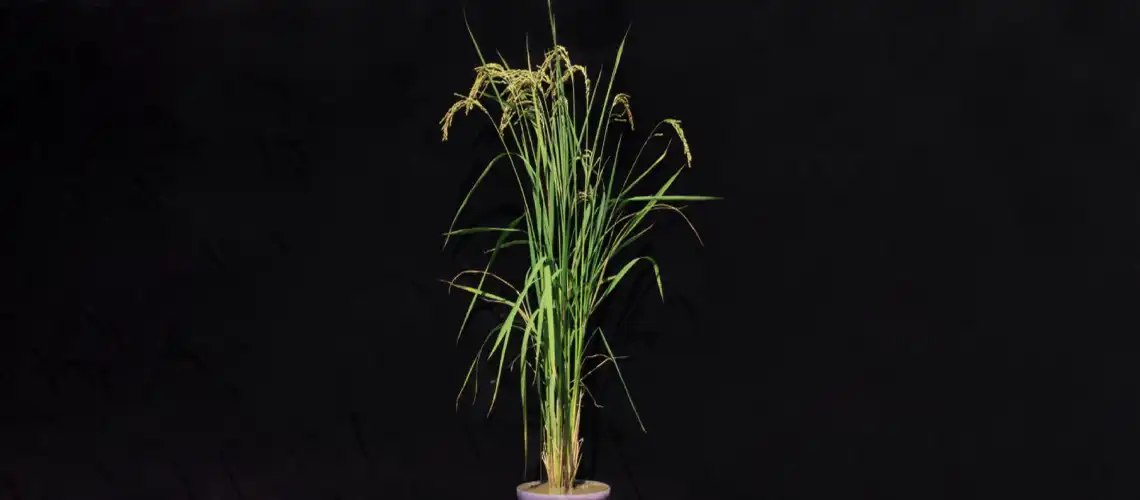
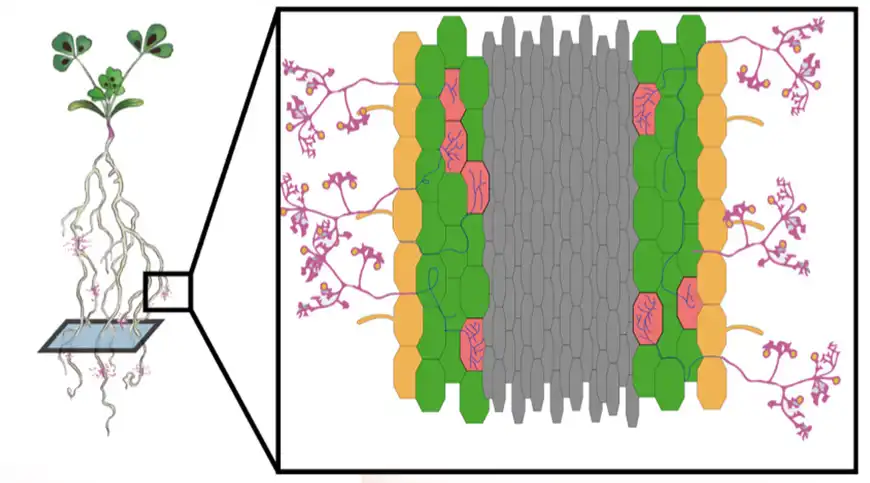
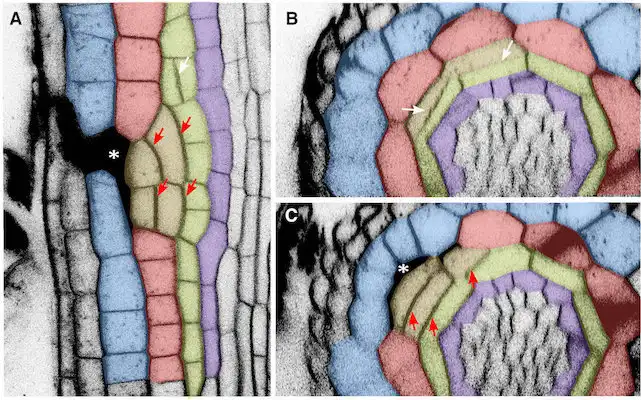
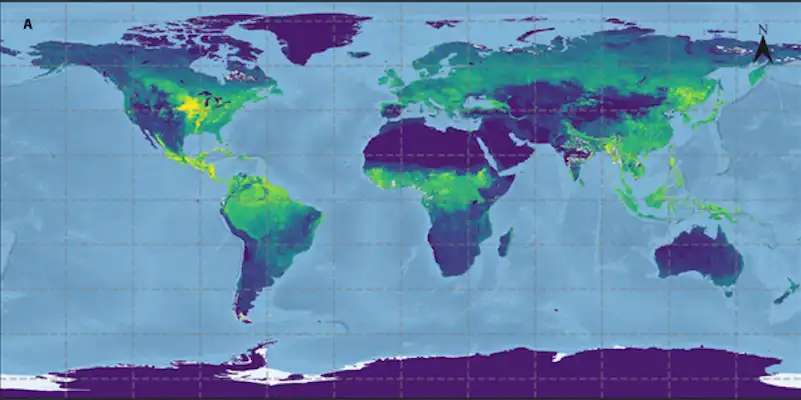
Vitamin B1 is an essential micronutrient for human beings. Its deficiency is the cause of numerous diseases of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. Researchers have achieved a significant advance in the fight against vitamin B1deficiency, frequently associated with a rice-based diet.
Read More