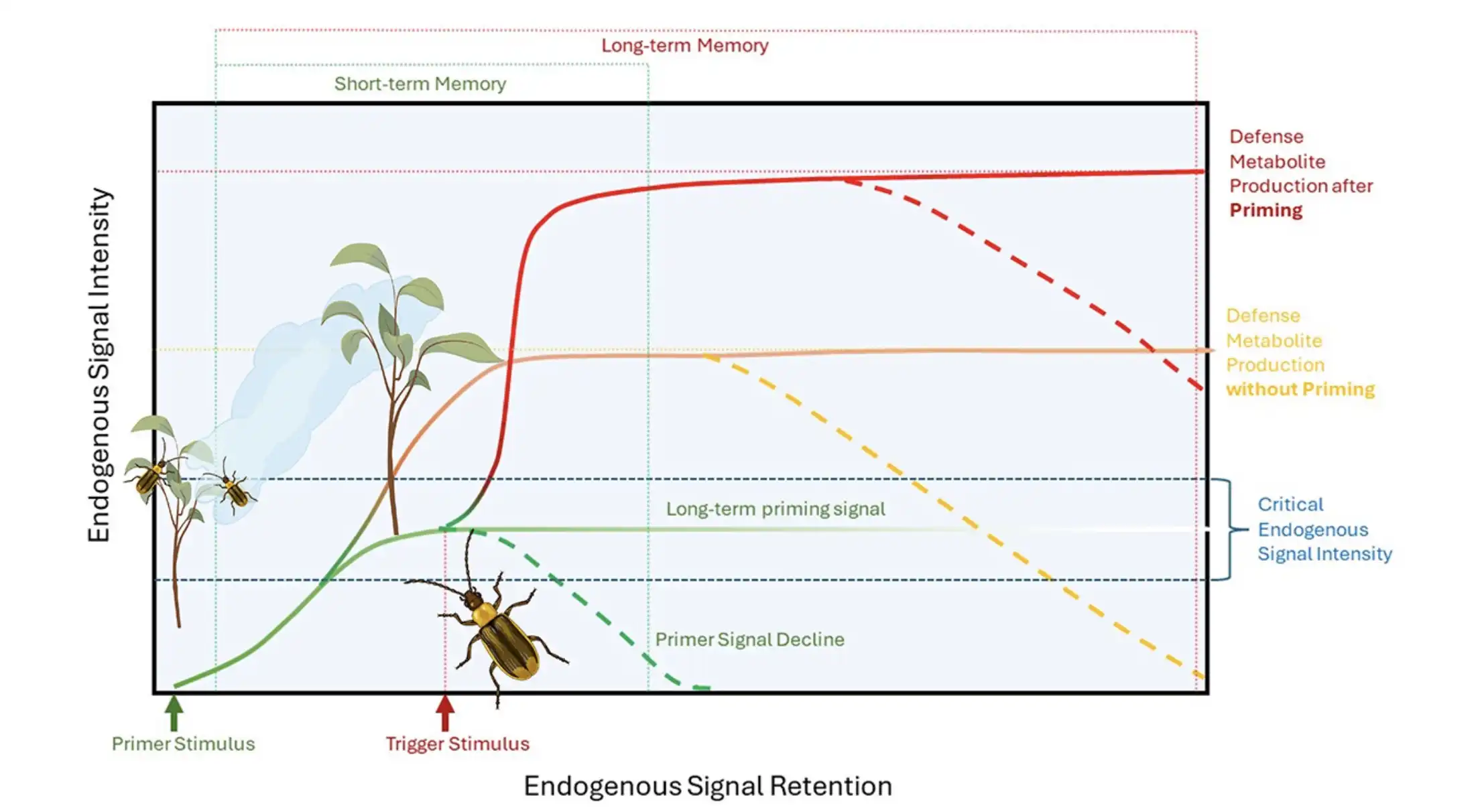
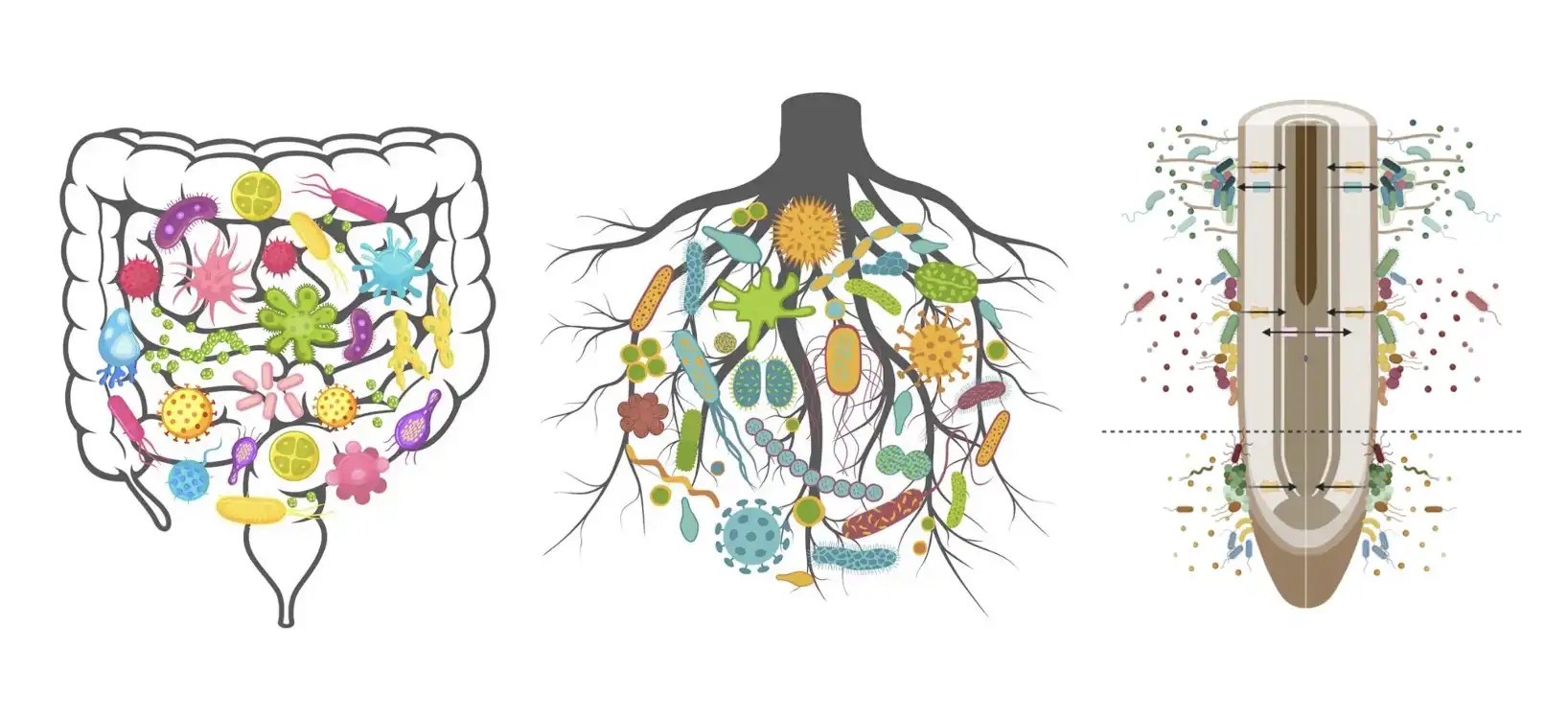
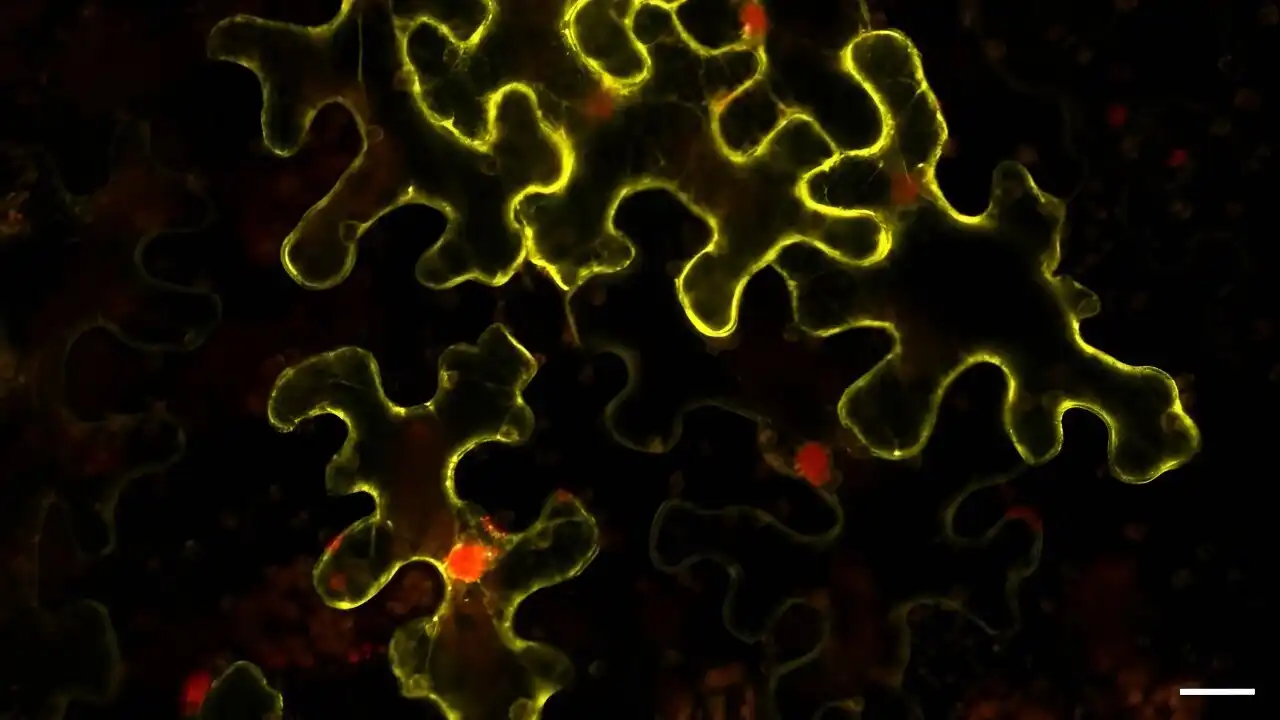
A recent survey of over 4,500 Americans reveals that increased knowledge about gene editing correlates with greater acceptance of its safety for agricultural and medical applications. The study emphasizes the need for effective science communication to shift public opinion, highlighting…
Read More