and flexibility of nucleosomes.
“In plants like Arabidopsis, we find three isoforms of H1,” says Sheikh. “Normally, H1 suppresses gene expression — this includes the defense genes of the immune system.”
The team explored mutant Arabidopsis plants with all three H1 isoforms knocked out. They grew wild-type and mutant plants under controlled conditions and then infected them with either the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae or the fungal pathogen Botrytis cinerea. After three days, they compared the severity of infection between the different groups of plants.
“The mutant plants were resistant to both bacterial and fungal infection when compared to wild-type plants,” says Sheikh. “The knockout mutant had higher levels of defense gene expression and the immune response hormone salicylic acid.”
Probing H1’s role further, however, the team were surprised to find that the mutant plants lacked defense-priming ability. In other words, when subjected to a small dose of a pathogen some time after initial infection, the plants showed no enhanced immune response. Like vaccination, priming a plant with a small pathogen dose can boost its immunity. The lack of defense priming in the mutant plants suggests H1 plays a critical role in priming.
“This fundamental knowledge could help generate smart crops that are resistant to multiple infectious agents simultaneously,” says Hirt. “However, this study also serves as a cautionary warning that it is important to study both the direct and indirect effects of a given mutation in genetically modified plants.”
Read the paper: Nucleic Acid Research
Article source: KAUST
Image: Illustration of the model plant Arabidopsis. The genetic material is present as chromatin, which consists of DNA wrapped around a histone protein complex in cells. The linker histone H1 modulates the plant’s immunity against pathogens. Credit 2023 KAUST; Arsheed Sheikh.