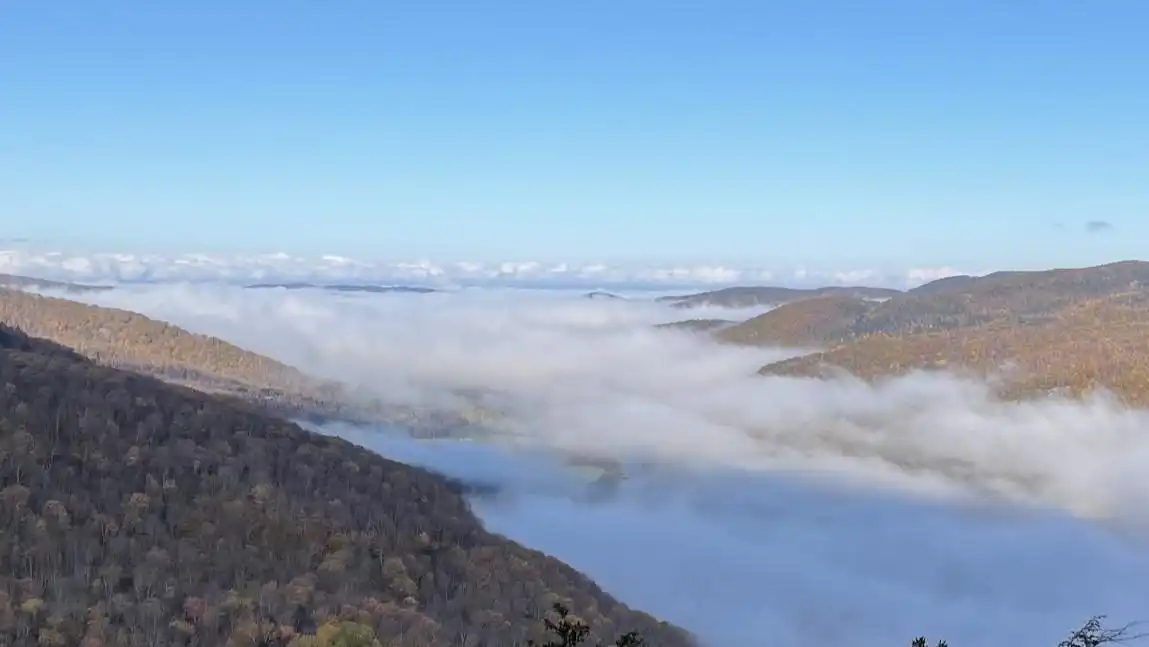
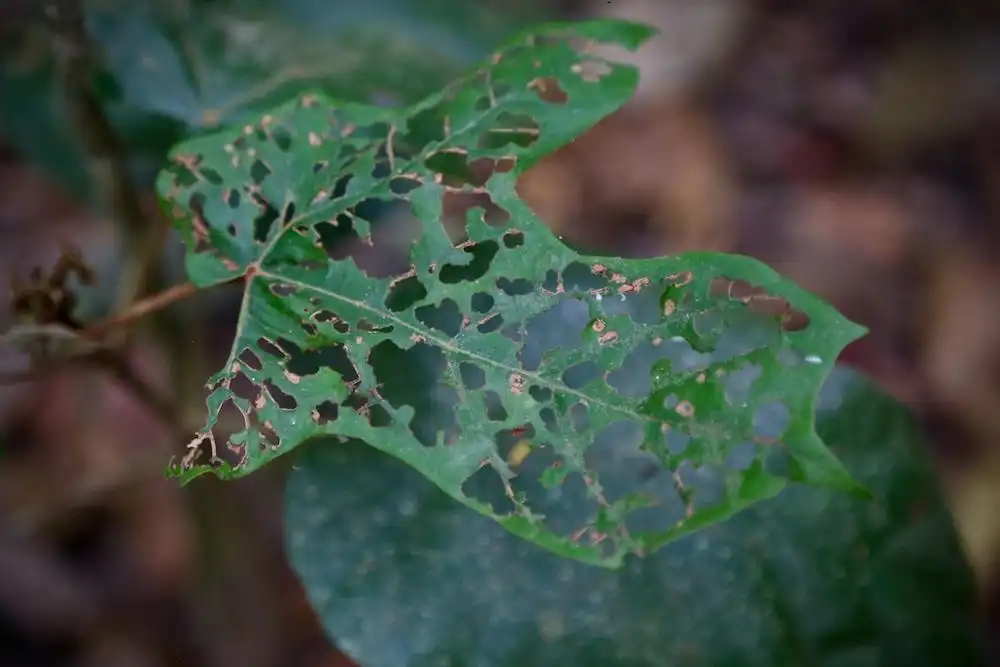
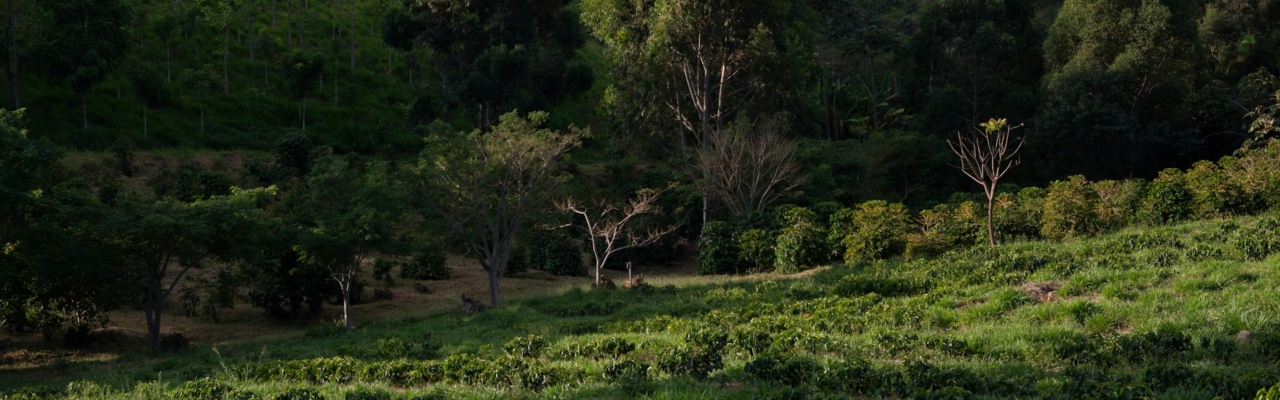
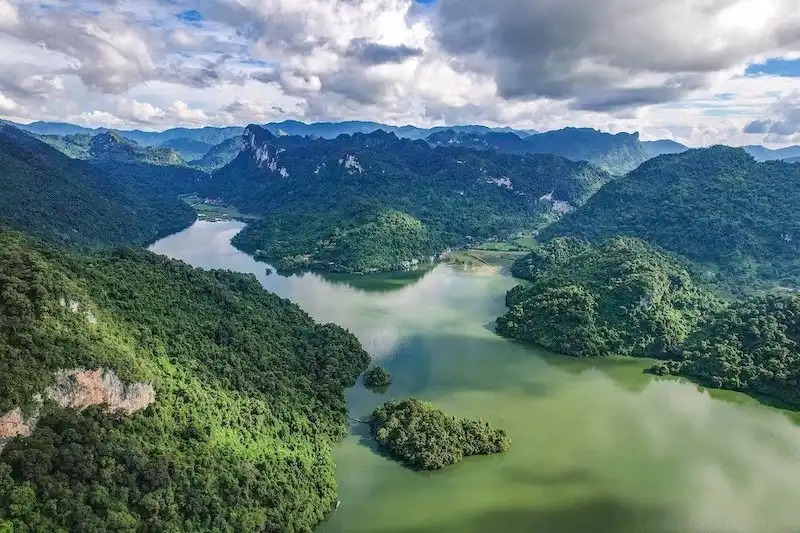
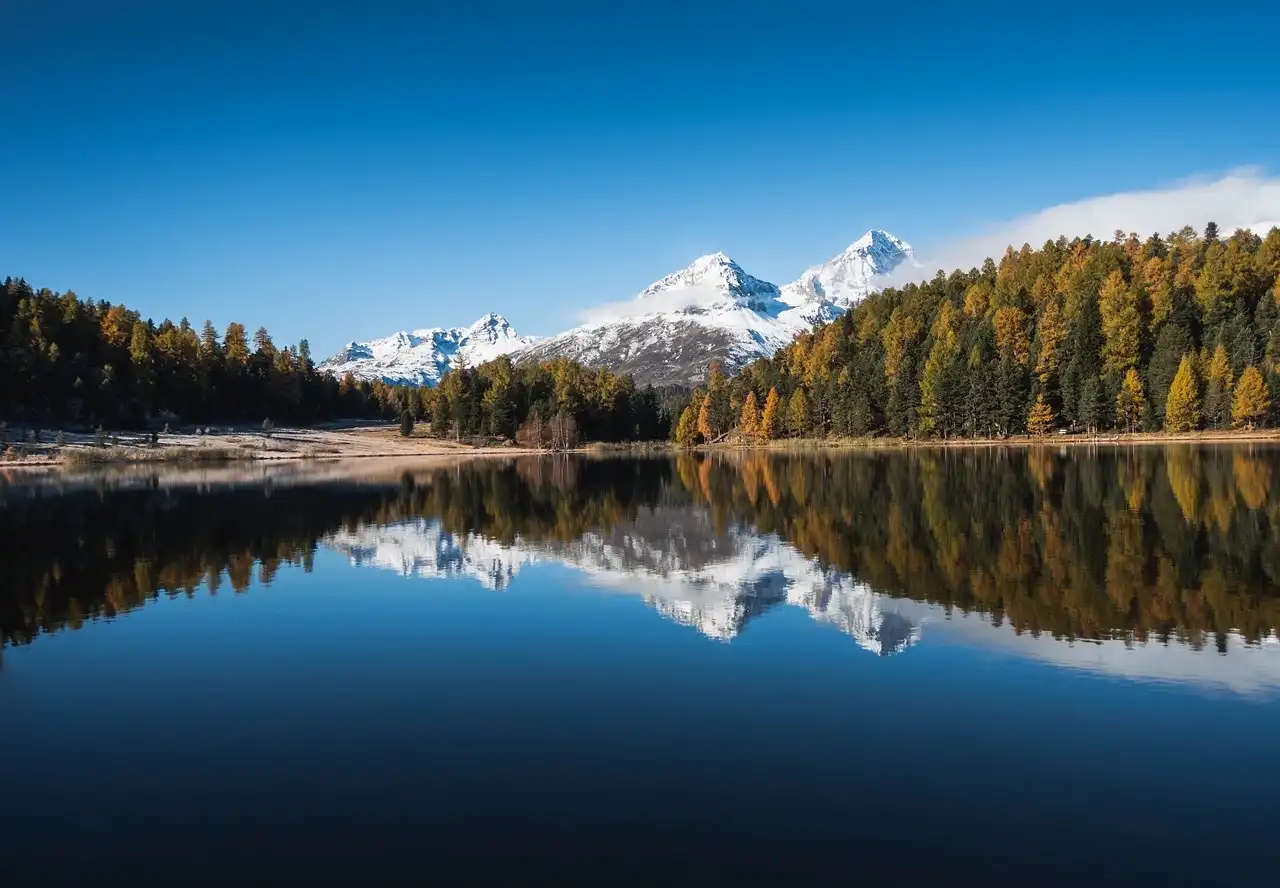
Researchers discovered forests with cold-air pooling, where colder air settles in valleys, reversing typical temperature patterns. These areas could protect cold-adapted species from climate change, serving as refuges and aiding conservation efforts. The study emphasizes the importance of such forests…
Read More